What exactly is “decentralized finance” (DeFi)?
Following the introduction of Bitcoin in 2009, a thriving industry has developed as a result of the asset itself, the idea behind it, and the technology that underpins it. The cryptocurrency and blockchain space is home to a variety of subcommunities in which companies and projects develop solutions for a wide range of applications.
One of these subsectors is the decentralized finance (DeFi) industry, which emerged as an alternative to conventional financial services when it was founded.
To be more specific, DeFi is made up of smart contracts, which in turn provide the power for decentralized applications (DApps) and protocols. The majority of the total value locked (TVL) in the DeFi ecosystem is still concentrated on Ethereum, which was the platform on which the majority of the initial DeFi applications were built.
At its foundation, Bitcoin (BTC) possesses characteristics that have been hailed as the cornerstones of decentralization. DeFi, on the other hand, builds upon those qualities and adds additional capabilities to the mix.
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is a subcategory that falls under the umbrella of the broader crypto space. DeFi provides many of the same services as the traditional financial world, but in a manner that is managed by the general public rather than by a central entity or entities.
It’s possible that lending was the spark that started the whole thing, but distributed finance applications now have many use cases, providing participants with access to saving, investing, trading, market-making, and other activities.
The ultimate objective of decentralized finance is to compete with and, in the long run, supplant traditional providers of financial services. DeFi frequently makes use of open-source code, which gives anyone the opportunity to build on top of already existing applications in a way that does not require permission and is composable.
The word “finance” is fairly simple to grasp, but what exactly does “decentralization” mean? In a nutshell, decentralization indicates that something is not controlled by a primary body. Banks and other financial institutions have some control over your money, although not complete control. These organizations have the ability to freeze your assets, and you are at their mercy with regard to the hours they are open and the cash they have on hand.
The decentralized nature of decentralized finance (DeFi) not only results in a dispersion of power, but it also results in a dispersion of risk. For instance, if a company stores all of its customer data in a single location, all a hacker needs to do to obtain a significant amount of information is access the location in question. On the other hand, the security of the data could be improved by storing it in multiple locations or by removing the vulnerable single point of failure.
This article will provide an explanation of what “DeFi” stands for, how “DeFi” operates, as well as some insight into “DeFi trading” and “decentralized banking.”
DeFi vs. CeFi (Centralized Finance)
In order to better understand this comparison, we will use commercial banks as an example. In the conventional world, you can utilize financial institutions to store your money, borrow capital, earn interest, send transactions, and do a variety of other things. Commercial banks have a long and successful track record that can be looked back on.
Commercial banks are able to offer insurance, and they also have safety precautions in place so that they can deter and protect customers from theft.
On the other hand, such establishments have a degree of ownership and control over your assets. You are restricted in the actions that you can take due to the hours that banks are open, and transactions can be difficult and time-consuming, requiring settlement periods on the back end.
In addition, in order to participate, commercial banks necessitate certain customer particulars as well as identifying documents.
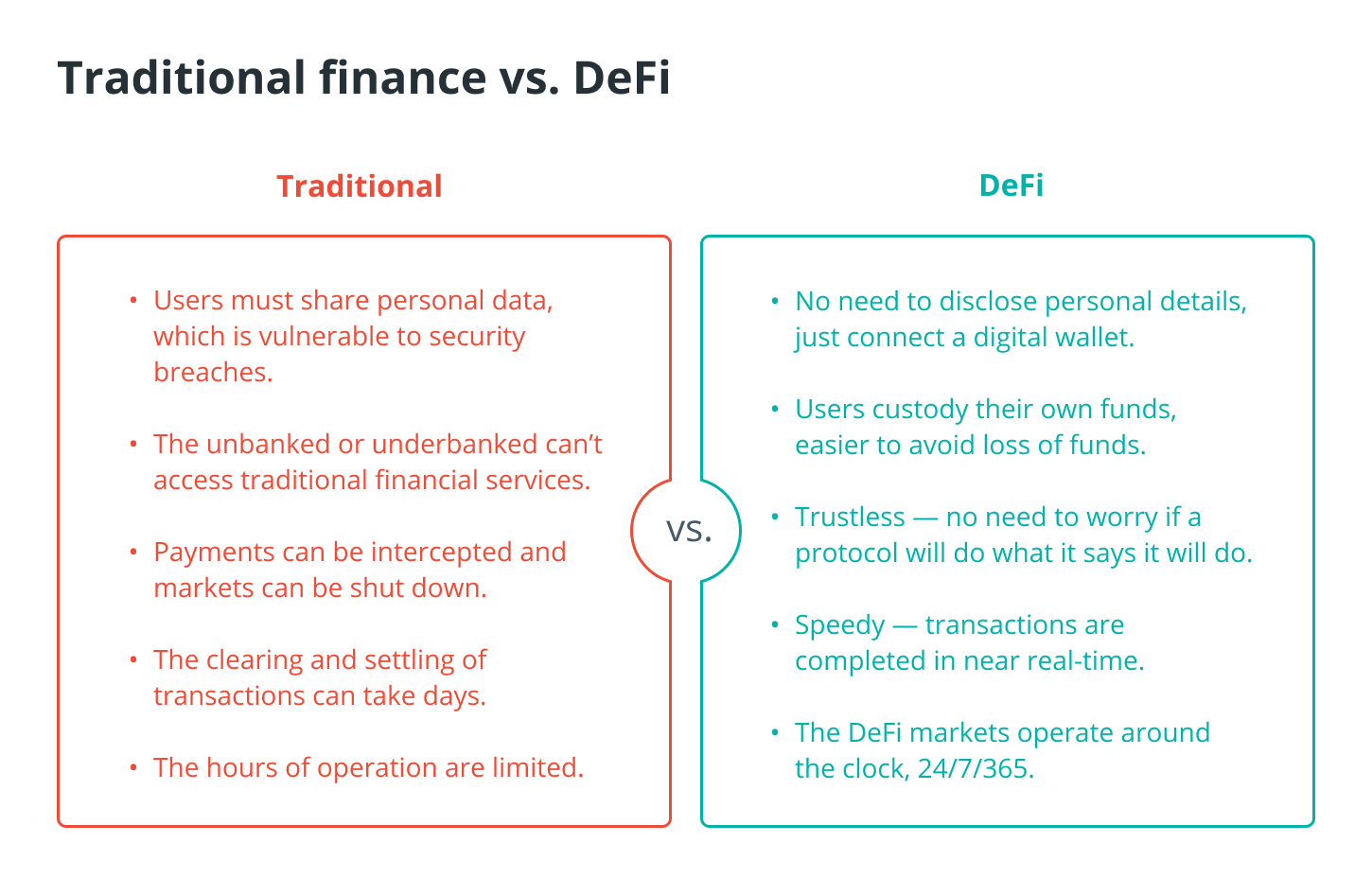
DeFi is a subsector of the financial services industry that is comprised of financial products and services that are available to anyone with an internet connection and that function independently from the participation of banks or any other types of third-party businesses.
As a result of the nonstop operation of the decentralized financial market, transactions are completed around the clock and in close proximity to real time, and no intermediary possesses the authority to halt them. You are able to retrieve your cryptocurrency from storage locations such as computers, hardware wallets, and other locations at any time.
Because of the underlying technology that supports these assets, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and the vast majority of other cryptocurrencies exhibit these characteristics. Because the DeFi platform relies on blockchain technology, the completion of transactions occurs much more quickly, at a lower cost, and, in some instances, with a higher level of security than it would if humans were involved.
The goal of decentralized finance is to use cryptographic technologies to solve a variety of problems that are present in conventional financial markets. These problems include the following:
 Those in charge of the asset class and the processes that go along with it work in centralized finance. In contrast, decentralized finance relies on a collection of intelligent protocols to manage its assets.
Those in charge of the asset class and the processes that go along with it work in centralized finance. In contrast, decentralized finance relies on a collection of intelligent protocols to manage its assets.
The most important thing is to have confidence in the people or organization that are driving the platform. Custodial platforms, such as Coinbase.com, are CeFi platforms. This means that they store cryptocurrency on your behalf.
However, you can use a Coinbase wallet in the same way that you would use a traditional cash wallet, and this will give you complete control over your cryptocurrency assets.
In general, DeFi gives participants the opportunity to access markets for borrowing and lending, to take long and short positions on cryptocurrencies, to earn returns through yield farming, and to do many other things.
Decentralized finance has the potential to be a game-changer for the world’s 2 billion unbanked people, in particular, who are unable to gain access to traditional financial services for a variety of different reasons.
DeFi solutions are built on a variety of blockchains, and the ecosystems they exist in are made up of participants who interact with one another in a peer-to-peer (P2P) manner. This type of interaction is made possible by distributed ledger technology and smart contracts, which monitor the systems to ensure that they are functioning properly.
These kinds of outcomes are not constrained by geographical borders and do not call for the submission of identifying documentation in order to participate.
The rules that are programmed into this framework for this financial system ensure that it functions properly. When you need to borrow money, rather than going through an intermediary like a bank, you would use something called a smart contract to send amounts of a particular cryptocurrency to a safe online location as collateral for the loan. In exchange, you would receive another type of asset.
After that, the assets you provided as collateral would be kept in a secure location until you paid off the loan.
In spite of the fact that when you use DeFi solutions, you might or might not interact in a straightforward peer-to-peer manner, the process itself is inherently peer-to-peer due to the fact that third parties are replaced with technology that is not governed by a centralized authority.
Why is it important to have decentralized finance (DeFi)?
By utilizing a peer-to-peer (P2P) network, DeFi is able to do away with the need for intermediaries and make decentralized banking a reality. This was previously impossible because transactions needed to be validated by third parties.
The global financial crisis that occurred in 2008–2009 demonstrated that customers are frequently unaware of the underlying regulations that govern financial products and services, which makes it impossible for middlemen to be trusted.
The mission of DeFi is to build a financial market that is trustless, permissionless, and open to all participants. A significant portion of the technology that can be found in the DeFi space is geared toward enhancing the existing monetary system and, consequently, the user experience (for both businesses and their clients).
How does DeFi work?
Despite the fact that decentralized finance (DeFi) is frequently discussed in relation to cryptocurrencies, it extends further than the production of new digital money or value. The’smart contracts’ offered by DeFi are meant to operate in place of more conventional types of financial systems.
Because there are no intermediaries to authorize transactions for DeFi applications, there are no banks or other institutions to which you can entrust the management of your money.
In addition, the code is accessible to anyone who wishes to examine it, creating an air of openness and transparency within the DeFi protocols.
Additionally, there are open networks that operate across the borders of different countries. The majority of the user applications that are currently available were developed on the Ethereum blockchain. Users can choose from a wide variety of applications.
 What makes up decentralized finance(DeFi) ?
What makes up decentralized finance(DeFi) ?
The year 2020 was a banner year for decentralized finance (DeFi), which ushered in a wave of new projects into the cryptocurrency space and popularized a new financial movement. The beginning of the DeFi industry cannot be pinpointed to a specific year because Bitcoin already possessed the majority of the defining characteristics of the DeFi space when it was first introduced in 2009.
Since 2017, numerous ecosystems, such as Compound Finance and MakerDAO, have gained popularity, which has resulted in the proliferation of additional financial capabilities for cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance. The year 2020 saw the emergence of additional platforms, which coincided with an increase in the number of people utilizing DeFi solutions for various strategies, such as yield farming, which led to the niche of DeFi experiencing explosive growth.
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs)
Users of a DEX are able to engage in noncustodial trading of digital assets without the involvement of an intermediary or other third-party service provider. DEXs have been a part of the overall cryptocurrency industry for years, despite the fact that they are only a single component of the DeFi sector.
Participants are given the opportunity to buy and sell digital currency through these platforms without having to register for an account on an underlying exchange.
DEXs enable you to hold assets outside of a centralized platform while still enabling you to trade at will from your wallets through the use of transactions involving blockchain technology. The year 2020 marked the widespread adoption of automated market makers, which are a subcategory of DEXs. These market makers facilitate the buying and selling of crypto assets by utilizing smart contracts and liquidity pools.
DEXs are typically developed on top of separate blockchains, which means that the DEXs’ compatibility is highly dependent on the underlying technology on which they are based. DEXs that are constructed on Ethereum’s blockchain, for instance, make it possible to trade assets that are constructed on Ethereum, such as ERC-20 tokens.
Using DEXs requires wallets that are compatible with the platform. Self-custody cryptocurrency wallets, in general, give you control over your assets, and some of them are compatible with decentralized exchanges (DEXs).
However, you will have a greater responsibility for the safety of your funds if you choose to store your assets in this manner. Additionally, compared to centralized exchanges, decentralized exchanges may have a lower number of available features and higher transaction fees.
In terms of liquidity and amassing a regular user base, which is still expanding, DEXs have come a long way and made significant progress. It is anticipated that the trading volumes of DEXs will increase even further as they become more scalable, which means that they will become faster and more efficient.
The aggregators and wallets
Users communicate with the DeFi market through a variety of interfaces, one of which is called an aggregator. They are, in the most fundamental sense, decentralized asset management platforms that enable users’ crypto assets to be automatically moved between various yield-farming platforms in order to generate the highest possible returns.
Wallets are storage spaces that allow for the purchase and sale of digital assets. Wallets can be used to store a wide variety of assets, or they can be used to store just one asset. Wallets can also come in a variety of forms, such as software, hardware, or exchange wallets.
Depending on the wallet, self-hosted wallets, also known as wallets for which you manage the private keys, can be an essential part of the DeFi platform, serving to facilitate a variety of different uses of the DeFi platform.
Wallets based on exchanges, on the other hand, govern your private keys for you, giving you less control but also relieving you of some of the responsibility for their safety.
Decentralized marketplaces
One of the most important applications for blockchain technology is the creation of decentralized marketplaces. They put the “peer” in peer-to-peer networks by enabling users to conduct business with one another in a trustless manner, which means that they don’t require the presence of an intermediary to complete the transaction.
The leading blockchain for facilitating decentralized marketplaces is called Ethereum, which is a smart contract platform. However, there are many other blockchains out there that allow users to trade or exchange specific assets, such as nonfungible tokens (NFTs).
Oracles and prediction markets
Oracles are applications that bring real-world, off-chain data to a blockchain network through the use of a third-party provider. Oracles have paved the way for the creation of prediction markets on DeFi crypto platforms. These prediction markets allow users to place bets on the outcome of various events, such as elections and price movements, and the payouts for these bets are determined by an automated process that is governed by smart contracts.
Layer 1
The blockchain that the developers decide to build on is denoted by the first layer (Layer 1). It is the location where the applications and protocols for DeFi are installed.
As was previously mentioned, Ethereum is the primary layer-1 solution for decentralized finance; however, there are other competing solutions, such as Polkadot (DOT), Tezos (XTZ), Solana (SOL), BNB, and Cosmos (ATOM). Inevitably, these solutions will communicate with one another as the decentralized finance space develops.
The potential advantages of having solutions for the decentralized finance sector run on multiple blockchains are numerous.
As a result of the performance of other competing blockchains, blockchains may be forced to improve their speed and reduce their fees, thereby creating a competitive environment that may potentially result in improved functionality.
Instead of everyone trying to pile onto a single layer-1 option, the existence of multiple layer-1 blockchains leaves more room for development and traffic. This is because there is more than one layer-1 option.

DeFi use cases
Investigating the various applications of DeFi is a good place to start when attempting to find an answer to the question “What is DeFi?” There are new ways to fulfill a variety of requirements, including the ability to lend or borrow, trade on decentralized exchanges (DEXs), stake digital assets, and participate in various other activities, including gaming. Here is a rundown of some of the most important applications for decentralized financial systems.
Platforms for lending
The practice of lending and borrowing money has emerged as one of the most well-liked pastimes in DeFi. Users are given the ability to borrow money using their cryptocurrency holdings as collateral thanks to the existence of lending protocols.
Lending solutions currently command billions of dollars in total value locked, also known as TVL, which refers to the amount of capital that is held locked in any solution at any given time. Decentralized finance has witnessed massive amounts of capital flow through its ecosystem.
Payments and stablecoins
It is necessary for there to be a consistent unit of account, or asset, for DeFi to be considered a financial system that is capable of supporting transactions and contracts. It is imperative that participants have reasonable grounds for anticipating that the value of the asset they are utilizing will not suddenly plummet. Stablecoins are a solution to this problem.
Lending and borrowing are two activities that are common in the decentralized finance market. Stablecoins bring stability to these activities. Because stablecoins are typically pegged to a fiat currency like the US dollar or the euro, they do not exhibit nearly as much volatility as cryptocurrencies do, making them desirable for use in commercial transactions and trade.
Leverage and margin
The margin and leverage components bring the decentralized finance market to the next level by enabling users to borrow cryptocurrencies on margin using other cryptocurrencies as collateral. This opens up new opportunities for users to participate in the market.
In addition, leverage, which has the potential to increase the user’s returns, can be programmed into smart contracts so that they can be used. The utilization of these DeFi components also heightens the risk that the user is exposed to, which is especially concerning when one considers that the system is predicated on algorithms and that there is no human component to intervene in the event of an issue.
DeFi-native activities
Trading is made easier on many decentralized exchanges by the use of liquidity pools, which are essential trading tools. They make trading more liquid for buyers and sellers, who each pay a fee for the privilege of doing business with them.
To participate in a pool, liquidity providers can send certain funds to a smart contract and receive pool tokens in return. This allows them to make a passive profit off of the fees that traders pay to interact with the pool in question. To recover the money you’ve deposited in the pool, you’ll need to use pool tokens.
Yield farming is another activity in the DeFi space that involves searching for profit via various DeFi projects by participating in liquidity pools. This practice is also known as liquidity mining on occasion.
Although there are many complexities involved in yield farming, there is one primary reason why market participants are rushing to take advantage of this phenomenon: It enables you to use the cryptocurrency you already possess to earn even more cryptocurrency.
When participating in yield farming, users lend their cryptocurrency to other users in order to earn interest, which is also paid in cryptocurrency. The interest is typically paid in “governance tokens,” which give liquidity providers a voice in the protocol’s operation.
It is a key innovation in the decentralized finance market that allows investors to put their cryptocurrency to work in order to increase their returns. Yield farming has been dubbed the “Wild West” of DeFi, with market participants hunting down the best strategies, which they then often keep close to the vest in order to not tip their hand to other traders and lose the magic. This has led to yield farming being referred to as the “Wild West” of DeFi.
DeFi risks?
Despite all of the promise that surrounds it, the decentralized finance space is still in its infancy and is going through some growing pains at the moment.
To date, there has been no widespread adoption of DeFi, and in order for this to occur, blockchains will need to become more scalable. The infrastructure supporting blockchain technology is still in its infant stage, with much of it being difficult to use for both developers and market participants alike.
This will continue to be the case until scalability is improved, which is the idea behind the development of Ethereum 2.0, which is also known as Eth2. Fiat on-ramps to DeFi platforms can also be excruciatingly slow, which poses a threat to user adoption because it slows down the process.
The size of DeFi has significantly increased.
Because of its relative youth and innovative nature, the legal particulars surrounding DeFi are probably not yet completely formed. It is possible that governments all over the world will attempt to incorporate decentralized finance into the regulatory frameworks they already have in place, or they may draft brand new laws that are specific to the industry. On the other hand, DeFi and the people who use it might already be subject to certain regulations.
When it comes to adoption, it is difficult to predict how exactly the future will play out and what will happen. Instead of completely replacing traditional financial options with decentralized alternatives, one outcome that is possible is that traditional finance will adopt some aspects of decentralized finance while keeping other aspects of centralization. Any solution that is entirely decentralized, on the other hand, may continue to function outside of the mainstream financial system.
How exactly does one make money utilizing DeFi?
The most straightforward method for earning a passive income through DeFi is to deposit your cryptocurrency onto a platform or protocol that will pay you an annual percentage yield. This will allow you to earn a return on your investment.
The process of locking tokens into a smart contract in exchange for additional copies of the same token is referred to as staking. The practice of yield farming is another method by which you can reward yourself with additional instances of the same token or an entirely new token.
Your first order of business will be to make a purchase of some cryptocurrency using a fiat on-ramp (i.e., using cash to buy cryptocurrencies).
However, before you continue with the purchase of your cryptocurrency, you should keep in mind that the vast majority of DeFi is based on the Ethereum blockchain, so BTC is rarely accepted. This is something you should keep in mind before you proceed.
Is it safe to invest in DeFi?
In general, an investment in a token carries a higher level of risk if that token has a market capitalization that is lower than average. Therefore, before committing your funds, you should investigate the liquidity of the tokens. Before making an investment, you should make sure you are aware of how long a Defi protocol has been in operation and how much money has been deposited into it in total.
You can check the company’s website to see if it has taken any steps that are considered to be reasonable to reduce the risks it faces. You could also search for articles on news websites that discuss the protocol being hacked on the internet and the measures that have been taken to prevent it from happening again.
Before you invest your money in any protocol, it is important to understand that there is no decentralized finance protocol that is risk-free; however, the factors that have been discussed can assist you in performing an accurate risk assessment.