Creating a Nonfungible Token: A Step-by-Step Guide
The phrase “nonfungible token” (NFT) is typically used to refer to a cryptographic asset on a blockchain that represents an intangible and one-of-a-kind digital item, such as a work of art, a photograph, an in-game collectible, or a tweet. Other assets cannot replace this type of asset because it possesses a unique combination of characteristics that no other asset does.
Each NFT is one of a kind, and there are only a certain number produced; they cannot be traded with one another, and they can serve as evidence of ownership and authenticity.
Metadata and one-of-a-kind identifiers, such as barcodes, are used to differentiate non-fungible tokens (NFTs) from one another.
Metadata is a term that refers to the information that constitutes the asset. Users are able to buy and sell objects based solely on the metadata associated with those objects rather than the entire object itself.
The purpose of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) is to imitate the tangible properties of physical items, such as their uniqueness, scarcity, and ownership proof.
On the other hand, fungible goods are those that can be interchanged due to the fact that their value, and not their individual characteristics, define them. On the other hand, digital products are only legitimate when used in conjunction with their respective physical counterparts.
The first iterations of non-fiat currencies, or NFTs, took the form of coloured coins, which are experimental assets that were first introduced to the Bitcoin network in 2012.
In 2014, as an experiment for the Seven on Seven conferences that was held at the New Museum in New York City, the first asset that represented a nonfungible tradable blockchain marker was created. This asset was a digital token.
Even though digital collectibles and art NFTs continue to command the majority of attention in the cryptocurrency community, the number of use cases that can be implemented with them keeps growing.
They extend beyond the typical use cases, such as digital art and games, into other industries, such as the fashion industry, the music industry, academic institutions, the tokenization of real-world objects, patents, membership sales, and loyalty programs.
The benefits of NFT technology can be combined with the operational efficiencies of decentralized finance (DeFi). Non-fungible tokens, for instance, can be lent, borrowed, and even used as collateral to secure a loan. This is because it is possible to borrow and lend non-fungible tokens.
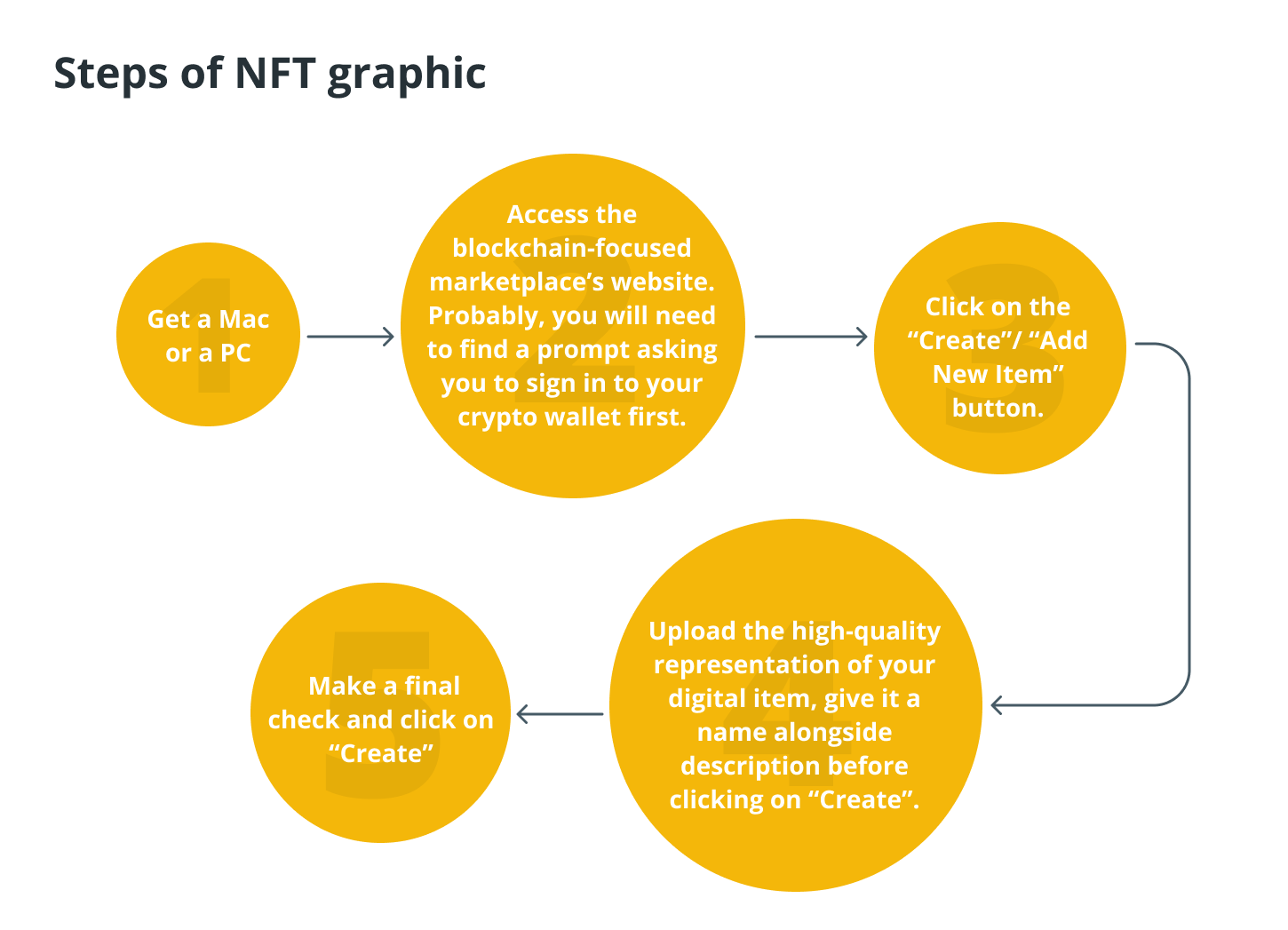
NFTs can be created by anyone who has an interest in selling and sharing their digital creations, including content, art, music, and photography. To help you successfully jump on the bandwagon of creating a nonfungible token, here is a step-by-step guide that you can follow.
Developing an NFT is a relatively uncomplicated process. Users, for instance, have the ability to select their own content and obtain a cryptocurrency wallet.
They can select an appropriate NFT marketplace and then follow the instructions provided by that marketplace. Once an NFT has been created, it can either be shared with other people or offered for sale to collectors.
The following provides the information that you need to learn more about the process of creating NFTs.
Understanding NFTs
The digital artwork titled “Everydays: The First 5000 Days” by Mike Winkelmann, also known as Beeple, was purchased by an NFT collector for the price of $69.3 million; this price makes the NFT the most expensive piece of crypto art in the history of the medium.
The CryptoPunks collection, which was pioneered in 2015 on the Ethereum blockchain and consisted of 10,000 pixelated images of punks with a set of distinctive characteristics and sells for thousands of dollars, has a set of said characteristics.
The question that needs to be asked is, “What exactly is the value of these digital creations, and why are collectors spending so much money on them?”
The creation of Beeple’s “Everydays,” a collage consisting of 5,000 drawings that each make a reference to a different day over the course of thirteen and a half years, was a challenging endeavour.
On the other hand, many NFT collections, including those that have achieved an incredible level of success, most likely do not call for an exceptionally complex contribution from the author.
Therefore, to become an NFT artist, one must possess a high degree of creativity and a clear idea of what one wants to accomplish in their career.
Developing an NFT is unquestionably something that should be attempted, and this holds true even for individuals who do not possess the same level of expertise as Leonardo da Vinci but do have a number of ideas.
In addition, this could be an excellent place to begin for artists who work professionally and who most likely already have several artworks that are comparable to Beeples sitting unused in their digital studios and just waiting in the wings to be bought and sold as NFTs.
An original and captivating piece of digital art created by an unknown artist is not likely to become as popular as works produced by famous people, such as the 10 digital paintings produced by the Canadian singer Grimes, which have been sold for approximately $6 million, the NFT releases produced by Kings of Leon, which have generated $2 million in sales, or an exciting NFT which presents Jack Dorsey’s very first tweet, which has been sold for more than $3 million.
After all, the technology of non-fungible tokens (NFT) is perfect for maintaining scarcity and establishing ownership of both digital and physical assets.
It provides digital creators with reliable options for monetizing their work as well as a level of flexibility that is frequently absent from the models utilized by traditional creative industries.
When selling digital content online, a method that is both secure and verifiable is to attach it to the blockchain in the form of a nonfungible token. In addition, NFT creation grants artists unrestricted access to a worldwide community of collectors and individuals who share their values and perspectives.
To our good fortune, the process of generating an NFT does not involve any technical, complex, or financial challenges. Anyone can create an NFT so long as they have the proper guidance and don’t need to write any codes.
Choose the format and pick your content.
The first step for creators is to determine the file type that will be used for their NFT. Any multimedia file can be used to create a nonfungible token. It could be a photograph, a digital painting, a text, an audio file, or a video clip documenting an important event.
Other creative products such as crypto-collectibles, virtual items from video games such as avatars, weapons, and currency, and virtual land in metaverses are all examples of things that can be represented as NFTs.
There is, without a doubt, room for the ideas of creators in this area, given that it appears that anything digital could be an NFT these days.
For instance, it could be the source code of the World Wide Web, which was sold by its creator, Sir Tim Berners-Lee, in the form of NFT for the price of $5.4 million; a “high-res artistic representation” of genetic data compiled by professor George Church; or the data of the very first person to ever sequence their own DNA.
In addition, there is still a market for non-digital real-world assets that have been tokenized, such as real estate, diamonds, designer sneakers, and so on. These assets are all sold in the form of non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Regarding the format, the creators have complete freedom to choose what they want to use. It is possible that it is dependent on the subject matter of their artwork as well as their level of imagination.
It is important to keep in mind that after creators decide what content and in what format they want to represent as an NFT, they will need to convert it to an appropriate file type, mainly if it is not already digital. This is the case even if the content is already digital.
The vast majority of things are typically saved in either graphics interchange format (GIF) or portable network graphics (PNG) format.
Texts would typically be made available in the portable document format (PDF), while music would probably be kept in MP3 format and video would probably be kept in MP4 format.

How to create and mint NFTs
The fact that NFTs are one-of-a-kind is what gives them their value. There are times when users might want to make multiple copies of their creations that are completely identical to one another.
If you sell collectibles, for instance, you might provide several different versions of the item, some of which are more rare than others.
If this is the case, you will need to make a decision regarding how many identical copies of a specific NFT you will include within the blockchain. This number will be fixed, and as a result, your NFTs will become immune to any modifications made to them after they have been created.
Minting refers to the process of producing a nonfungible token. The transformation of a digital object into an asset that can be stored on a blockchain is what this term refers to.
After being created, NFTs are put into circulation through a process called “minting,” which is analogous to the production and distribution of metal coins. After going through the procedure, the digital object will be impossible to corrupt, significantly more secure, and difficult to manipulate.
The fact that it is portrayed as a nonfungible token means that it can be bought, sold, and traded; additionally, it can be digitally tracked whenever it is resold or collected once more in the future.
Certain NFT technologies make it possible to continue paying commissions to the original creator whenever the owner of an item that was referenced in the transaction changes.
During the process of minting a token, creators have the ability to program a royalty clause that will allow them to generate passive income from subsequent sales of their digital items. They stand to gain financially from their work if it is successful in gaining popularity and going up in price over time.
After you have signed your NFT and paid the gas fee, the process of minting your coin will start. After the transaction has been verified, your newly created NFT will be displayed on your profile for your viewing pleasure.
Choose the NFT marketplace.
After the digital item that will be used in a future NFT has been completed, it is time to select an NFT marketplace where the item will be sold.
The process of minting non-fungible tokens (NFTs) begins with the selection of a platform, which is an essential step.
The right choice for this step depends on a number of factors, including the types of blockchains supported, supported standards and formats, accessibility, and the cost to mint an NFT.
ERC-721 was the initial standard that was developed for the representation of non-fungible digital assets on the Ethereum blockchain. Semi-fungibility is available through the ERC-1155 standard.
In contrast to the ERC-721 token, in which the unique identifier only represents one asset, the ERC-1155 token’s unique identifier represents a whole class of fungible assets. The user is able to transfer any number of these assets to other people.
In accordance with the templates provided by components that are based on the ERC-998 standard, nonfungible tokens (NFTs) can be either fungible or nonfungible assets.
NFTs are not an area in which Ethereum enjoys a monopoly. Nevertheless, Ethereum serves as the foundation for the vast majority of these platforms. Other non-Ethereum NFT marketplaces, such as Cosmos and Polkadot, as well as Binance Smart Chain, are examples of blockchain ecosystems that these marketplaces are a part of.
Each of the NFT marketplaces operates in a slightly different way and provides its users with a unique set of instructions, in addition to presenting both positive and negative aspects. For instance, some of the NFTs are curated, while others are built around the concept of self-service.
On some platforms, the creation of NFTs is more cost-effective than it is on others, while all marketplaces do not support certain file formats. Some platforms have a straightforward user interface (UI), while others have more complicated interfaces that may be overwhelming to first-time users.
At this time, the cryptocurrency industry is home to a large number of NFT marketplaces. Because they offer unrestricted access to all users, non-curated platforms have recently emerged as a competitive alternative to curated ones.
Users are only required to register and pay the transaction fee in order to mint a token in order to be able to upload NFTs onto them.
OpenSea is one example of a non-curated platform that gives users the ability to mint and trade NFTs, as well as view data on them and examine statistics.
OpenSea was established in 2017, and it currently stores almost all crypto art collections, in addition to a large number of items from a variety of well-known blockchain games.
Users are able to generate a nonfungible token in a time- and cost-effective manner thanks to the platform’s user-friendly creation interface.
Rarible is yet another self-service platform that functions as a mass marketplace, and it just so happens to be connected to OpenSea.
Although the procedure for making an NFT on Rarible is extremely similar to that of OpenSea, the functionality of Rarible is a little bit different.
For instance, the number of formats available is reduced, and the dimensions of the artworks are shrunk down. Rarible, on the other hand, has a significant amount of traffic and gives users the ability to mint tokens before selling them. In contrast, OpenSea only handles the minting process after a token has been sold.
Curated platforms, as opposed to self-service platforms, are more selective when it comes to the creators they accept. Creators are required to submit an application form that includes stringent selection criteria and a lengthy waiting period before the experts make their decision. This is necessary before the creators can begin selling digital content on SuperRare or Nifty Gateway.

Set up a wallet and own some crypto.
Any blockchain infrastructure must have cryptocurrency wallets as one of its essential components. Wallets are required for users to access various platforms, sign transactions, and manage their balances in accordance with the fundamental principles underlying blockchain technology.
Because of this, NFT marketplaces do not require the storage of user account data, which results in the platform having a higher level of security.
On smartphones, users can download a variety of cryptocurrency wallet applications that allow them to buy and store cryptocurrencies.
Many are tailored to be user-friendly for people who are just getting started with blockchain technology and can help them navigate transaction fees, security, and privacy concerns.
When it comes to gaining access to blockchain-based applications, there is no shortage of crypto wallets or browser extensions that are capable of doing the job.
A simple email address and password are not enough protection for some websites; instead, they require users to enter a twelve-word access seed phrase.
Before you begin the process of setting up a wallet, it is essential to make certain that it is compatible with the digital currency that is utilized by the platform that you plan to use.
Users are required to pay a gas fee in order to mint a token on a blockchain. This fee is deducted from the token’s supply. A payment that the user makes to compensate for the amount of computing energy that is required to process and validate transactions on the blockchain is referred to as a gas fee.
The maximum amount of gas that a user is willing to spend on a specific transaction is referred to as that user’s gas limit.
The amount that customers must pay for gas is highly variable because of the fluctuating demand for completing transactions. There is no cost associated with minting NFTs. However, the price could range anywhere from ten dollars to one hundred dollars depending on the market chosen.
On the weekends, when fewer people are transacting, gas fees are significantly cheaper (on average), which will help NFT enthusiasts keep costs down if they are minting multiple items. In addition, fewer people are transacting on the weekends.
The process of minting multiple items is not the same as double minting, which means minting the same NFT more than once. Users are free to move the same digital item that has been minted on one NFT marketplace to a different NFT marketplace, mint it a second time, and then sell it again as a new NFT without running into any restrictions.
The user’s credibility may be put in jeopardy if they do something that lowers the value of the specified NFT and any subsequent digital item that the user may want to sell. Users are responsible for keeping all potential repercussions for their reputation in mind, such as these examples:
As a result, double minting should be avoided by inserting an invisible code into the file that represents a digital item. This should be done in a way that does not significantly alter how the item appears to the naked eye.
After that, users can access NFT sales receipts by downloading the cryptocurrency wallet app to their smartphones and personal computers. This is necessary because users will need a way to receive cryptocurrency and convert it into traditional money whenever they choose. Users can download the cryptocurrency wallet app.
Two primary methods can be used to exchange digital currency for fiat currency and then move that cash into a bank account. To begin, you have the option of utilizing third parties, such as cryptocurrency exchanges, ATMs, and debit cards.
The utilization of a peer-to-peer (P2P) network is the second available choice. Both of these approaches are uncomplicated and risk-free. The use of a peer-to-peer transaction, on the other hand, is likely to be a method that is both more discreet and more expedient when it comes to exchanging your cryptocurrency for a fixed amount of cash.
Follow the instructions provided by the NFT platform.
To create a nonfungible token, creators will need to adhere to the specific instructions provided by each NFT marketplace.
To begin, the marketplace will typically request that users upload a file they wish to convert into an NFT, along with a title and a brief description of the file.
To achieve the best results, users of the NFT platform should devote some time to filling in the details of their nonfungible tokens and perfecting them. This will increase the likelihood that their creations will be purchased by collectors and increase the users’ earnings.
After uploading the digital item, they will be required to make a decision regarding the creation of a single token or a collection of tokens.
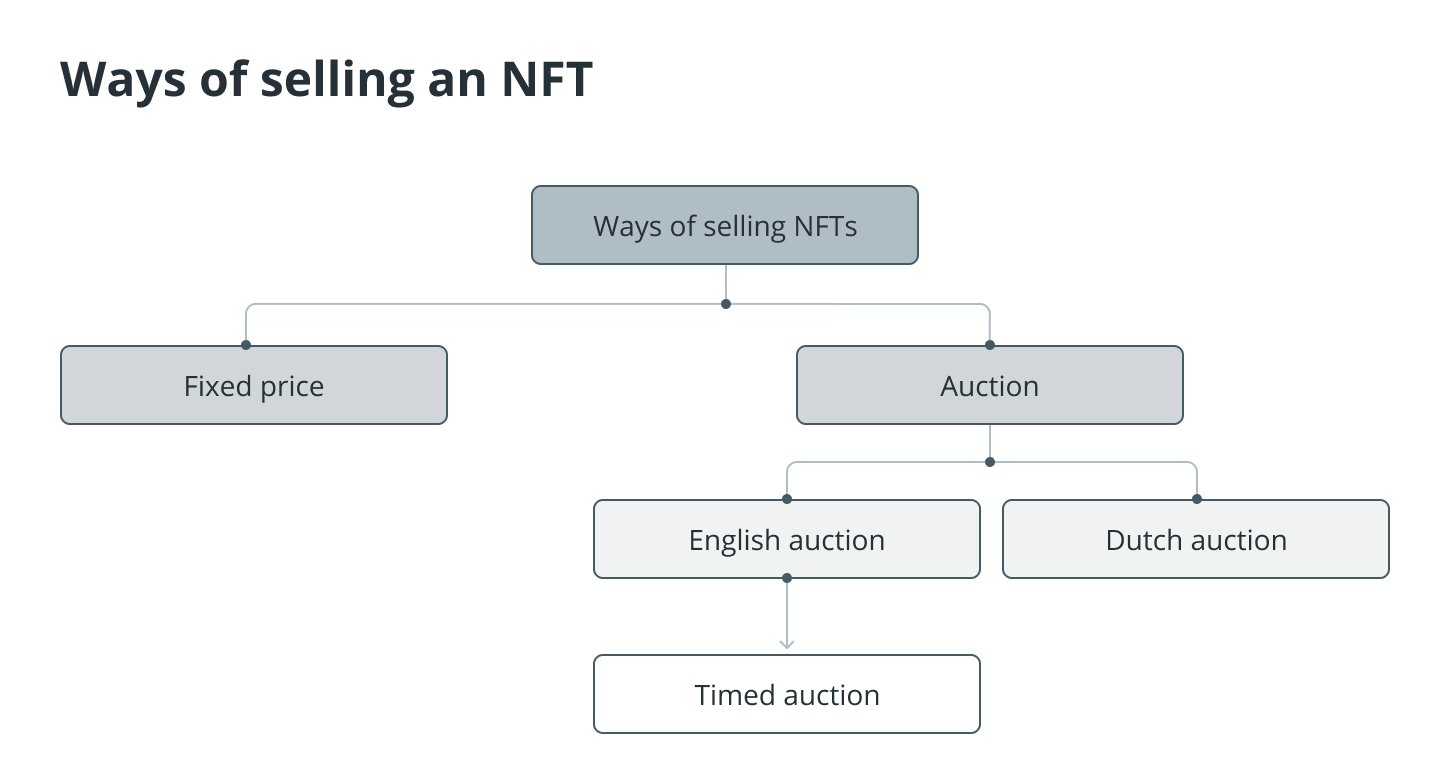
Second, when it comes to selling non-traded stocks, you have the choice between an auction or a fixed price. Users can choose a price at which they want to sell their NFTs as part of a transaction known as a fixed-price sale.
It is fairly open and honest in its presentation. Another option is to use exciting methods, such as auctions, to sell NFT creations. On most different NFT marketplaces, there are typically two distinct kinds of auctions to choose from.
The first kind of auction is called an English auction, which features escalating prices with the winner being the person who placed the highest bid.
There is another type of English auction known as a timed auction. In this type of auction, each lot is up for bidding for a predetermined amount of time. At the conclusion of the allotted time, the collector who placed the highest bid is the winner and receives the NFT.
The second kind of auction is called a Dutch auction, and it is also known as a decreasing-price auction. In a Dutch auction, the price of an NFT continues to decrease until someone purchases it.
The next step for users will be to establish an initial price for their NFT, and this step will vary depending on the marketplace they select. Some marketplaces will also ask users to specify a royalty percentage, which users will earn when subsequent collectors sell their NFT.
The setting of a percentage is a balancing act because a higher percentage will make you more money from each sale. Still, it will discourage people from reselling your artwork in the first place because they will have a lower chance of making a profit for themselves.
In addition, there will be an option to add file properties, such as a resolution and size, that are optimal for the file. At last, the token will undergo validation on the platform, and if everything checks out, it will be made available for purchase.
Promoting the NFTs
When everything is said and done, users have the option of actively promoting their newly minted NFT creation if they so choose. The promotion of an NFT will be contingent on the particulars of the user’s NFT.
Nevertheless, there are a few fundamentals that creators should focus on, such as gaining an understanding of their target audience or developing an effective marketing strategy.
Public relations, or the process of cultivating a positive reputation within the community by spreading favourable information about yourself and your NFT collection, is one of the most effective methods of promotion. It is also one of the oldest forms of communication.
In addition, it could be promoted through social media promotion and online advertising, such as publications in specialized newspapers and appearances on crypto podcasts. Online advertising could also be used.
If creators want to attract the largest number of collectors, it makes sense for them to appeal to the largest audience possible. Using social media is one strategy that could be very helpful in this endeavour because users can share links to their digital items on both their own social media and the social media of the NFT marketplace.
Users are able to create personal accounts on Twitter, Telegram, and Discord, which have already been established as communication channels for the cryptocurrency community. These platforms allow users to promote their non-fungible tokens (NFTs), establish a reputation, and increase general awareness.
As a consequence of this, they have the opportunity to meet some influential people and artists with whom they can collaborate, as well as journalists from well-known publications who are willing to write about them and their NFT collection.
Developing a devoted community may prove to be essential for the promotion efforts of NFT creators, given that these individuals will provide consistent support, spread the word about the creators, invest in the creators, and willingly purchase their NFT creations.










