What Is Algorand blockchain
Algorand is a blockchain network that doesn’t have a central point of control. It has a wide range of applications that are safe, efficient, and scalable. It was made for the future of money and is the world’s first blockchain based on pure proof-of-stake (PoS). But what’s the point of Algorand?
Algorand’s technology is a group of high-performance layer 1 blockchains that offer security, scalability, privacy, and the finality of transactions. A layer-1 blockchain is a group of solutions that improve the basic protocol so the system can be used on a larger scale. The two most common layer-1 options are the changes to the consensus protocol and sharding.
Silvio Micali, a computer science professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, started Algorand in 2019. Silvio helped come up with many of the most important ideas in modern cryptography, like verifiable random functions, zero-knowledge proofs, and other protocols. In 2017, Silvio started Algorand with the main goal of managing important research projects in theory, security, and crypto finance.
The Algorand Foundation runs the Algorand blockchain, which can be used by any company or person who wants to. Algorand’s technical innovation is focused on performance, interoperability, scaling, layer-2 smart contracts, and both private and public models. Layer-2 scaling solutions can add more features, such as the ability to scale payments and do computing outside of the blockchain.
Algorand can handle a lot of users and confirms transactions in about a minute. Even if some users are bad and the network is temporarily split up, Algorand makes sure that users will never have different ideas about transactions that have already been confirmed. On the other hand, existing cryptocurrencies allow for temporary splits and need a lot of time, on the order of an hour, to confirm transactions with high confidence.
In this article, we’ll talk about Algorand staking, Algorand governance rewards, why you should buy Algorand, and the difference between the Ethereum, Cardano, and Algorand blockchains.
What makes Algorand so unique?
Bitcoin (BTC) is based on the idea that most of the computing power used to make blocks is not controlled by a single bad actor. On the other hand, Bitcoin has a number of problems, such as the fact that its proof-of-work method for making blocks requires a lot of computation.
PoW also lets forks happen, which are when two different blockchains with the same length coexist and neither one takes over the other. Because of this, a Bitcoin transaction takes about an hour to be confirmed. Also, the pseudo-anonymity that BTC payments provide could be used to launder money and fund criminals or terrorist groups.
Algorand is a decentralized network, just like every other public blockchain platform. Algorand, on the other hand, wants to solve the “blockchain trilemma” by tackling the three biggest problems the ecosystem is facing right now: scalability, speed, and security.
How does Algorand solve the three problems with blockchains?
The Algorand blockchain is better than other blockchain protocols because it has more improvements, such as the unique pure-proof-of-stake (PPoS) approach (Algorand’s proof-of-stake protocol), which is used to reach decentralized consensus. PPoS is meant to stop the “rich getting richer” problem. In essence, PoS pays the miners with the most money invested in the system, while PPoS chooses miners at random, no matter how much money they have in the system.
Byzantine agreement protocol
When PPoS is paired with a Byzantine agreement (BA) protocol, the mechanism decides how people can join the decentralized network, discourages fraud, and creates a single source of truth that can be checked.
The Byzantine agreement mechanism can handle a large number of users and lets Algorand agree on a new block quickly and without any splits. Verifiable random functions (VRFs) are used to pick users at random in a private, non-interactive way. This is one of the main ways that BA is good for Algorand. VRF is a pseudorandom function with a public key that shows that its outputs are correct.
The agreed-upon block is then confirmed with digital signatures from the right verifiers and sent through the network. On Algorand, only one block can get the minimum number of votes from the committee, so two blocks can never be added to the chain at the same time. This means that in a properly decentralized network, all transactions are finished within seconds, ensuring speed.
Two-tiered blockchain architecture
Algorand uses a two-tiered blockchain design to keep applications running quickly even though they are complex. The layer 1 tier lets Algorand Standard Assets be made (ASA). ASA stands for new tokens or tokens that already exist on the blockchain. It also stands for atomic swaps and simple Algorand smart contracts.
The layer-2 level is for smart contracts and decentralized apps that are more complicated and run off-chain. With this method, the Algorand blockchain can process transactions at the same speed as large payment networks.
Staking for security
Anyone who wants to help keep the Algorand network safe can show their interest with an account that has ALGO, the Algorand cryptocurrency and the blockchain’s native token. The amount of ALGO a user has compared to other users on the network who showed interest in taking part determines how likely they are to be chosen.
But Algorand has to deal with three problems. First, Algorand needs to protect itself from Sybil attacks, which happen when an attacker makes a lot of fake names to mess with the Byzantine agreement protocol.
Second, BA must be able to handle millions of users, which is a lot more than what current Byzantine agreement protocols can do. Lastly, Algorand must be able to withstand denial-of-service attacks. This means that it can keep working even if an attacker disconnects some users. How does Algorand deal with these problems?
Algorand uses different methods to solve the above problems, which are described in the sections that follow:
Users with weight
The protocol can handle dishonest users as long as more than two-thirds of the total stake comes from honest users who follow the protocol’s rules.
Consensus by committee
BA makes its system scalable by giving each step of its protocol to a committee, which is a small group of users chosen at random based on their weights. So, Algorand knows that a good number of committee members are telling the truth.
Participant replacement
After a member of a committee sends a message in BA, an enemy can target that member. BA stops this threat by letting each committee member speak only once. So, if a committee member tells an enemy who he or she is, that person is no longer important to BA.
BA gets this quality by avoiding any private state (other than the user’s private key), letting all users participate equally, and electing new committee members for each step of the Byzantine agreement protocol.
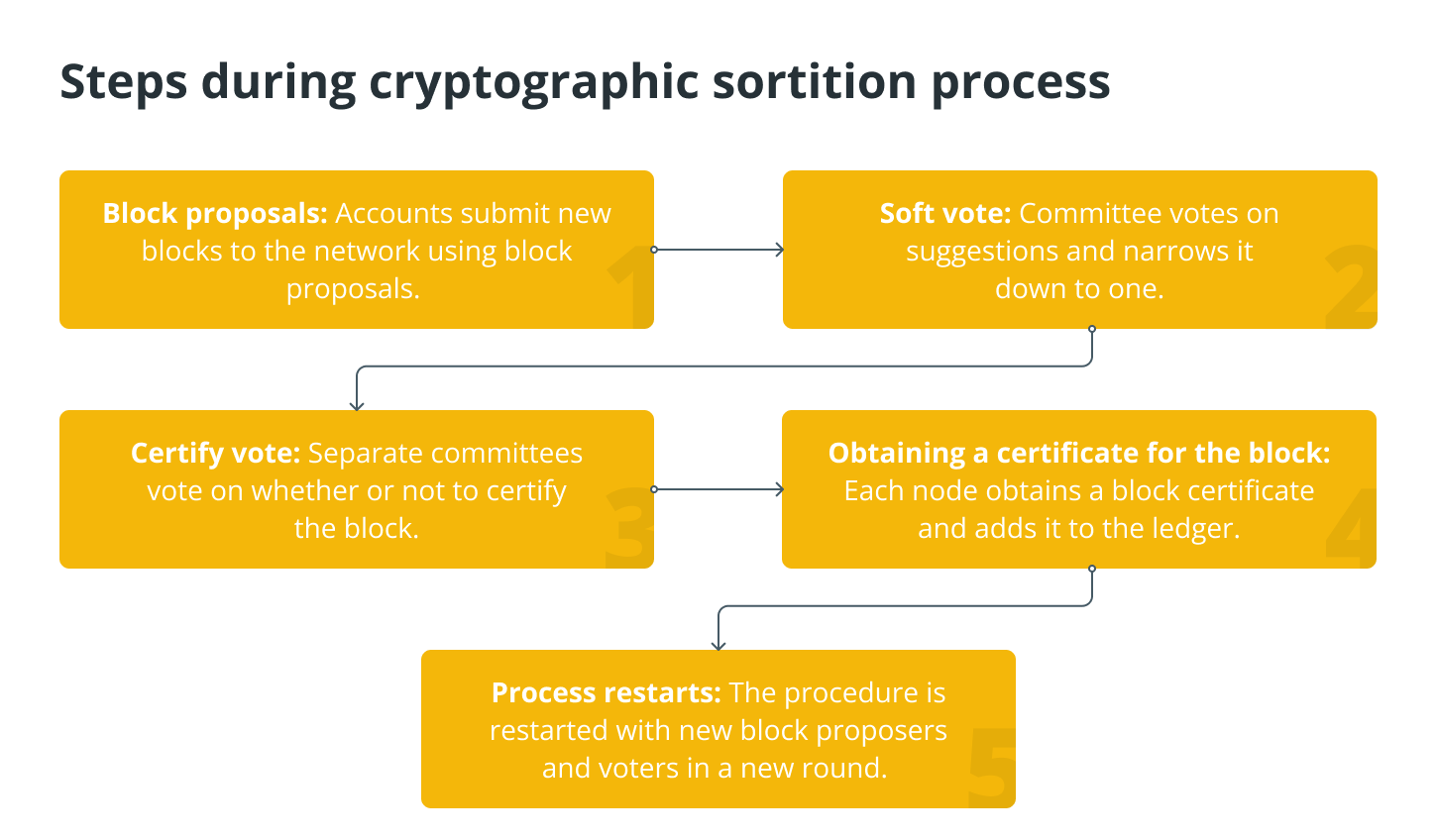
Cryptographic sortition
BA chooses committee members in secret, hands-off way so that an enemy can’t target them. This means that each person who uses the system can decide for themselves if they want to be on the committee.
If the user is chosen, the function makes a short string that other users can use to see that the user is on the committee. The user can include this string in his network messages. For example, a bad guy doesn’t know which user to go after until that person starts using BA, because choosing who to be a member isn’t interactive.
Here are the steps that make up the cryptographic sorting process:
 How does Algorand work?
How does Algorand work?
In the Algorand network, there are two kinds of nodes: participation nodes and relay nodes. The relay nodes keep the connection between Algorand and the rest of the system’s nodes going. Participation nodes use their computing power to verify transactions, and they are the nodes that get the biggest rewards.
The participation nodes use the relay nodes to connect to each other and keep track of the ledger. In Algorand, anyone can run a relay or a participation node, but participation nodes get paid for their work, while relay nodes can’t “mine” ALGO. Instead, the Algorand Foundation has set up a reward system for relay nodes that will end in two to five years. To connect to the Algorand network, they need Algorand Virtual Machine, which is a piece of virtualization software (AVM).
On the Algorand network, the AVM is a piece of software that works on both relay and participation nodes. The smart contracts on the Algorand network are checked by the stack engine of the AVM. The AVM also looks at all of the logic in smart contracts before deciding whether or not to carry them out.
Algorand takes care of smart contracts in two ways: on-chain and off-chain. On layer 1, the system makes it possible for smart contracts to work “on-chain,” which is similar to how the Ethereum blockchain works. This means that each smart contract adds to the amount of traffic on the network, and if there are too many of them, the network can slow down.
Algorand has layer 2 smart contracts that are run “off-chain” to get around this problem. The smart contract doesn’t add more traffic to the network. Instead, it runs outside of the network and is recorded in the blockchain ledger.
 How to mine Algorand?
How to mine Algorand?
At the moment, computer hardware can’t be used to mine Algorand. But because Algorand uses the pure proof-of-stake consensus method, it is possible to get ALGO rewards just by staking Algorand in a crypto or Algorand wallet. So, is Algorand a Coin or a Token?
 Algorand is an altcoin that offers many services with added value because it can be used in smart contracts. With the new feature, the platform can be used for more things, like decentralized finance (DeFi) and businesses that use non-fungible tokens (NFT).
Algorand is an altcoin that offers many services with added value because it can be used in smart contracts. With the new feature, the platform can be used for more things, like decentralized finance (DeFi) and businesses that use non-fungible tokens (NFT).
At the moment, these reasons for growth back up Algorand’s bull thesis. ALGO-USD will stand out from the rest of the altcoins as the one with the most potential as more investors add crypto assets to their portfolios.
How do you buy Algorand?
Cryptocurrency exchanges like Coinbase and Binance are places where you can buy ALGO. Follow the steps below to buy ALGO from Coinbase:
• If you don’t already have one, sign up for a Coinbase account. Get your account checked out and add a way to pay.
• Choose “Agorand” from the list of assets to start a trade.
•
To buy ALGO coins, enter the fiat amount, which will automatically be converted to the Algorand amount.
• Look over your purchase again before you pay for it.
If you want to buy ALGO on Binance, you can exchange it on the Binance exchange. For ALGO, you’ll need to use a token in a trading pair like BNB or BUSD. You can also use a debit card, credit card, or PayPal to buy ALGO by doing the following:
Make a cryptocurrency wallet. Once you’ve verified your identity and your crypto wallet account is live, you can buy BTC quickly with your debit card, credit card, or PayPal account.
•Choose a reputable cryptocurrency exchange platform that accepts Algorand and send your newly bought Bitcoin to the exchange platform.
•The last step is to change the BTC you just got into ALGO.
How do you stake Algorand?
Using the mobile wallet app, which is available for both Android and iOS devices, Algorand can be staked right away. Put the ALGO coin directly into your wallet to stake it. Over time, ALGO will be added to the wallet on its own.
Also, on October 1, 2020, Algorand started a program called “community governance,” which gives ALGO holders the chance to decide what will happen to Algorand in the future. People can take part in governance by pledging their ALGO for the 90-day voting period and then voting on the ideas. When the 90-day voting session is over, participants can also get their prizes for governance.
How do ALGO auctions work?
IEO was the first company to offer ALGO on Binance. Pioneers thought that the market should decide how much something was worth, so tokens were given out through a Dutch auction.
A Dutch auction is a type of public auction in which the price of the offering is set after all bids have been made. This price is the highest price at which the whole offering can be sold. In this type of auction, investors put in a bid for the amount they are willing to buy in terms of both price and amount.
The main job of the Algorand Foundation is to give out ALGO tokens. The fund also has a policy for giving money back to everyone who took part in the Dutch auction. On June 19, 2019, the first auction took place, and 25 million tokens were sold for $2.40 each.
Is Algorand a good investment?
Algorand has already shown that it is a strong platform with a lot of developer support, cutting-edge technology, and real-world applications. It is also setting new standards in the digital asset ecosystem by solving the blockchain trilemma, which speeds up the adoption of digital assets around the world by both individuals and institutions.
But from an investment point of view, you should keep an eye on how the ALGO market moves before putting your money into it. The network’s potential is also a good reason for investors looking for growing cryptocurrency networks to buy ALGO, its digital token.
Algorand versus Ethereum: Is Algorand going to kill Ethereum?
No one knows for sure if Agorand is going to kill Ethereum. Algorand is faster than Ethereum, and there are no gas fees. On Algorand, the smallest transaction fee is 0.001 ALGO coins, and it is only based on the size of the transaction.
Both the ASA and the ERC-20 token make it possible to make smart contracts, which is why they are similar. On the other hand, ERC-20 smart contracts always send traffic to Ethereum’s network, which increases gas costs. ASA smart contracts, on the other hand, can be run off-chain, which lowers transaction costs.
Also, bridges between ASA and ERC-20 make it possible for Algorand apps to talk to Ethereum apps. So, money like Tether (USDT) can be sent to ALGO at a rate of 1000 transactions per second.
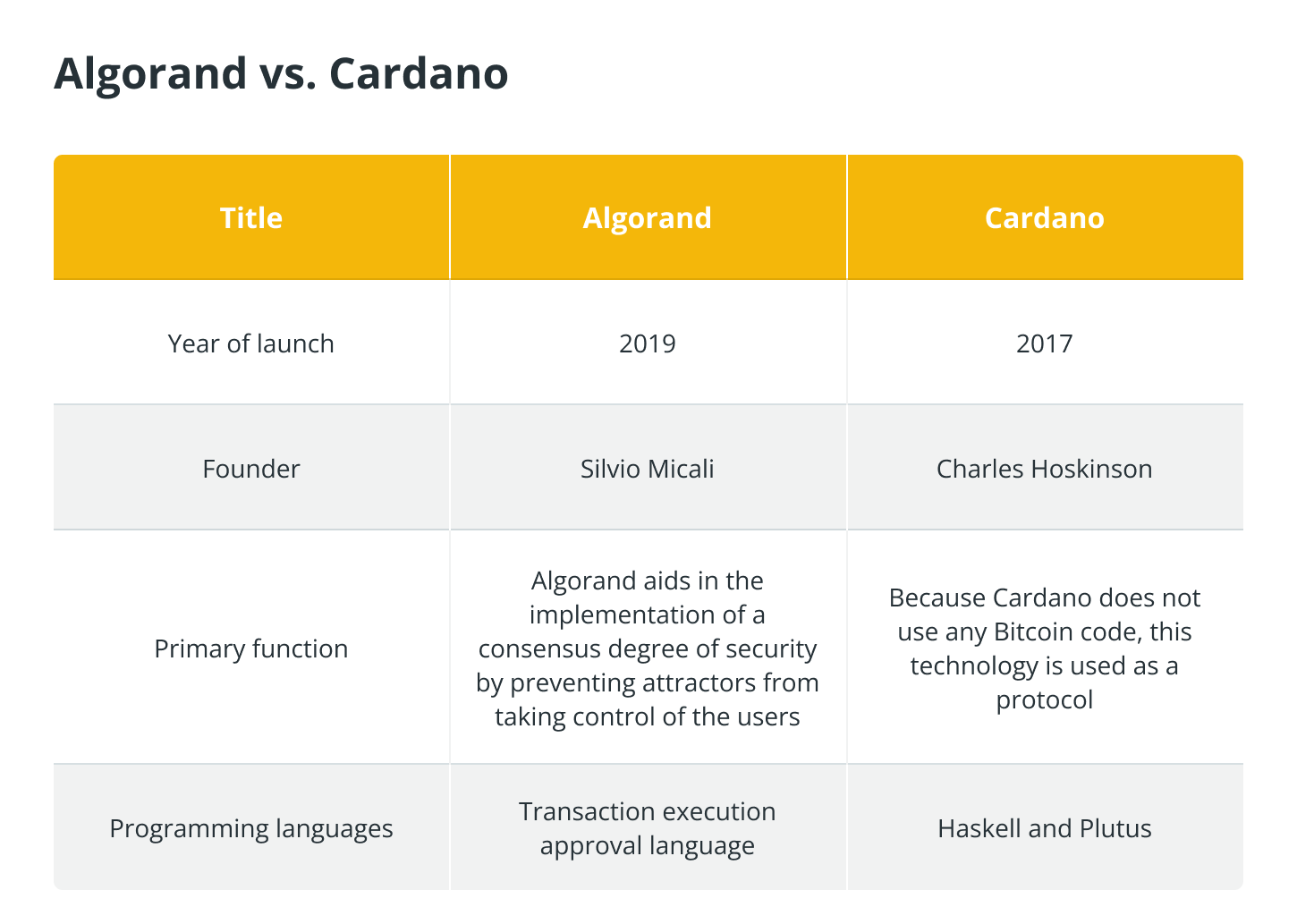
Algorand vs. Cardano
The main difference between Algorand and Cardano is that Algorand was made to use other technologies with pure-proof-of-stake, which addresses security, scalability, and speed issues. Cardano, on the other hand, was made to solve problems with scaling.
In the table below, we compare the main differences between Algorand and Cardano:
The way forward
Algorand says on its website that it is “the future of finance.” Algorand has become such a hot name because its core team is focused on making the best possible technology in the DeFi and NFT spaces, and because it has some of the most sought-after partnership lists out there.
In the world of Ethereum, Cardano, Polkadot, and other blockchains, Algorand, which is led by one of the best living cryptographers, seems to be the most likely winner of the smart contract race.
The future of Algorand blockchain will depend on how hard the team works to make it stand out from competitors and how well it can solve problems that are already happening in blockchain.







