What exactly is “DeFi”?
Centralization serves as the bedrock upon which every economic system is constructed. People have put their faith in centralized authorities like banks, governments, and public enterprises throughout history, in the hopes that these institutions will protect the monetary value and keep economic order.
Because we lacked the technological capability to conduct transactions with one another on a peer-to-peer basis, we were forced to rely on centralized authorities.
However, because of the faith that was placed in those organizations to keep the financial and economic system running smoothly, those organizations have been given a great deal of authority, and they have abused that power by imposing entry and adoption barriers, excessive fees, and usage limits.
Instead of relying on a central authority or intermediaries like brokerages, exchanges, or banks, the innovative and experimental field of finance known as decentralized finance, or DeFi for short, uses smart contracts that are stored on blockchains.
This new system intends to improve the disintermediation principles by creating a financial system that is accessible to anyone, where trust can be verified through the use of code, and which does not require users to have unwavering faith in it.
Decentralization does not imply that there is no centre; rather, it means that nodes have the freedom to choose the centre of their network or organization.
For instance, DeFi creates a global financial environment that is prompt, inexpensive, trustworthy, efficient, and completely transparent by combining traditional banking and investment services with decentralized technologies such as cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications (DApps). These technologies include blockchain and cryptocurrencies.
This new decentralized ecosystem eliminates status, wealth, and geographical barriers by giving unbanked people access to financial services such as digital payments and remittances.
They will be able to use their smartphones to digitally register details and obtain the information necessary to open bank accounts as a result of this.
Because their digital profiles are protected by blockchain technology, anyone, including refugees, can receive loans and launch businesses regardless of where they are physically located.
In addition to this, it will make a contribution toward ending the issue of poverty on a global scale. Additionally, because DeFi eliminates the requirement for certain intermediaries, transaction fees for international payments are reduced.
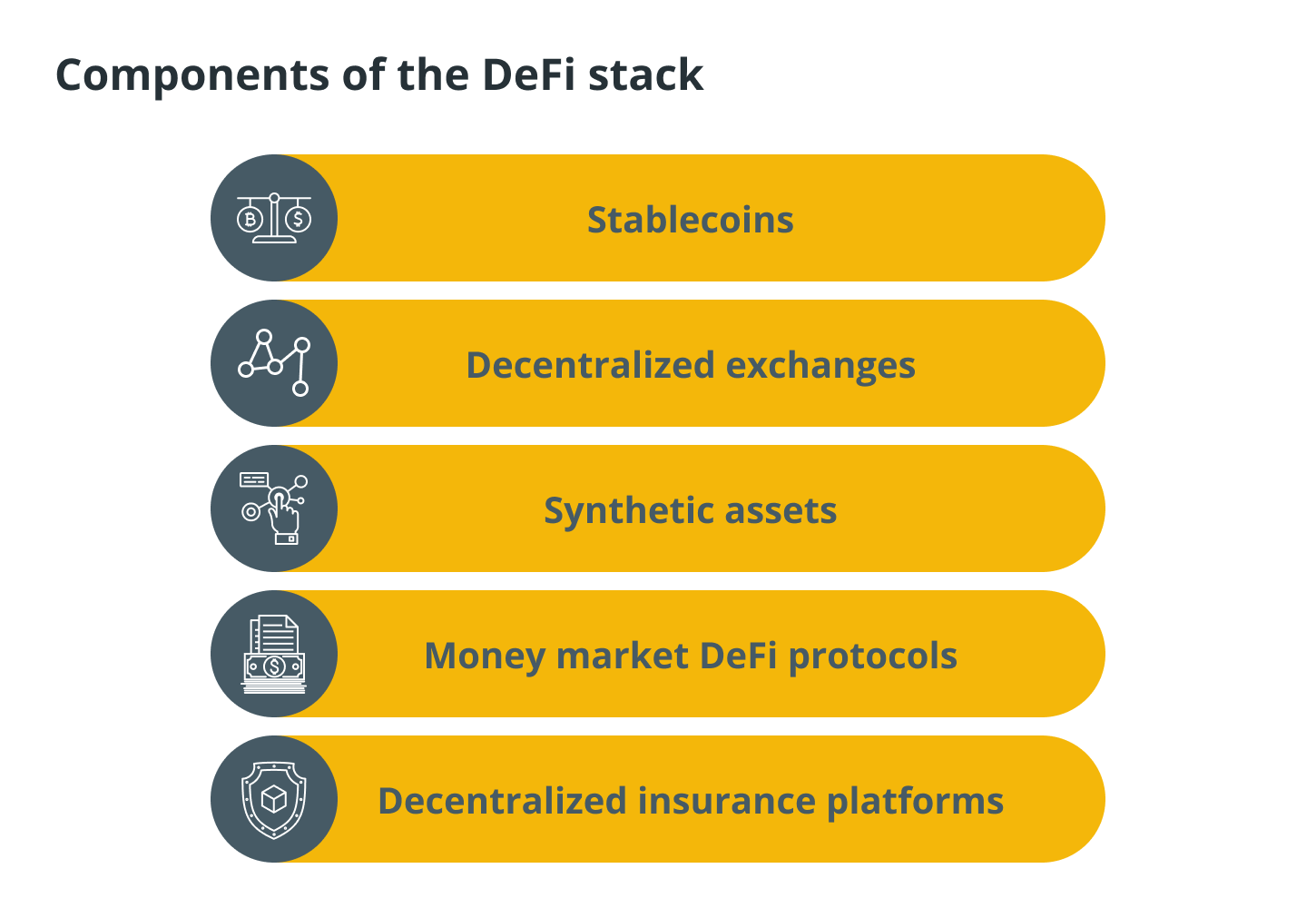
In this article, we are going to talk about the DeFi stack, which consists of stablecoins in DeFi, decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges, DeFi synthetic assets, money market DeFi protocols, and decentralized insurance platforms.
DeFi stack
Blockchain technology is being put to use in the digital currencies Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH), each of which has its own unique set of objectives.
The first is a form of digital currency that can be exchanged for goods and services or held as a store of value. Ethereum, on the other hand, is a programmable blockchain that can be used by programmers to create assets of value.
As a result of the characteristics of blockchain technology, the pieces of software that are developed on the Ethereum blockchain are referred to as DApps.
These decentralized applications were the spark that ignited the DeFi movement, which aims to make the current financial system into one that is more trustworthy, transparent, and decentralized than it currently is. The sections that follow will go over the individual parts that make up the DeFi stack.
Stablecoins in decentralized finance
By linking their value to price-stable assets like gold or the U.S. dollar, stablecoins attempt to achieve a level of volatility that is either low or nonexistent. The Tether (USDT) tokens are pegged to the value of the United States dollar, which means that one Tether is equivalent to one dollar.
Stablecoins can come in a few different flavours, the two most common of which are custody-backed and algorithmic currencies. To keep the same value as the underlying currency, custodial tokens like USDT must have a currency reserve. The backing ratio for these coins is 1:1, and the backing ratio for USDT should not deviate from what it currently is.
The other type of stablecoin relies on the use of algorithms and smart contracts in order to maintain its operation and stability. This method is very similar to the fiat-collateralized process; the only difference is that the underlying collateral asset, in this case, is a cryptocurrency rather than a real-world commodity or a fiat currency.
DAI is an algorithmic cryptocurrency that is based on Ethereum. It uses digital currencies as an economic incentive to encourage arbitrageurs to keep the currency pegged to the United States dollar.
These coins were developed to bridge the gap between traditional currencies and cryptocurrencies and to reduce the risk of loss associated with cryptocurrency holdings. This was accomplished by enabling holders to switch to stablecoins at any time while the value of their holdings remained essentially unchanged.
In order to forestall any issues with liquidity, the reserve asset that underpins these stablecoins is always greater than the amount of stablecoins currently in circulation.
Due to the fact that they help to keep the cryptocurrency market stable, decentralized stablecoins issued by DeFi are an essential part of the distributed financial system.

The DeFi cryptocurrency exchange
In most markets, centralized exchanges and firms act as intermediaries to enable the trading of assets. These exchanges and firms are typically under-collateralized, charge some trading fees, and cause concerns about liquidity when placing orders.
On the other hand, crypto assets found on the DeFi market may be traded through decentralized exchanges (DEXs) without the participation of a third party acting as an intermediary.
Decentralized exchanges, such as Uniswap, enable users to trade without incurring significant trading fees and with only a small amount of exposure to custodial risk. This enables users to keep full ownership of the assets they trade.
The Uniswap cryptocurrency exchange has been running since November 2018, when it first opened for business. This innovative method of providing liquidity, which is known as “automatic market making,” is used by this prosperous exchange rather than a traditional centralized limit order book. This is one of the most notable aspects of this successful exchange.

Within an automated market maker (AMM) such as Uniswap, each asset combination is considered to be its own distinct pool or market.
Liquidity is provided by agents, who do so by adding the pair to the existing pool in the appropriate proportion.
Agents can demand liquidity by first introducing one item and then removing the other.
The relative proportion of the two assets that were traded is used in the calculation that determines the average price paid.
This proportion is determined by a convex relationship with a specified downward slope (a bonding curve).
Because of the convexity, the price has a more significant impact on orders that are more substantial.
DeFi synthetic assets
Synthetic financial assets are engineered to behave in a manner that is similar to that of other financial assets. These synthetic cryptocurrencies are referred to as crypto derivatives, which means that their value is derived from and dependent on the value of other assets.
The risk, exposure, and cash flow patterns that investors face can be highly customized thanks to the availability of synthetic products such as swaps, options, and futures contracts.
In order to replicate operations in decentralized finance, such as liquidity, funding, and market access, this type of financial instrument is required.
As a result of the decentralized nature of the trading system for synthetic assets, there are synthetic platforms available, such as Synthetix.io, on which anybody can exchange, mint, and offer liquidity for a wide variety of assets.
Are you curious about the operation of synthetic investment? Please proceed in the following manner:
• Users mint (or create) synthetic assets by placing collateral on their accounts (SNX for Synthetix). The synthetic asset that was just created uses the collateral to back up its value with something more tangible.
• Oracles supply real-time data to the platform regarding the price of the target asset, which enables the synthetic to track value accurately.
• Traders make use of Synthetix so that they can trade assets such as sUSD (synthetic USD).
• Minters are compensated in the protocol’s native asset, which is referred to as SNX, for minting exchange-traded assets and creating liquidity for those assets.

DeFi money market
In the current economic system, liquidity (which takes the form of loans) is an essential part of any financial market, and banks are the only institutions that can provide it.
In a similar vein, loans are an essential component of the DeFi ecosystem. Through the use of a variety of protocols, individuals are able to lend and borrow crypto assets.
One of the most notable characteristics of decentralized lending systems is that neither the borrower nor the lender is required to reveal their identities.
Additionally, anyone can use the platform to either lend money or borrow money in exchange for interest, and both options are available to everyone.
As a consequence of this, loans through DeFi do not need to be approved and are not contingent on having trusted relationships. The money markets in a decentralized financial system both provide liquidity and make it possible for users to borrow and lend money without the involvement of banks or central authorities.
Money market projects developed by DeFi make use of a liquidity pool architecture similar to that used by Compound to enable users to lend or borrow money outside of the traditional banking system.
Borrowers are required to obtain a loan with an interest rate that is determined by supply and demand. In contrast, lenders have the opportunity to receive passive income by contributing their cryptocurrency to a pool.
To ensure that the liquidity pool is not over-collateralized, distributed finance money markets, in contrast to centralized banking systems, make it possible for anyone to verify the total amount of loans taken out from a lending pool.
Additionally, DeFi products offer significantly higher average returns, with some platforms providing an average percentage yield on deposits of more than 10%. In addition, a borrower’s credit history is not linked to their DeFi account, which protects their confidentiality.
DeFi insurance
The contemporary realm of decentralized finance (DeFi) makes available to millions of people all over the world financial instruments to which they might not have been able to gain access through the conventional banking system.
However, what exactly is meant by “decentralized insurance”? And what part does it play in the world of science fiction and fantasy?
Hackers with keen eyes are constantly seeking new methods to exploit, manipulate, and profit from shiny DeFi systems like Poly Network and a variety of other biggest heists, which results in significant losses for both the company and its customers.
Decentralized insurance is utilized to protect users of decentralized finance from any potential dangers. This helps to limit and cover the risks that are associated with decentralized finance platform usage.
In order to build a community-based business model in which governance decides the outcome of each and every insurance claim, DeFi insurance applications or protocols like Nexus Mutual rely on smart contracts.
As a result, decentralized insurance products offer investors a feeling of safety by providing comprehensive protection for DeFi deposits, hedging risk against the volatility of cryptocurrencies, and keeping cryptocurrency wallets safe from theft.
The future of decentralized finance
In addition to providing customers with a seamless experience from any location on the planet, DeFi solves some of the problems that plague the current monetary system.
These problems include high transaction costs, a lack of access to financial services, slow processing speeds, and security concerns.
The existing monetary systems are primarily overseen and controlled by a group of large and influential institutions. On the other hand, DeFi endeavors to lessen or do away with centralization, as well as a portion of the power and control already possessed by intermediaries.
In addition, the goal of this revolution is to create a permissionless and transparent financial environment that is open to the possibility of being utilized by anyone, including those who do not have bank accounts.
The reform of traditional financial services through the application of a decentralized strategy is both beneficial and innovative. This brand-new ecosystem has a great deal of untapped potential and has the potential to have a significant influence on how people handle their financial dealings in the future.