What is Fantom (FTM)?
Fantom is a smart contract platform for decentralized applications that is based on the DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) protocol (DApps). So, to answer your question, Fantom is either centralized or decentralized.
Fantom is a platform for the development of decentralized applications (DApps) that is highly scalable, decentralized, permissionless, and open source. In contrast to blockchains, which are composed of individual blocks, the data modeling and structuring technology known as DAG uses networks that are made up of vertices and edges. As a direct consequence of this, cryptographic transactions are represented by vertices and are piled one on top of the other.
To put it another way, the structure of a blockchain network is analogous to a chain, whereas the DAG design is analogous to a graph. The Fantom Foundation was established in 2018 by Dr. Ahn Byung Ik of South Korea. Since then, the smart contract project has grown to become one of the most popular blockchains for DeFi transactions.
It was developed to address the shortcomings of earlier blockchain platforms, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, which included the lengthy transaction times that those platforms required. FTM is the native coin of the Fantom network and can be used for a variety of purposes, including governance activities, validator compensation, and the provision of network security.
The purpose of this introduction to the Fantom blockchain protocol is to educate the community about the Fantom ecosystem. This will be accomplished by discussing topics such as the operation of the Fantom Network, the purchase of Fantom (FTM), and the distinctions between FTM and Polygon (MATIC).
What is so unique about Fantom?
Traditional blockchain systems, such as the blockchain used by Bitcoin, are not designed for scalability; rather, they put an emphasis on decentralization and security. For example, the time required to complete a transaction on the Bitcoin network can range anywhere from ten to fifteen minutes. Because of this, it is difficult to scale the network in terms of the number of transactions.
This void is something that the Fantom team hopes to fill by implementing a leaderless proof-of-stake (PoS) protocol as a means of providing security for the network (i.e., the blockchain does not compromise security or decentralization). In addition, the completion of a transaction on the FTM network takes between one and two seconds. In addition to this, the fees associated with transactions are a lot more reasonable.
The Fantom Opera mainnet is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), and it provides full support for the functionality of smart contracts written in Solidity. The Fantom network is one of a kind because it is self-contained. This means that the performance of one region’s traffic congestion has no bearing on how other regions of the network handle their congestion. Therefore, does Fantom have its very own blockchain?
As a result of Fantom’s high level of scalability, each application receives its very own individualized blockchain that is completely autonomous and comes equipped with unique tokens, governance rules, and tokenomics. Fantom is made up of an infinite number of decentralized systems, all of which communicate with one another while operating independently within their own domains.
 How does Fantom solve the trilemma problem that blockchain technology presents?
How does Fantom solve the trilemma problem that blockchain technology presents?
A significant problem is the so-called “Blockchain Trilemma,” which can be solved by Fantom. The term “blockchain trilemma” refers to the impossibility of simultaneously achieving optimal levels of speed, security, and decentralization in a distributed ledger system. Fantom achieves decentralization and security through the use of a permissionless protocol and aBFT to process transactions asynchronously. This speeds up the process overall and helps Fantom achieve its goals.
Lachesis, Fantom’s DAG-based asynchronous Byzantine fault tolerance (aBFT) algorithm, outperforms both the Classical and Nakamoto models. aBFT stands for asynchronous byzantine fault tolerance. Lachesis is an alternative that is superior in terms of its efficiency, scalability, and security, and it enables developers to create peer-to-peer applications without having to build their own networking layer.
Lachesis is an asynchronous system, which means that participants can decide how quickly they want to process commands. In addition, there is no leader, and no one serves in a “special” capacity within the group. In addition, Lachesis is Byzantine fault-tolerant (BFT), which indicates that it is capable of reaching consensus even in the presence of problematic nodes, such as those that are engaged in malicious activity. At long last, the output of Lachesis can be immediately put to use. Because transactions are validated in one to two seconds, there is no need to wait for the validation of entire blocks.
Lachesis is connected to other Lachesis nodes through the use of peer-to-peer networking and a DAG aBFT consensus algorithm. This is done to guarantee that the same commands are processed in the same exact order. Because of the consistent occurrence of the same event across all of the elections, there are fewer new consensus messages being developed. When compared to synchronous BFT, the Lachesis algorithm achieves both a shorter amount of time required to reach finality as well as a lower amount of communication overhead.
What exactly is the use of FTM?
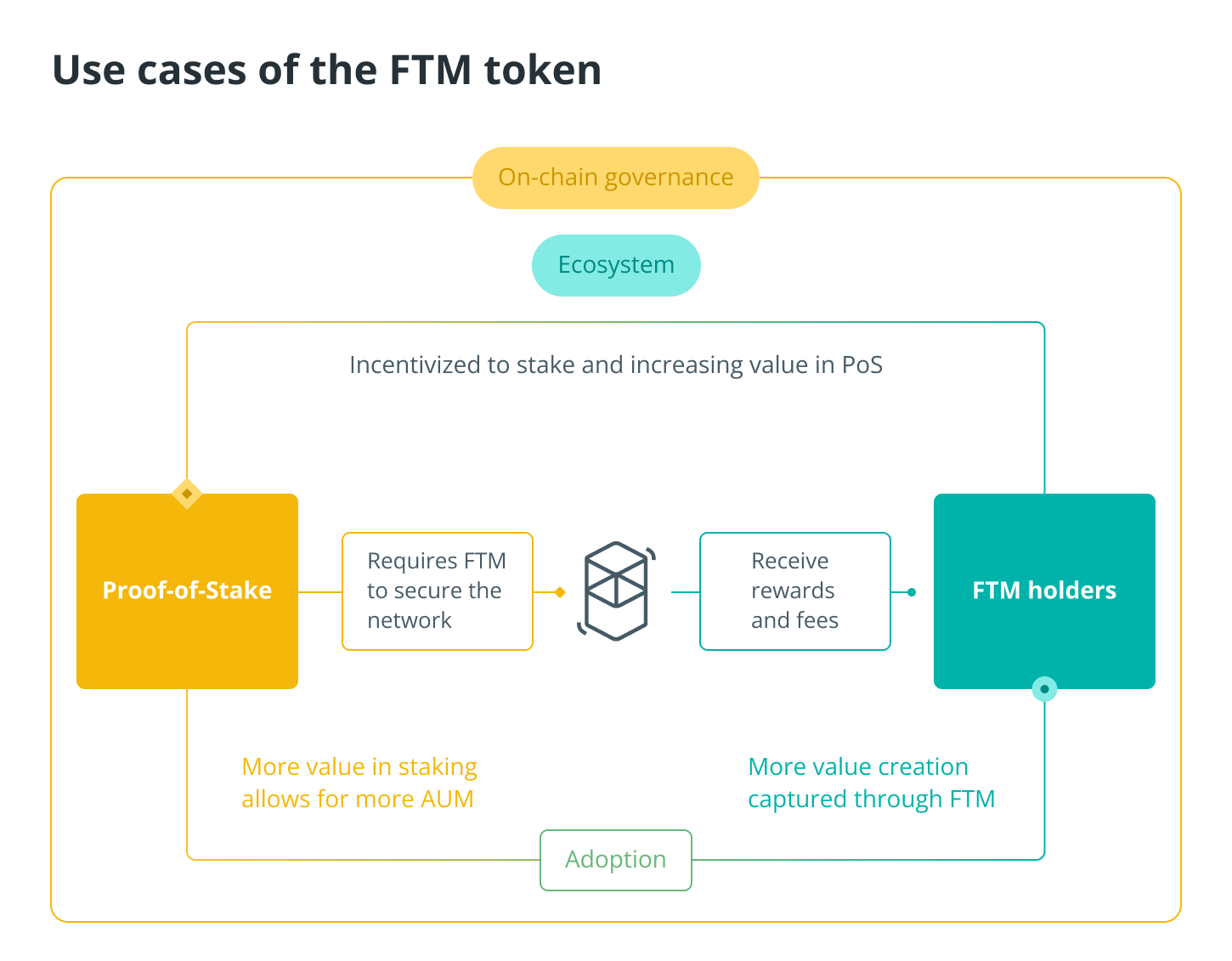
The Fantom network’s primary token is called FTM, and it is used for a variety of purposes, including payments, governance, staking, fees, and network protection.
Payments
Because of the rapid finality of the Fantom network, payments are processed more quickly (take around a second). In addition, the FTM token is ideal for use in monetary transactions due to its high throughput and extremely low costs (approximately $0.0000001).
Governance
FTM is required for on-chain governance, which means that stakeholders will need to be able to propose and vote on modifications and improvements to the governance system. On-chain governance is in charge of all network decisions because Fantom is a completely decentralized ecosystem that does not require any permissions and does not have a leader. As a result, the governance token, also known as FTM, is required to take part in the voting process.
Staking
Without the need for any specialized hardware or software, FTM can be staked in order to contribute to the security of the Fantom network and receive additional FTM tokens as a reward. It is as easy as that, and you can do it from either your phone or your computer!
Network fees
In order to pay for network fees, such as those associated with the deployment of Fantom smart contracts, the creation of new networks, or even transaction fees, FTM is utilized.
The fee ensures that the network is not an easy target for spam and that a malicious user cannot cause speed issues or clog the ledger with meaningless data. Both of these problems are prevented by the fee.
Although the fees on Fantom aren’t particularly high, they are high enough to deter would-be malicious actors and keep them at bay. This is because they make it extremely expensive for them to enter the system.
Network security
The FTM token is designed to protect the network by utilizing a proof-of-stake protocol, which requires token holders to lock their holdings and requires validators to have a minimum of 3,175,000 FTM in their possession before they can take part. Stakeholders and validators are compensated with fees and epoch rewards for their services.
 Where can I buy Fantom cryptocurrency?
Where can I buy Fantom cryptocurrency?
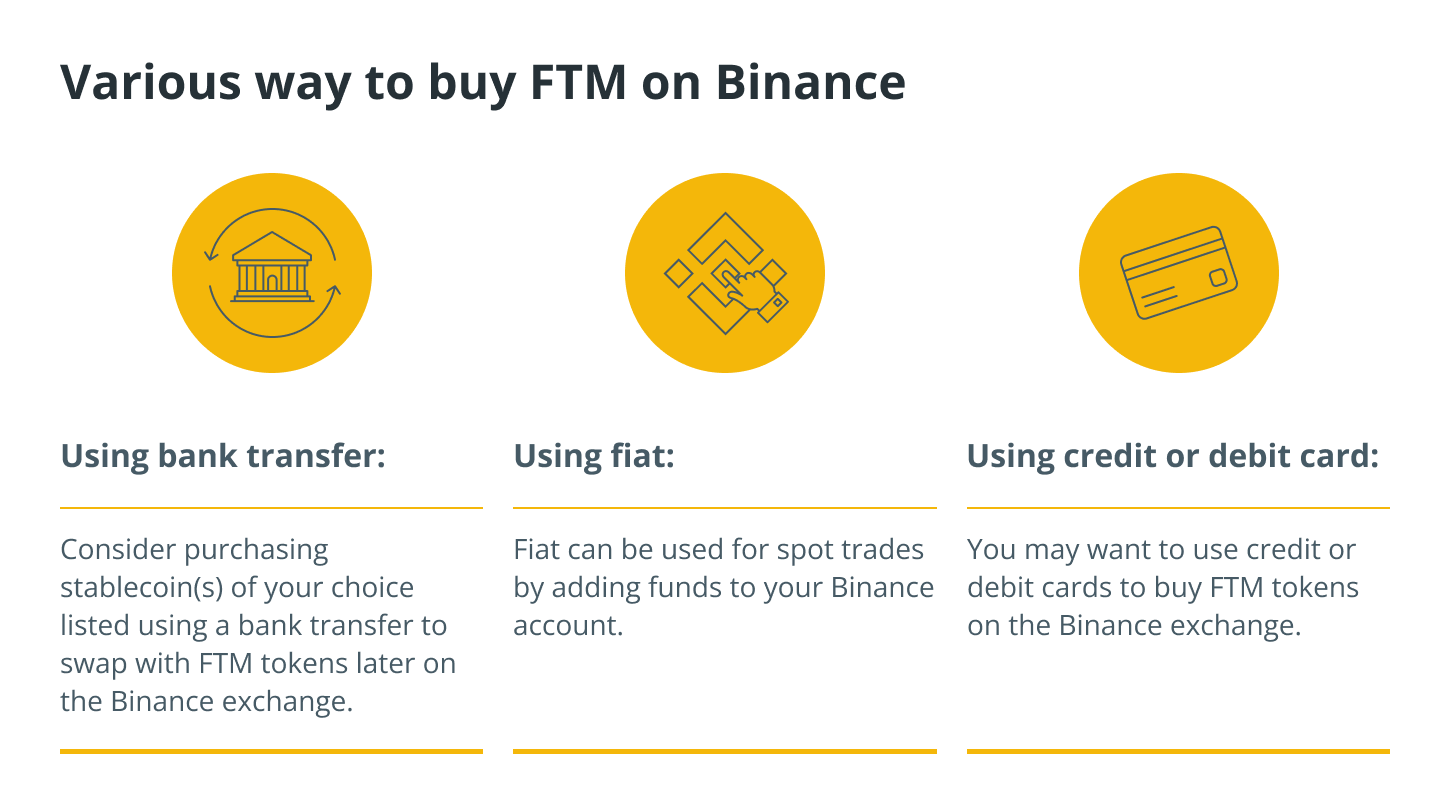
You can buy FTM on all of the major cryptocurrency exchanges, such as Binance and KuCoin, but Binance is the exchange with the highest volume and the least amount of slippage. KuCoin is also an option. Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Tether (USDT), or Binance Coin (BNB) can all be used to purchase FTM.
Any of the following methods may be utilized in order to acquire Fantom tokens on Binance:
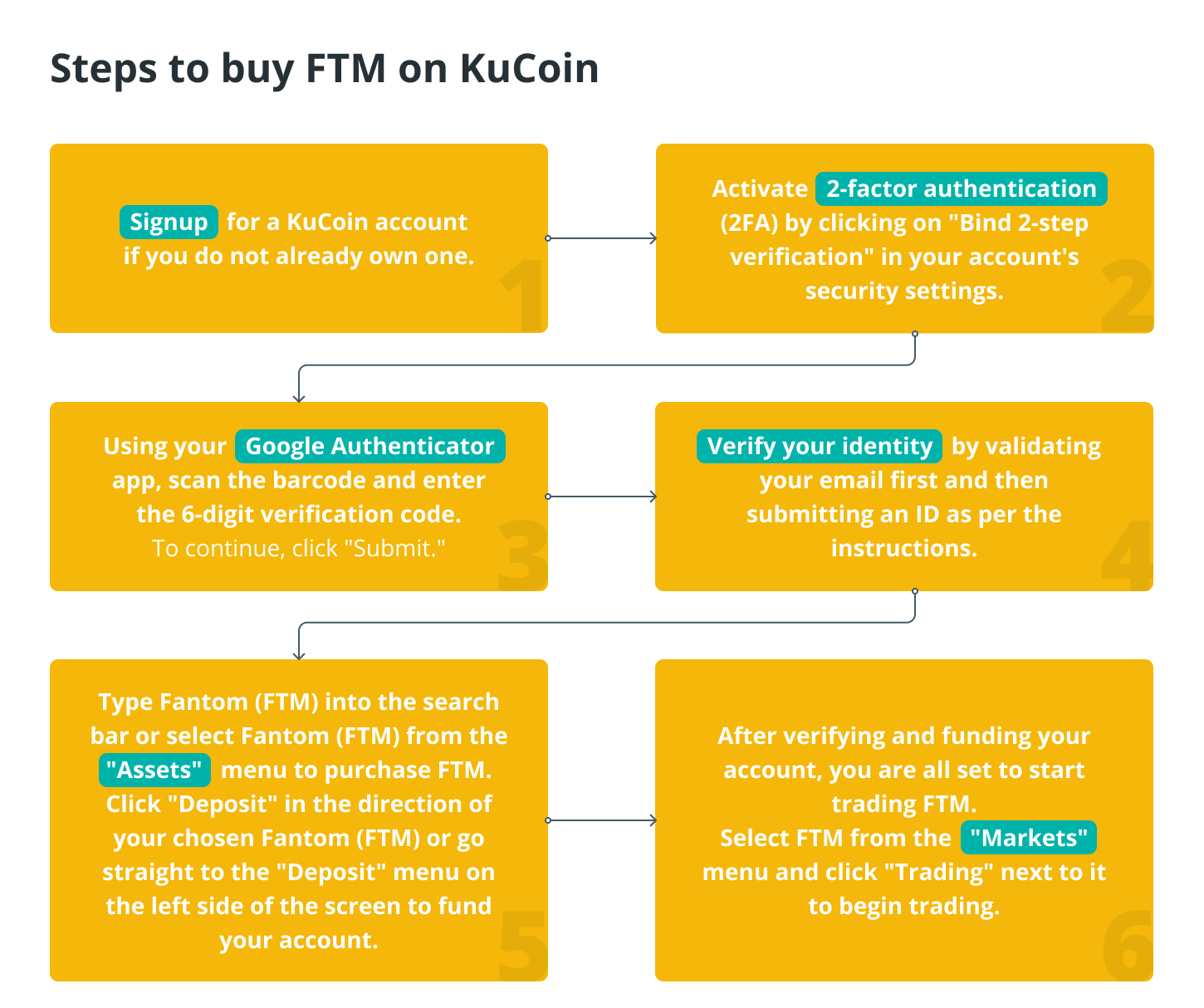
 If you are passionate about KuCoin, then you should follow the steps below to purchase FTM:
If you are passionate about KuCoin, then you should follow the steps below to purchase FTM:
 How should FTM be stored?
How should FTM be stored?
You should try to avoid storing your FTM on exchanges because of the risks associated with custodial services. If you use custodial services, you won’t be eligible for any staking rewards, which is another disadvantage. Wallets such as fWallet (Fantom wallet), MetaMask, Ledger, and other popular mobile wallets can be used to store FTM and Fantom-based coins such as USD Coin (USDC) and fUSDT in a secure manner. These coins include USD Coin.
fWallet grants you access to the Fantom DeFi ecosystem as well as the ability to receive, transfer, and stake your FTM. You will be able to communicate with Fantom decentralized applications (DApps) and store mainnet FTM if you use MetaMask.
The Ledger Nano is currently the most popular hardware wallet technology and the safest way to store your mainnet FTM and interact with DApps on Fantom. More than one million users are able to use the Coinbase wallet to store FTM and gain access to the Fantom network with ease. You can find a variety of other wallets compatible with the FTM token.
Staking on the Fantom network
At Fantom, a scalable blockchain platform for DeFi, the proof-of-stake consensus algorithm serves as the backbone of the staking process.
It is necessary to stake your FTM token in order to validate transactions on the Fantom network; in exchange for doing so, you will be rewarded with FTM tokens. Only you have access to the tokens that have been staked, and you have complete control over when you unlock or unstake them.
On the other hand, validator nodes and stakers are required to adhere to a few staking parameters, which are as follows:
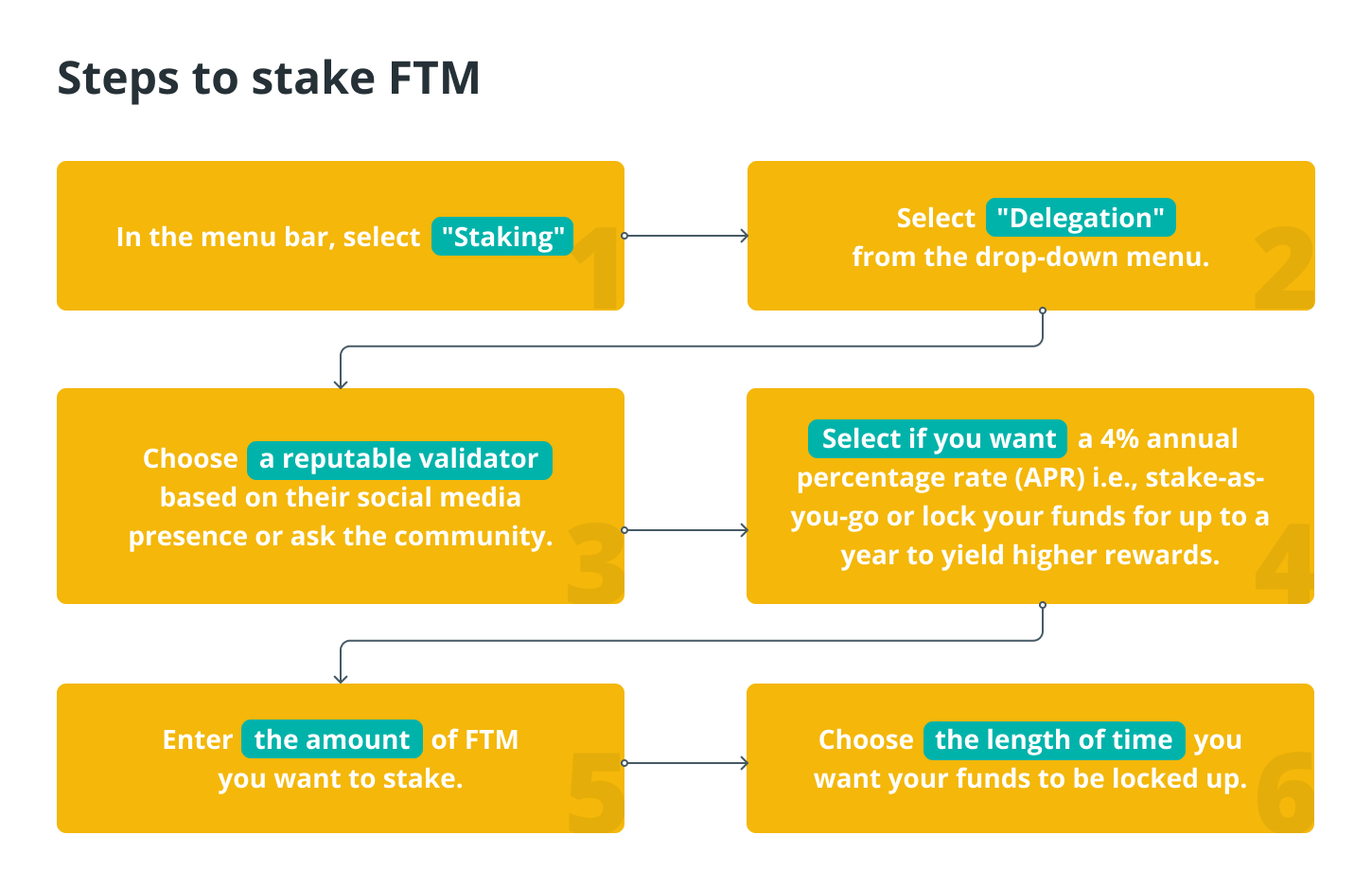
 If you think that staking FTM might be interesting to you, then you should follow these steps:
If you think that staking FTM might be interesting to you, then you should follow these steps:
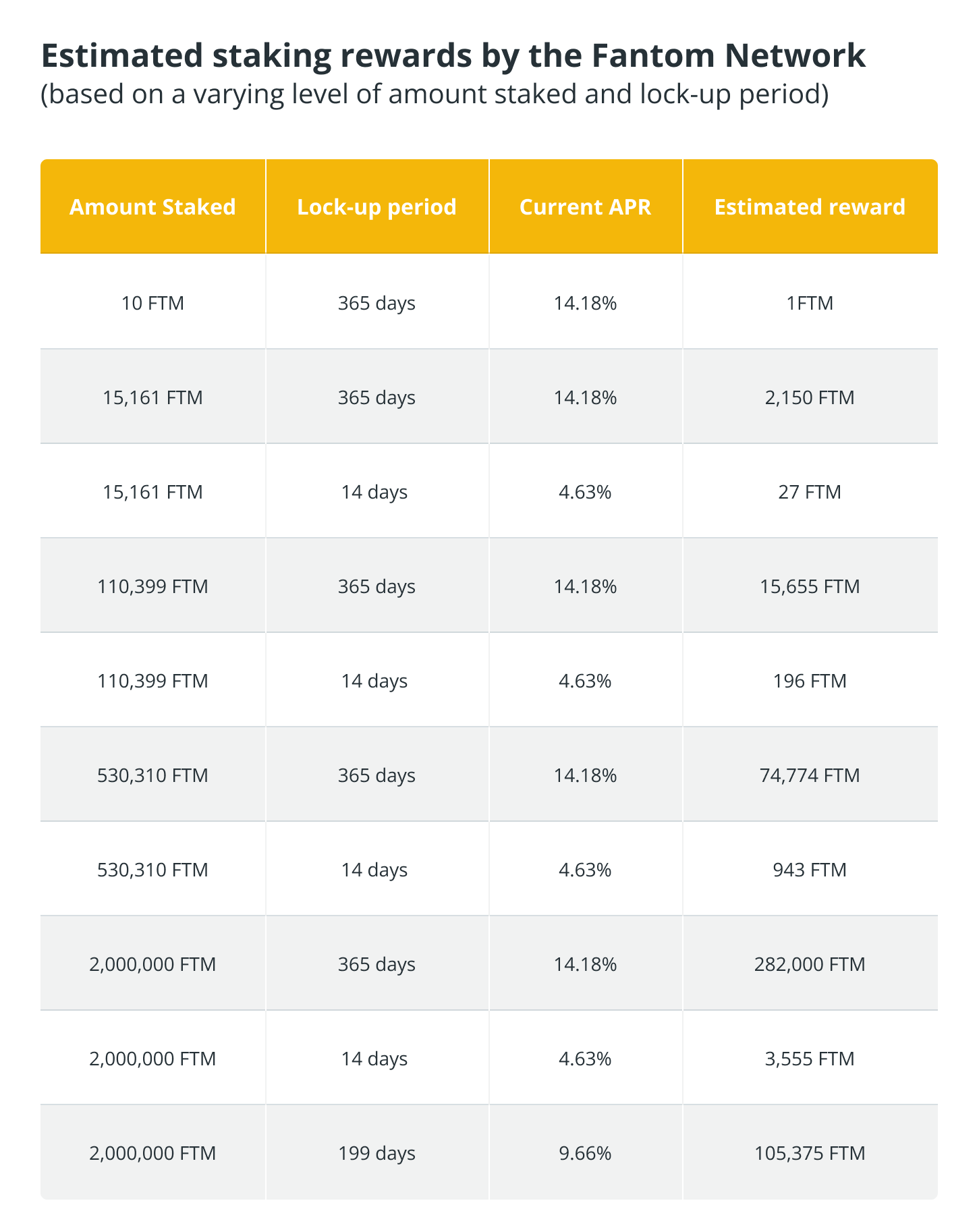
 You will be able to get an estimate of the rewards you will receive here. On the other hand, we have also compiled a short list of rewards for you, which can be found in the table below:
You will be able to get an estimate of the rewards you will receive here. On the other hand, we have also compiled a short list of rewards for you, which can be found in the table below:
 If you decide to unstake your FTM holdings but then change your mind and want to reclaim them at a later time, you can do so by selecting the “claim and restake” option from the drop-down menu.
If you decide to unstake your FTM holdings but then change your mind and want to reclaim them at a later time, you can do so by selecting the “claim and restake” option from the drop-down menu.
What is the distinction between claiming rewards and claiming and restaking rewards?
When you claim rewards, any pending awards that were stored in your wallet will be removed at that time. You will, however, be able to multiply the benefits under the same terms as your initial delegation if you claim and restake the delegation.
For instance, if you lock up your tokens for a year at the maximum APR, you will continue to receive that APR even if you restake your tokens at a later time during the lock-up period. On the other hand, if you want to stake your rewards after you have claimed them, you will need to begin a new delegation in order to do so.
Is Fantom a good investment?
When the volatility of the cryptocurrency market is taken into consideration, no investment can produce returns that can match your expectations. As a consequence of this, prior to contributing any money, you should always conduct research into the procedure, the team, the sponsors, and the partnerships. Never put more money into the market than you can comfortably spare.
Although it is a highly scalable platform for enterprise applications and cryptocurrency DApps, an investment in Fantom is not without risk. Should you put your money into Fantom (FTM), then? Due to the fact that the crypto market is unregulated and therefore vulnerable to frequent hacks, scams, and cyber threats, FTM is an unsafe investment asset just like many others. Investing is therefore done at your own peril.
Stay up to date on the various methods that crypto heists use, and protect yourself by employing a variety of different security measures, such as two-factor authentication and staying away from custodial wallets, for example.
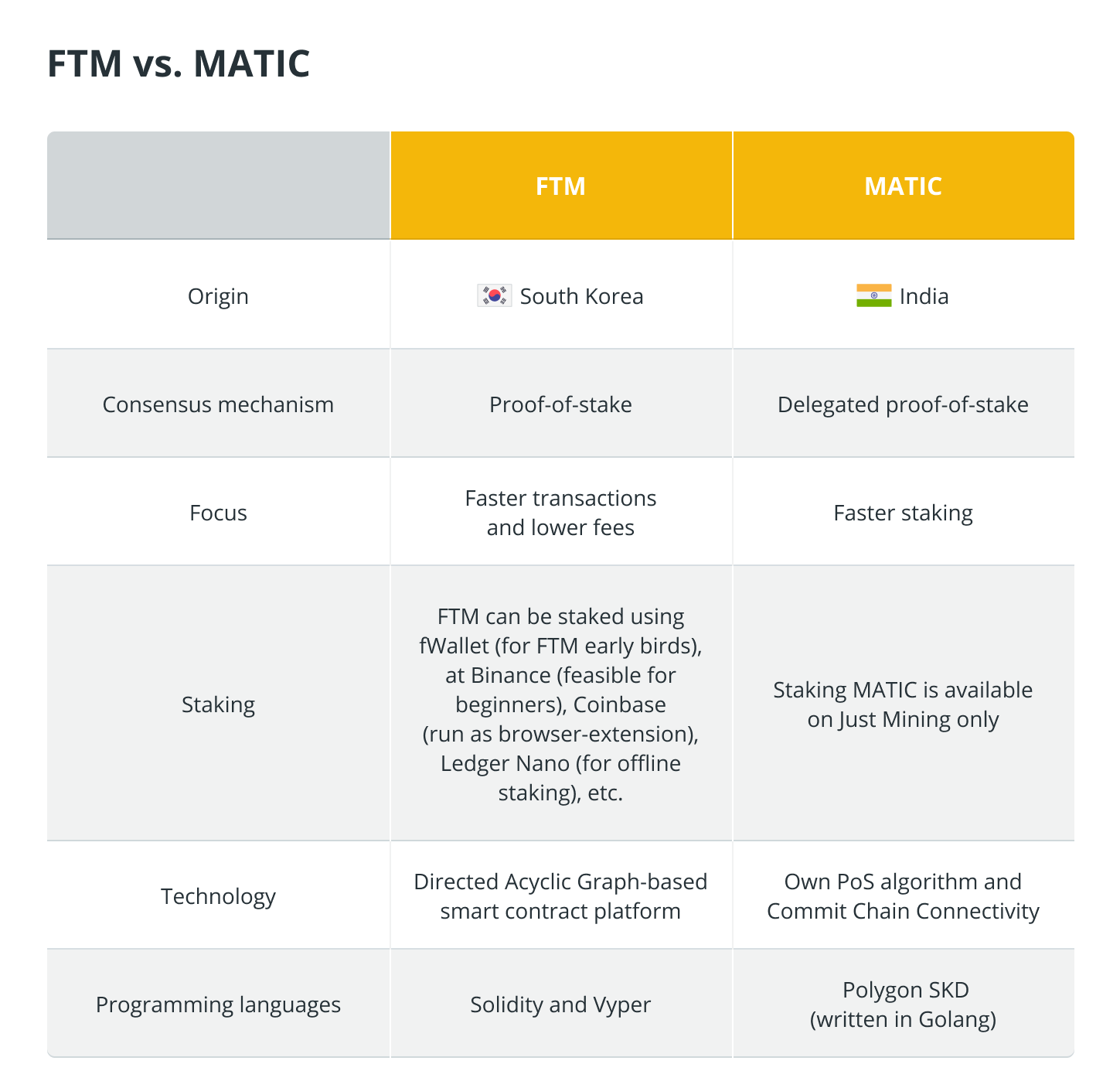
FTM vs. MATIC
Fantom and Polygon (MATIC) are alternative cryptocurrencies that can scale compared to preexisting blockchains. Nevertheless, they are not the same, as will be shown in the following examples:
What lies ahead for the Fantom cryptocurrency
Fantom utilizes the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus method and Lachesis, which is Fantom’s aBFT consensus algorithm, to set the nodes’ communication rules. This allows Fantom to be more secure and less harmful to the environment than traditional cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Andre Cronje has dropped hints that the community will soon see new additions to the Ve(3,3) project that he is working on. Reportedly, the project will launch its own “emission-based” coin on Fantom in order to strike a balance between the various players in the Fantom ecosystem.
In addition, because there is already a lot of competition in the cryptocurrency industry, the platform’s creators and developers will be on the lookout for new partnerships and sponsors in order to improve the platform’s functionality and win the trust of the community.