The provision of decentralized financial services is the primary focus of the decentralized finance (DeFi) industry, which is a subset of the cryptocurrency industry. It is made up of a variety of different financial services that have been developed by developers and are available to anyone.
These services are distinct from their centralized counterparts in that they are managed by groups of individuals collaborating through decentralized organizations. Furthermore, users have greater control over the funds associated with their accounts.
The DeFi industry is a hive of activity when it comes to innovation, as weekly additions of new decentralized and non-custodial financial services demonstrate. These services are available to anyone from any location in the world, and they can be used to their advantage.
According to data provided by the World Bank in the year 2017, it was estimated that approximately 1.7 billion adults across the globe did not have access to banking services, meaning they did not have an account at a financial institution.
Because there are no entry requirements for the financial services provided on the DeFi protocols, anyone can use them to gain access to financial services. The only real obstacle to entry is the required level of expertise.
In order to guarantee that everyone has equal access to financial services, the DeFi ecosystem is constructed on top of publicly distributed networks. It uses self-executing agreements written into lines of code and is referred to as smart contracts.
How to use DeFi protocols
The vast majority of DeFi protocols are built on top of existing networks such as Ethereum or Binance Smart Chain. The number of competing blockchain networks that offer support for smart contracts is continuously expanding. It is essential to select a network before settling on the decision to use services available via DeFi.
The ease of use and transaction fees are typically the primary differentiating factors among the numerous blockchains now supported by most large protocols.
Wallet extensions such as MetaMask allow access to networks such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Polygon. Switching networks requires only the modification of a few parameters in the extension’s configuration file.
Users are essentially granted access to their funds directly within their browsers through the use of these wallet extensions. They are installed in the same manner as any other extension, and users are typically required to either import an existing wallet by providing a seed phrase or a private key, or generate a new wallet in order to use them.
They are also protected by a password, which adds an additional layer of safety. Some web browsers already have these wallets pre-installed on their systems.
In addition, these wallets frequently come with mobile applications that can be used to gain access to different decentralized finance initiatives. These applications are wallets equipped with their own web browsers and ready to interact with other DeFi applications.
Users are able to keep their wallets in sync by first creating them on one device and then importing them to another using the seed phrase or private key.
These mobile applications typically also integrate the open-source WalletConnect protocol in order to make things simpler for their respective users. Users are able to connect their wallets to DeFi applications running on desktop devices by simply scanning a QR code with their mobile devices, which is made possible by this protocol.
Before we get started, it is important to make clear that the area in which we will be working is highly experimental and carries a number of potential dangers with it. Since exit scams, fraudulent projects, rug pulls, and other scams are fairly common, it is imperative that you conduct independent research before investing any money.
In order to avoid falling prey to these scams, here is how to take your security precautions one step further: It is in everyone’s best interest to determine whether or not the projects have been audited. Finding out this information may require doing some research; however, in most cases, all that is required is a simple search using the name of the project followed by the word “audits” to determine whether or not the project has been audited.
Audits help weed out potential vulnerabilities while also discouraging people from engaging in malicious behavior. It is highly unlikely that projects with less-than-stellar potential will spend the time and resources necessary to get audited by reputable firms.
Buying cryptocurrencies (Coins / Tokens)
DeFi applications are built on top of networks and each network has its own native tokens that are easily identifiable through the ticker symbol they use on exchanges: Ethereum (ETH), Polygon (MATIC), Binance Coin (BNB) and so on.
These native tokens are used to pay for transactions on these blockchains, so you’ll need some of those tokens to move funds around. You can choose to just buy these native assets before delving into DeFi, or you can add stablecoins or other assets.
When you have completed the purchase of the funds on a centralized exchange, you will need to transfer those funds to a wallet you control that is compatible with the desired network. It is essential to prevent funds from being moved to the incorrect network; therefore, before withdrawing, check that you are making use of the appropriate network.
Some exchanges let users, for example, withdraw Bitcoin (BTC) to an Ethereum address or Ethereum to the Binance Smart Chain. These withdrawals are for tokenized versions of BTC or ETH on those networks, which can be used in DeFi. Those networks are Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Because every transaction carried out using DeFi protocols needs to be manually approved and incurs a transaction fee, it is essential to select a network that has low transaction fees in order to avoid incurring excessive costs.
What are DeFi services?
The next step, following creating a wallet and selecting an application with which to interact, is to begin using DeFi services. The three simplest actions to take are trading using a decentralized exchange (DEX), providing liquidity and earning fees over time, or lending funds using a lending protocol.
Because there are so many options available, we will not go into detail about each and every project; instead, we will provide an overview of the different products and services that are at your disposal, as well as the factors that you ought to take into consideration before employing any of them.
To begin using a wallet that is compatible with DeFi protocols, you must go to the website of these protocols and connect your wallet to them. This is the only thing you need to do. Either a pop-up window or a button that says “connect” can be used to accomplish this on the website. You can find the button in one of the website’s upper corners.
The process of connecting your wallet to the service is analogous to “logging in” to the service using your account, which in this case is the address of your wallet. You are going to have to enable each token individually before you can lend, borrow, or trade tokens using DeFi protocols. This is necessary so that the protocol can access the tokens stored in your wallet. There is a nominal charge associated with this method of connection.
Making your crypto work for you with DeFi
It is essential to have an understanding that, despite the fact that the DeFi industry offers a wide variety of products and services, the industry as a whole is highly interconnected and composable. This means that intricate strategies to increase yields are feasible but that a flaw in one protocol could cause losses in another.
The fact that there are no trusted third parties is the most significant benefit of utilizing DeFi. Because most of these protocols are run by decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) rather than centralized companies, the code written in the smart contracts that DeFi protocols use is accessible to anyone who wishes to read it.
Before venturing into space, prospective users are strongly encouraged to familiarize themselves with the DeFi ecosystem’s various service offerings.
Lending
The DeFi protocols aim to eliminate the need for intermediaries while facilitating the lending and borrowing of cryptocurrencies. Because they are determined by supply and demand, interest rates are subject to change over the course of time. Most protocols demand that borrowers provide excessive collateral for their loans to guarantee that lenders will be repaid if the market becomes volatile.
Imagine that a user has a short-term obligation that requires them to pay $1,000. If they do not have access to DeFi, they might be compelled to liquidate their Bitcoin or Ethereum holdings to obtain the necessary funds.
They could, for instance, deposit $1,500 worth of Bitcoin into a protocol in order to obtain a loan of $1,000 denominated in a stablecoin by utilizing the DeFi lending services. They are able to fulfil their obligation without suffering a reduction in their exposure to BTC, and then they are only required to repay the loan with interest attached to it.
In the event that the price of Bitcoin plummets and the value of their collateral falls below $1,000, the smart contracts that are a part of the DeFi protocol will sell the coins in order to repay the lender. If the price of Bitcoin goes up while they are paying back the loan, the move will have been justified because the user will not have lost exposure to the market.
Liquidity mining and yield farming
The leading DeFi protocols include decentralized exchanges as one of their components. To execute trades on the blockchain using smart contracts, rather than order books like centralized exchanges, they use a model known as an automated market maker (AMM).
This model does away with the use of traditional order books and instead relies on pre-funded liquidity pools that contain both assets in a trading pair. Users provide liquidity in these pools, which are then eligible to earn fees from trades executed on that pair. The process of users earning money by merely contributing liquidity to various pools is called “liquidity mining.”
Mining for liquidity comes with certain risks that lending does not, including the possibility of temporary loss. Because liquidity providers are required to deposit both assets of a trading pair into a liquidity pool, for example, ETH and stablecoin DAI, a temporary loss occurs as a result of this requirement.
When the trades that are being carried out reduce the quantity of one asset in the pool — in this case, ETH — and the price of that asset rises, the liquidity provider suffers a temporary loss because they now hold less ETH despite the fact that its value has increased.
Because the price of the asset could still move back to when it was first added to the pool, and because the fees collected could make up for the loss over time, the loss is only temporary. Nevertheless, it is something that needs to be taken into consideration as a risk.
Mining for liquidity is frequently accompanied by the distribution of a governance token associated with a DeFi protocol. The process that results in yield farming is called “some protocols distribute governance tokens to anyone who interacts with them over time.” It began with Compound’s COMP governance token and has since expanded to include the vast majority of major DeFi protocols.
Asset management
Users are able to monitor, deploy, and manage their capital through a single interface with the help of asset management platforms for DeFi.
When lenders and liquidity providers deposit funds on a DeFi protocol, they are given tokens representing these interest-earning positions. These tokens are frequently referred to as compound tokens (cTokens) and liquidity provider tokens. When a lender or liquidity provider makes a deposit, they receive a token (lpTokens).
After that, these tokens need to be redeemed for the principal invested, also known as the amount initially invested. When a user deposits 100 DAI into a platform, they are rewarded with a variable amount of cDAI worth the same amount they deposited. In a similar fashion, if a user deposits 100 DAI and 100 ETH into a liquidity pool, that user will have lpETHDAI sent to their wallets.
By utilizing asset management platforms, it is possible to manage numerous positions across a variety of DeFi protocols more easily and to put into action more complicated strategies. For instance, it is possible to use a cToken generated by one protocol to provide liquidity for another protocol, which significantly increases the yield that is generated.
Let’s assume that you have 1000 Dai and 1 Ether in a wallet so that we can simplify this complicated strategy and make it easier to understand. You would deposit the DAI and ETH using protocol A, and in return, you would receive 1000 cDAI and 1 cETH. These amounts would represent our lending positions on this protocol, which would enable us to earn interest.
When you are ready, you can make a liquidity pool deposit on protocol B using cDAI and cETH to increase the amount of cDAI and cETH you earn from trading fees. When cashing out, for example, you would withdraw 1100 cDAI and 1.1 cETH from protocol A because you earned more cTokens from the fees on protocol B. This is due to the fact that you earned more cTokens on protocol B. These tokens would then be able to be redeemed for the initial investment amount plus any interest that had accrued since the investment was made.
Although complex strategies tend to have higher yields, they also tend to have higher risks due to their composability. What is known as “lego money” is the digital currency that is created when DeFi protocols build on top of one another’s publicly available code and services. Every component is linked to the others.
Staying safe
As with initial coin offerings (ICOs), the decentralized finance industry is experiencing an explosion of innovation, and unscrupulous actors are attempting to take advantage of users by exploiting various loopholes in order to maximize their own financial gain.
Before using a DeFi application, it is important to determine whether it has been audited; however, users also need to ask themselves a number of questions before interacting with a protocol or purchasing its governance token.
In the world of decentralized finance, it is not unheard of for annual percentage yields (APYs) to reach triple digits. This is partly due to the possibilities associated with yield farming. However, one of the most important rules of investing is that risks must always be balanced by rewards: It is not uncommon for annual percentage yields (APYs) to be higher than average, but if they seem impossible to believe, further investigation is required.
This more in-depth look would involve investigating the group that was responsible for developing the DeFi protocol in the first place. A centralized team will work on the smart contracts for a protocol before it moves on to become a DAO.
It is not unusual for projects to be developed by anonymous teams; therefore, the most reliable method for determining whether or not the team can be trusted is to examine the team’s level of transparency regarding the protocol’s operations.
In conclusion, it is essential to determine whether or not the community surrounding the project is genuine. It has been done before to use bots on social media in order to generate excitement about a project; however, it is impossible to simulate an active community that candidly discusses governance proposals, future implementations, user experience, and other topics.
Quantifying the risks that come with permissionless lending protocols on DeFi has inspired the creation of open-source projects such as DeFi Score. These can assist users in comprehending how they are supposed to approach the risk posed by these protocols.
Can I make money in Defi
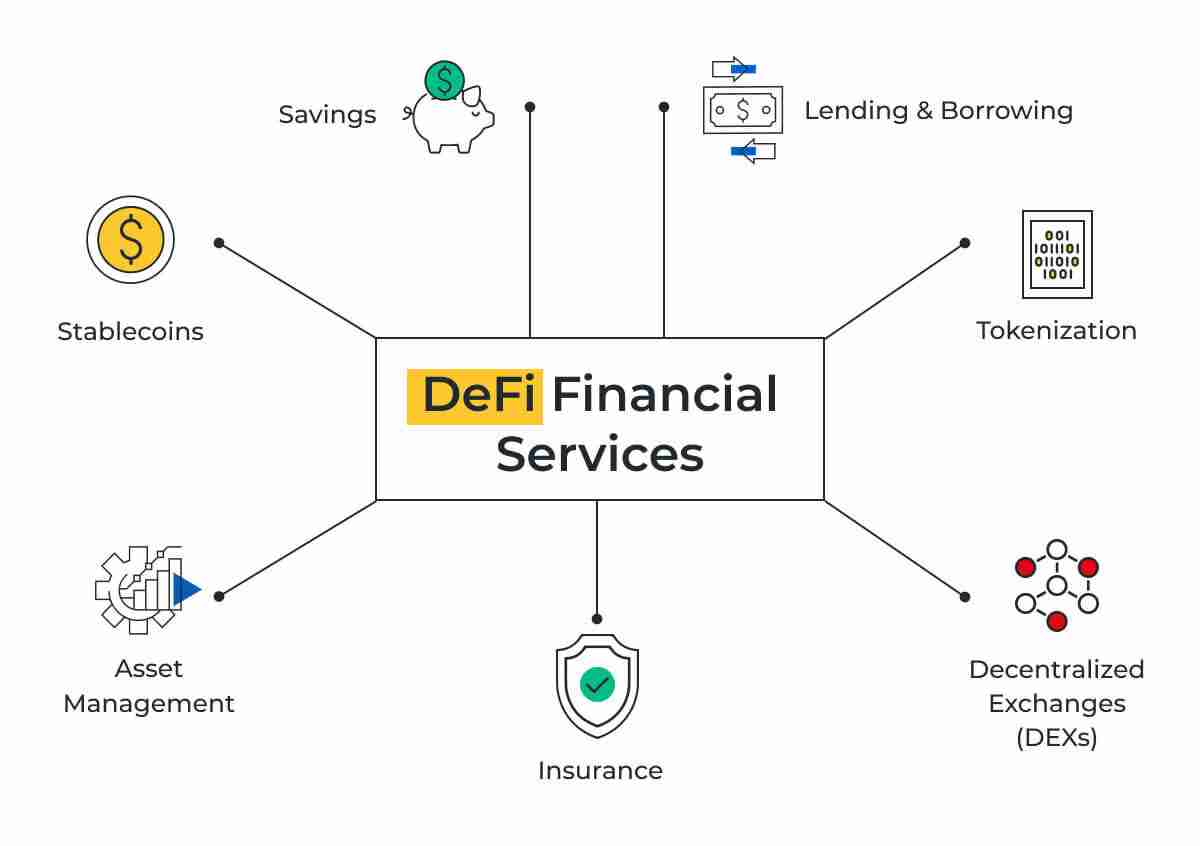
In Summary, Decentralized Finance, also known as DeFi, is the term used to describe decentralised financial services and available to anyone with an internet connection thanks to blockchain technology. You can engage in a number of financial activities in DeFi, including:
Lending and borrowing – You can borrow money from lenders and usually use crypto as collateral, or you can borrow money and lend your crypto assets to borrowers and earn interest.
Trading – On decentralized exchanges, you can trade various cryptographic assets.
Yield farming – allows you to support decentralized exchanges with liquidity while earning rewards like interest or new tokens.
Staking – You can stake your cryptocurrency assets to support a blockchain network’s security and receive rewards.
List of Defi trading platform
A decentralized exchange (DEX) is a place where people can trade cryptocurrencies. A DeFi trading platform is usually built on blockchain technology. These platforms let people trade with each other, so there is no need for a central authority to keep track of the flow of money. Uniswap, SushiSwap, Curve, Kyber Network, and Binance Smart Chain are all popular places to trade DeFi.
Here are some popular DeFi trading platforms:
Uniswap: A decentralized exchange (DEX) for trading Ethereum-based tokens.
SushiSwap: A yield farming and automated market maker (AMM) platform based on the Uniswap model.
Curve: A decentralized exchange focusing on stablecoins.
Aave: A decentralized lending platform that supports multiple cryptocurrencies.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC): A blockchain network designed to host DeFi applications and decentralized exchanges.
Compound: A decentralized lending platform where users can earn interest on their crypto assets.
MakerDAO: A decentralized lending platform that issues the stablecoin DAI, pegged to the US dollar.
Kyber Network: A decentralized exchange that enables the instant exchange and conversion of crypto assets.
It’s important to note that this is not an exhaustive list and new DeFi trading platforms are constantly being developed. However, it’s critical to realize that the DeFi market is still young and rapidly developing, and there is a significant chance of losing money. Research the protocols and projects you are interested in before making an investment, and only invest money you can afford to lose.