The key differences between active addresses and new addresses in crypto.
Fully understanding cryptocurrency addresses and the various states they can be in. In the realm of cryptocurrencies, addresses play a crucial part in facilitating the storage and transfer of digital assets using a distributed ledger called a blockchain. An address is a one-of-a-kind identifier that can be used for a cryptocurrency wallet. This address can be made public so that cryptocurrency transactions can take place.
Understanding the behaviour of a cryptocurrency wallet and its current state can reveal comprehensive insights about the ecosystem, its users, and the long-term viability of the cryptocurrency based on data from the past. The primary function of a cryptocurrency wallet is to send and receive digital currencies.
Crypto addresses play a very important part in ensuring the successful transfer of funds between two parties and giving each user a level of individuality that is not shared with any other user.
The purpose of this piece is to provide an in-depth examination of crypto addresses, including how they function, where they can be located, and, finally, how to determine the significance of the states of wallet addresses.
What is a crypto address? How does a crypto address work?
When a cryptocurrency wallet is created, a one-of-a-kind address is allotted to the wallet for each and every token that the wallet is capable of supporting. This address is essential for ensuring that the sender can successfully deliver cryptocurrency to the recipient that was intended for them.
A common wallet address is denoted by a one-of-a-kind string of alphanumeric characters, which is to say a combination of alphabetic letters and numeric digits. The string (Base58) is derived from the hashed version of the public key of the crypto wallet, along with a checksum that helps prevent typographical errors.
A Bitcoin (BTC) address typically consists of between 26 and 35 characters and can alternatively be represented by a QR code. The length of an address can be found by looking at its hash. The ability to easily copy and paste addresses is one of the many ways that digital wallets and platforms facilitate accuracy.
To send and receive tokens over a public blockchain, one need only use the corresponding address or scan the corresponding QR code on their device.
When a user wants to receive cryptocurrencies on a specific wallet, they must share the address that corresponds to that wallet. When cryptocurrencies are sent to a wallet that does not support receiving them, the user runs the risk of permanently losing the tokens that were sent to them.
How can I find and locate the address of my cryptocurrency wallet?
Finding the address of a cryptocurrency wallet can be accomplished in just two easy steps. When a user successfully creates a cryptocurrency wallet, the wallet provides them with two distinct addresses that can be used for either receiving or sending digital currency. These addresses can be used interchangeably.
Simply navigate to your cryptocurrency wallet and select either the send or receive button to see the address. The user will then be presented with the wallet’s corresponding address in the following step. This address will either be in the form of a QR code, which can be scanned, or a string of numbers and letters, which is also known as the address.
Users of hardware wallets or paper wallets may be able to get a physical printout of the QR code. This printout can be kept in traditional wallets for fiat currency or it can be shared with other people so that they can receive cryptocurrencies.
The various states of a crypto wallet address.
The only thing that can determine the status of a wallet address is the most recent time it was used for successfully sending or receiving cryptocurrency payments (also known as “transactions”). There are three main categories that crypto wallet addresses can be placed into, and these are active, new, and dormant addresses. Each category is named after the state that the address is in currently.
Understanding the current state of crypto addresses is helpful in getting a better grasp on the overall activity of the network. On the other hand, the number of unique users cannot be determined from either an active or a new address because there are no strict limits on the number of cryptocurrency wallets or addresses that an individual can create and operate.
On the other hand, determining the current state of the addresses can provide information about the level of participation in the network as well as support from other cryptocurrency investors. The consistent increase in the number of new and active wallet addresses is a good indication of the system’s overall health. This growth applies to both new and existing wallet addresses.
In the following, we will go into detail regarding the various nuances of active and new addresses:
Active addresses
When an email address is directly involved in a successful transaction, either as the sender or the receiver of the transaction, that address is referred to as active. As a consequence of this, active addresses are an excellent indicator of the number of daily users that any given blockchain has. To put it another way, the total number of active users on the network can be calculated from the active addresses.
For instance, monthly active addresses are a representation of all of the users who either sent or received cryptocurrency during a given month’s time period. On the other hand, a single address is only counted once over the course of any given time period, despite the fact that it may have been an active participant in two or more transactions.
An address must take part in an on-chain transaction in order for it to be considered active. An on-chain transaction is defined as a successful cryptocurrency exchange that is recorded on a blockchain and can be verified using the distributed ledger. On-chain transactions are always recorded on all blockchain networks, which include public blockchains, private blockchains, consortium blockchains, and hybrid blockchains. This is the case regardless of whether the blockchain network is public, private, consortium, or hybrid.
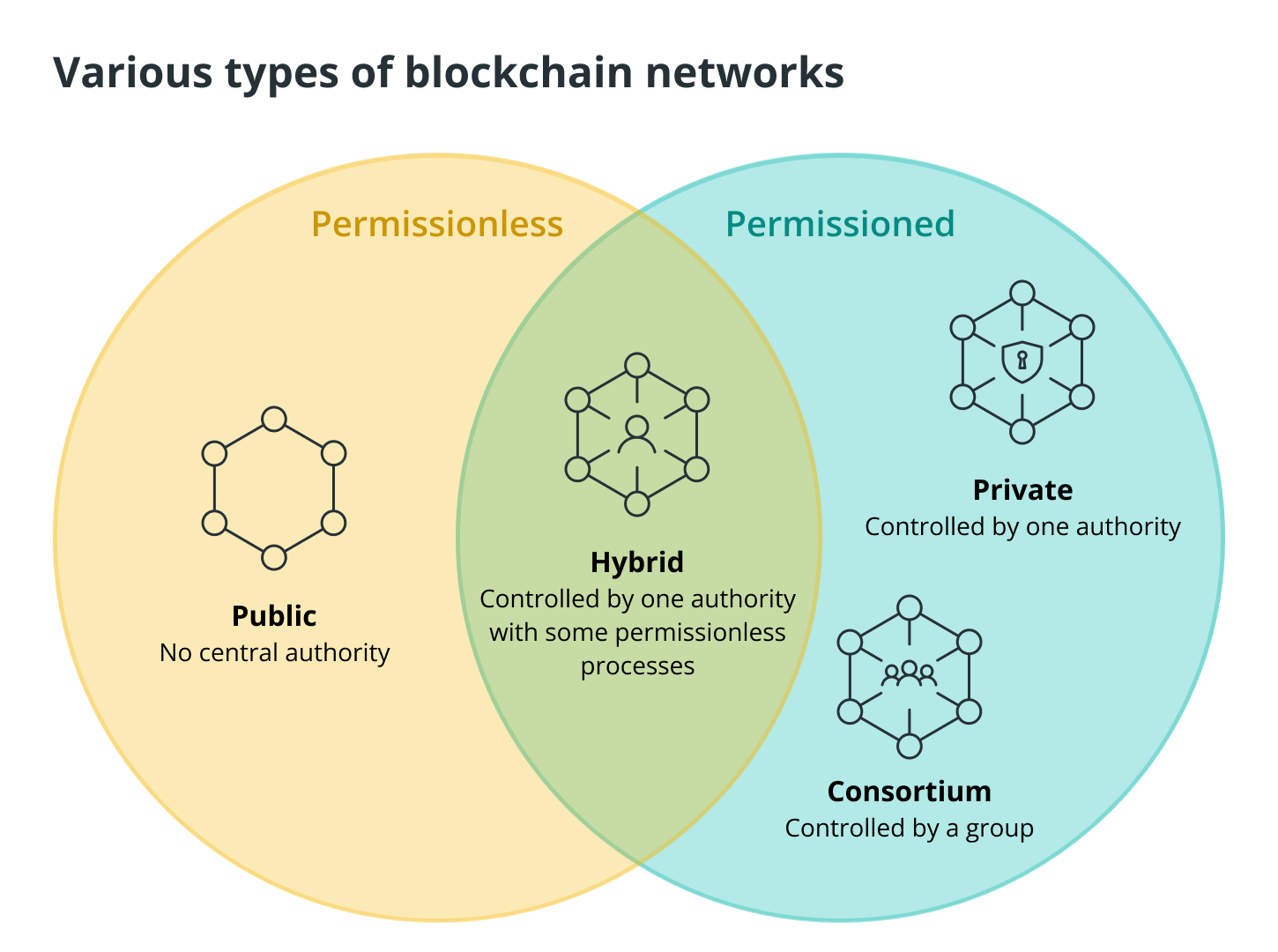
On the other hand, addresses that take part in transactions that are not recorded on the main blockchain are not eligible to be considered active. Because off-chain transactions are not recorded over the blockchains in the same way that on-chain transactions are, this is the result. Instead, they rely on the traditional peer-to-peer (P2P) means of transferring cryptocurrencies, which involve exchanging private keys and linking them to a new wallet.
Does price cash lead to fewer active addresses?
Yes, the precipitous drop in price may be one cause of the dramatic reduction in the number of active addresses. This is due to the fact that the majority of investors try to get out of the market when cryptocurrency prices start to fall.
People who bought cryptocurrencies at a discount, on the other hand, might want to cash out their holdings and convert their holdings into fiat currency before the price drops significantly further. This would mean selling their cryptocurrencies at a profit while the price was still relatively high.
In addition to the aforementioned, some people have a tendency to get out of the market during a market meltdown in order to avoid incurring losses. Some people don’t want to ride the emotional roller coaster that is investing because it can be risky and unpredictable.
People who can’t keep their feelings detached from the game typically find that selling their coins is the most satisfying solution. Because of the wild swings in price, some investors would sell their coins based solely on their feelings, which led to a decrease in the number of addresses that were actively being used.
For example, the number of active addresses on the Bitcoin network dropped from 1.3 million to approximately 500,000 in the month of July 2021, a decrease of nearly 60 percent. The significant decline in network hash rate that occurred during China’s crackdown on local Bitcoin mining companies may be contributing to the dramatic drop in the number of active Bitcoin addresses. This sell-off, which occurred after Bitcoin’s all-time highs in May 2021 and was followed by sideways market action, also may be contributing to the dramatic drop in active Bitcoin addresses.
New addresses
When discussing cryptocurrencies, the term “new address” refers to the process of creating a new wallet address on top of an existing blockchain. A crypto address is secured using a pair of keys, one of which is public and the other is private. Using the blockchain in question, an algorithm links the private key to the wallet that corresponds to the address.
Because of this, an address that is compatible with ERC-20 tokens will be unable to receive TRX-20 tokens, and the person who sent the funds runs the risk of permanently losing them. In the event that you send tokens to an unsupported wallet by accident, it is possible that you will be able to retrieve the assets by adding a supported smart chain network to the wallet in question. However, this only applies in certain circumstances.
A person needs to have an active wallet in order to generate a new crypto address. A wallet can be obtained from wallet service providers such as exchanges, as well as from software wallets and hardware wallets.
A brand-new cryptocurrency wallet address does not have any transactional history associated with it. When a transaction is completed successfully, some cryptocurrency exchanges will automatically generate new addresses for the user. This prevents other users from checking previous transactions or tracking the funds, which keeps the anonymity of the transaction history intact.
A new address does not necessarily represent the actual number of users who have signed up for a new cryptocurrency wallet for the reasons that have been stated above. It is also essential to take into account the fact that a new address can transform from its inactive state into an active address at any time. On the other hand, the opposite cannot happen.
Key differences: New address vs. Active address
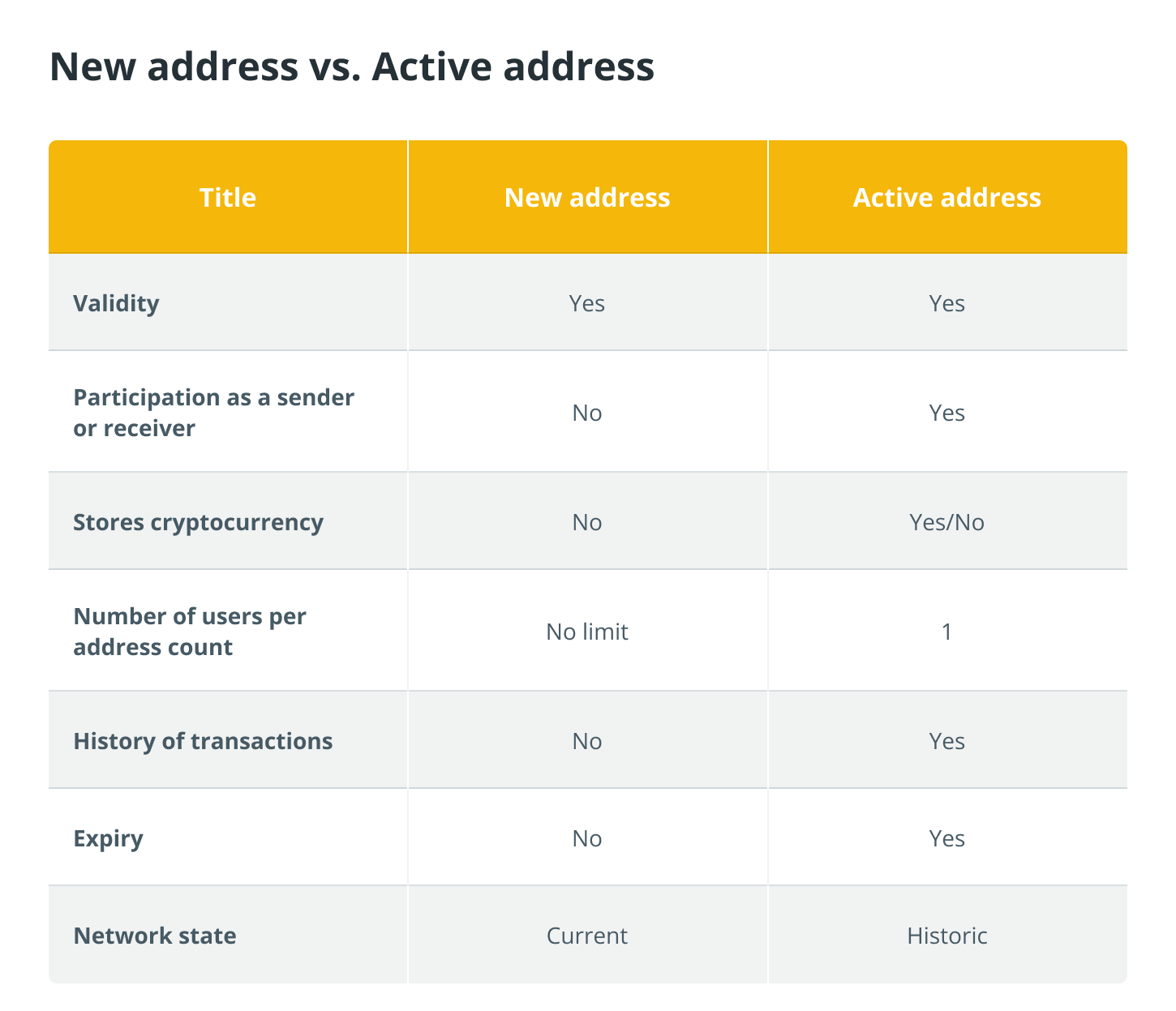
Determining active vs. new crypto addresses
Throughout the course of crypto’s history, addresses have been utilized for the purpose of gaining an accurate understanding of the network as well as gauging the activities of its participants.
When an address is first created, it is not considered new until it is used as an active participant in a successful transaction. During this time, it is considered to be new. When a transaction is completed successfully as either the sender or the receiver, the address will either be in an active state or a state of inactivity, depending on the timeframe that was used.
When it comes to determining which addresses are currently active on a blockchain network, on-chain transactions are the only ones that can be taken into account. Transactions that take place off-chain are ignored because they are not recorded on the blockchain and therefore are not relevant.
Even if an active address is involved in more than one successful transaction during a certain period of time, that address will only be counted as active once during that time period. The total number of users that are part of a blockchain network is not determined by a newly generated address.