Nonfungible tokens, also known as NFTs, represent a new development in the realm of cryptocurrencies as well as a significant advance in the process of reinventing modern finance and other fields.
Because there is no difference between one dollar and another, money can be converted into and used for anything. It’s common practice to trade one type of stock in one company for another, as well as to trade one quality of commodity for another.
NFTs, on the other hand, are nonfungible, which means that they represent unique physical and digital assets such as a piece of artwork, a song, or an in-game collectible that other investments cannot replace.
It is impossible for nonfungible tokens (NFTs) to be traded for or made equivalent to one another because each NFT has its own unique identifier, metadata, and blockchain record, which prevents them from being interchanged.
By enabling digital representations of individual items and combining this capability with the benefits of smart contracts, non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have the potential to eliminate intermediaries and connect content creators with audiences directly, offering certificates of authenticity for digital assets that are generated by the blockchain.
Therefore, the idea of NFTs has the potential to bring about a dramatic shift in both the current crypto landscape and the art world.
So, aside from their limited utility, what else draws collectors and artists to non-transferable tokens? Where can I buy NFTs, and how do I do it? How to sell an NFT, and which method of selling is the most effective to pick out of the available options.
In this article, we will discuss the answers to the questions that were presented earlier.
What exactly are NFTs?
Nonfungible tokens are “one-of-a-kind” cryptographic digital assets that represent real-world objects and digital items such as art, music, virtual land, in-game collectibles, videos, photographs, and other creative products. These tokens can only be used once and cannot be traded or exchanged for other tokens.
They are able to be bought and sold like any other piece of property in the digital world, despite the fact that they do not have a physical form of their own.
NFTs are one of a kind, produced in low quantities, and command a high price due to their rarity. They are impossible to replicate, and it is not difficult to verify their authenticity.
It is possible to regard non-fungible tokens (NFTs) as proof of authenticity and ownership certification for virtual or physical assets that are recorded on a blockchain.
The potential applications of NFTs include a variety of different use cases, some of which are more prominent than others. These use cases include digital art, collectibles within gaming, music, fashion, sports, and academia; tokenization of real-world objects; ownership of domain names; licenses and certifications; patents; documentation; and other use cases.
Additionally, NFTs have the potential to be utilized in the tracking of metadata, the improvement of event ticketing, and even the transformation of real estate.
Even though non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have been around since the early 2010s (the first prototypes of NFTs were experimental assets created on the Bitcoin network in 2012 and were given the name coloured coins), the popularity of NFTs has only recently been on the rise in the cryptocurrency community.
As a result, using NFTs as a means to buy and sell digital items is becoming an increasingly convenient option. NFTs provide artists and other content creators with the opportunity to monetize their work and sell it directly to the audience in the form of NFTs, with absolute independence on the creative industries’ middlemen embodied in galleries, auction houses, and major record labels. NFTs also provide artists and other content creators with the ability to sell their work in the form of NFTs.
How to buy NFTs?
It’s possible that some people will consider it irrational to spend thousands or millions of dollars to purchase portable network graphics (PNG) or graphics interchange format (GIF) files.
Despite this, consumers are still willing to shell out large sums of money for content that they could simply view, screenshot, and download from the internet at no cost to themselves. Why?
NFTs establish a direct connection between social capital and financial capital through the cultivation of a network of interpersonal connections between people and the demonstration of membership in a community.
The information that is recorded permanently on the blockchain comes with its own authentication already built in.
In essence, it grants content creators the ability to digitally “autograph” their NFTs and grants audience members the chance to connect with artists, own works of art that they admire, and become a part of a specific community.
Buying NFTs, which are known as “Investment-as-a-Status,” is considered to be one of the most effective ways to maximize social capital by forming more links and bonds in the cryptocurrency space. This is because NFTs are referred to as “Investment-as-a-Status.”
Even if an image or piece of music has been shared online hundreds of times, collectors who buy an NFT are purchasing something one-of-a-kind and scarce, which is the ultimate criterion for any true collector.
It is important to keep in mind that collectors are not purchasing the original content itself, as it is highly unlikely that they will have ownership of the copyright to it.
As a result of the technology, the content creator is able to keep ownership of the copyright, and the vast majority of NFT platforms give them the opportunity to pursue royalties in the event that the object is resold at some point in the future.
Instead, collectors buy tokens connecting their name with the content creator’s art on the blockchain when they purchase NFTs. This is the most valuable thing that can be purchased with NFTs.
Therefore, purchasing NFTs grants collectors the ability to possess original items, which are then recorded on the blockchain, which serves as proof of ownership. The following sections provide detailed instructions on purchasing NFTs in sequential order.
Choosing a crypto wallet and cryptocurrency to fund a wallet
In order for collectors to purchase NFTs after selecting a desirable collection and an NFT marketplace, they will first need to register for an account with the marketplace.
However, before they can do that, they will be required to link their cryptocurrency wallet to the NFT platform of their choice. If they don’t do this, they won’t be able to buy or sell anything until they’ve done so.
In order to store one’s digital assets in a safe and secure manner, a cryptocurrency wallet is an essential component of any blockchain-based system.
Members of the cryptocurrency community require wallets in order to use blockchain services, access a variety of platforms, sign transactions, and manage their balances in accordance with the fundamentals of blockchain.
Because there is no longer a need to store user account data, all cryptocurrency platforms, particularly NFT marketplaces, are able to conduct their business in a manner that is both more precise and secure.
Before a buyer sets up a wallet, they must make certain that the cryptocurrency supported by the wallet is compatible with the platform they plan to use. This is an essential step. Ether, the native cryptocurrency of Ethereum (ETH), is recognized as a valid form of payment by the majority of the NFT services because Ethereum is the platform on which they are based.
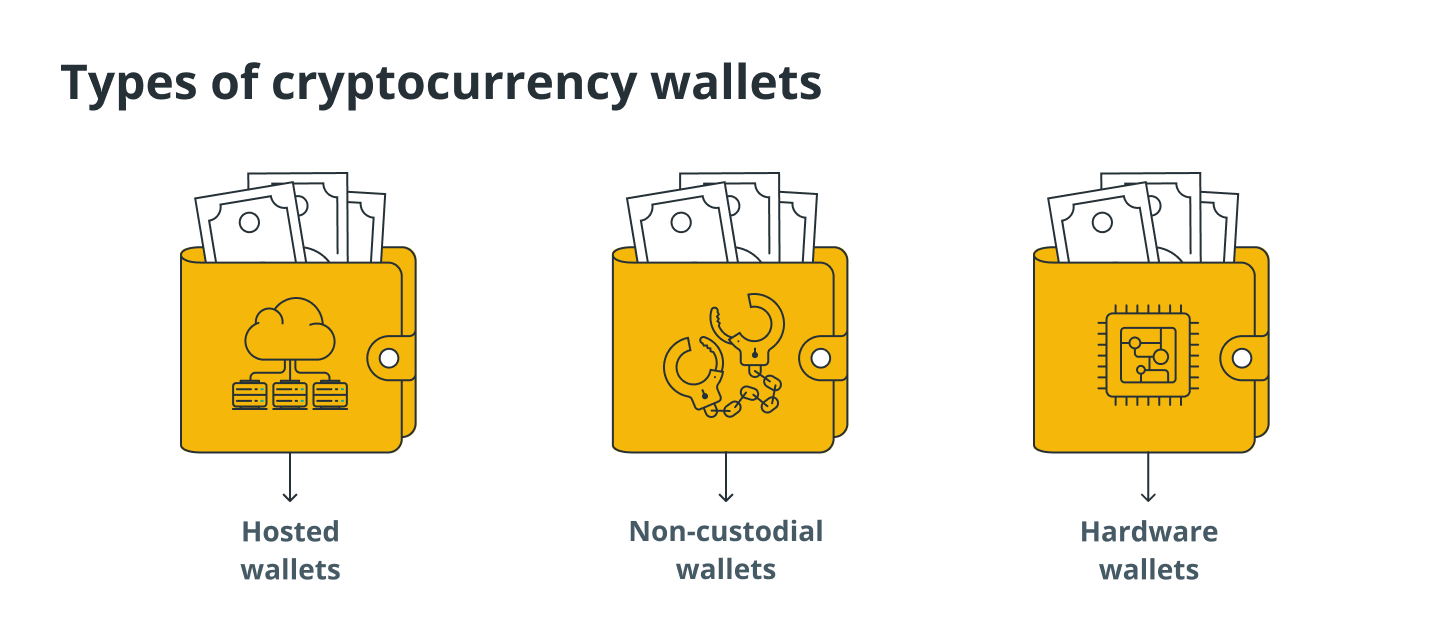
It is generally agreed that setting up a hosted wallet, which is also known as a custodial wallet, is the least complicated and most user-friendly option.
The cryptocurrency belonging to users is automatically kept in it by a third party, just like banks do with the money in checking and savings accounts. This is why it is referred to as being “hosted.”
Because third parties are responsible for the security of users’ cryptocurrency, users of this type of wallet have nothing to worry about because they will never lose their cryptocurrency even if they forget their password or private key. This is because third parties are responsible for the security of users’ cryptocurrency.
The most significant drawback of using a custodial wallet is a lack of autonomy and a loss of anonymity. This is due to the fact that this type of wallet frequently advises users to complete Know Your Customer (KYC) verification, which refers to the verification of an individual’s identification.
In addition to this, users are responsible for ensuring that the hosting company is reliable and knowledgeable in its field.
A non-custodial wallet is one that does not rely on the security of the user’s cryptocurrency being handled by a third party. On the contrary, it grants them unrestricted authority over the safety of their cryptocurrency funds.
Users are not required to submit a request each time they want to send cryptocurrency because they have the freedom to choose the type of transaction fee, which can either be the standard fee or a higher fee, depending on how quickly they want a transaction to be processed. Users are not required to submit a request because they have the freedom to choose the type of transaction fee.
Although these wallets provide the necessary software to store cryptocurrency, it is the sole responsibility of the user to both remember and safeguard their passwords. Users will be unable to access their wallets if they misplace or forget their passphrases, which are also referred to as mnemonic phrases and seed phrases, respectively.
The term “seed phrase” refers to a list of 12 to 24 words generated randomly (arranged in a specific order).
Users can regain access and control of their cryptocurrency funds on-chain by using it, which is generated by the cryptocurrency wallet software and used by users. It is recommended that an offline copy of the seed phrase be kept in order to ensure its safety.
Take this information, for instance, and jot it down before putting it away in a safe place. The method of storing the seed phrase on a device that is connected to the internet or leaving it in any digital format, such as a print file or a photograph, is not the one that is recommended.
If a malicious user obtains the user’s seed phrase, they will have complete access to the user’s cryptocurrency assets stored in the wallet.
Users have access to more advanced cryptocurrency operations such as staking, lending, borrowing, and more when they use wallets that do not perform custodial functions.
A hardware wallet is a physical device that is about the size of a USB flash drive. It is also sometimes referred to as a cold wallet. The operation of this type of wallet is fairly complicated, and it is fairly expensive.
The apparent advantage of using a hardware wallet is that it provides users with a secure location to store their private keys, eliminating the security risks associated with using online wallets.
Even if the user’s computer is compromised, a hardware wallet can store the user’s cryptocurrency offline and protect it from theft.
The collector’s preferences are a significant factor, and so is their level of comfort with various levels of protection when it comes to selecting the ideal wallet.
Collectors have the option of using a hosted wallet to simplify the purchasing process, a non-custodial wallet to maintain full control over their cryptocurrency holdings, or a hardware wallet to take additional precautions against the loss of their cryptocurrency holdings.
In conclusion, once collectors have set up their wallets and obtained sufficient crypto funds, they are free to proceed with connecting their wallets to an appropriate NFT marketplace, establishing an account, and beginning the process of purchasing NFTs.
Options for buying NFTs
When it comes to purchasing nonfungible tokens, there are a few different options available, the majority of which are similar to an eBay scheme. Therefore, it is not too difficult for a casual collector to understand how the process of purchasing NFTs works.
An auction is a choice that is used most frequently. The majority of NFT marketplaces operate in a manner similar to auction houses. In most cases, they will host two distinct kinds of auctions.
The first one is a traditional English auction, in which the person who places the highest bid at the end of the auction is the winner.
A timed auction is a type of English auction in which buyers have the opportunity to place bids on individual lots over the course of a predetermined amount of time. At the conclusion of the allotted time, the buyer who placed the highest bid is the winner and receives the NFT.
There is also something known as a Dutch auction, which is an auction with progressively lower prices. The price of an NFT begins at a predetermined level, known as the ceiling price, and then gradually falls by an amount that is predetermined (e.g., 0.1 BTC every 10 minutes). The NFT Dutch auction comes to a close when a user places a bid equal to the current price.
There is an additional method for acquiring nonfungible tokens known as NFT drops. In this scenario, collectors are required to sit tight until one of the drops is announced, at which point they can try their luck at purchasing rare NFTs before they are completely purchased up.
These sorts of drops can be sold within a matter of seconds, and collectors must sign up for the specific NFT platform in question and load their crypto wallets in advance. This is done to ensure that buyers do not miss out on the opportunity to purchase NFTs when they are dropped.
In addition, certain NFT platforms offer a “fixed price” or “buy now” option for their users. A sale at a predetermined price that NFT creators set at which they want to sell their nonfungible tokens immediately is what this term refers to. NFT creators set the price at which they want to sell their tokens.
A solution that does not require collectors to participate in auctions or to watch the clock in anticipation of a predetermined price drop could be considered the most convenient option for collectors.
Even so, collectors need to pay attention to the currency of the price as well as its format, as the prices are frequently listed in decimals of a cryptocurrency (such as ETH), and the value of the item in terms of fiat currency (such as USD) may or may not be included.
The volatility of the cryptocurrency market at any given time is something buyers must always keep in mind. This dollar value is subject to consistent change as a result of this volatility.
In addition to this, the amount of cryptocurrency that is held in the wallet must be greater than the cost of the NFT that the collector wishes to acquire. This is because it is highly likely that the collector will be required to pay a transaction fee, also known as a gas fee when making a purchase.
Transactions on the blockchain can only be processed and validated successfully if gas fees are paid. Gas fees are payments that are required to be made. Users require that they make up for the amount of computing energy that it requires.
Where can one buy NFTs?
It is possible to buy and sell nonfungible tokens on a variety of different online marketplaces, and the cryptocurrency industry has a plethora of these markets to choose from. Not all of them function in the same manner, offer the same kinds of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and provide the same functionality.
On the other hand, Ethereum’s blockchain serves as the foundation for the vast majority of platforms. Other non-Ethereum non-fungible token services are part of blockchains such as Cosmos, Polkadot, or Binance Smart Chain, to name a few examples.
Other aspects that differentiate NFT marketplaces include a variety of factors, such as whether or not they support required NFT standards and file formats, the accessibility of NFT platforms, a price to create (or mint) an NFT, and other particulars that may be of greater significance to content creators than to purchasers.
Even though each NFT marketplace operates in its own unique way, the majority of them offer customers a diverse selection of NFTs for purchase. At the same time, experienced buyers select a marketplace depending on the type of nonfungible token they wish to acquire.

How to sell an NFT?
How to sell the NFTs you minted
There are primarily two ways to sell NFTs: the first is to sell a freshly minted NFT, which is the path for those who create content; the second is to sell an NFT that a collector has already purchased but is now willing to trade.
The first path is most likely going to be where the process of creating non-fungible tokens, also known as minting, concludes.
The term “minting” refers to the simple process that occurs after innovative products, such as works of art, collectibles, songs, memes, etc., are represented. Following this procedure, the content transforms into an NFT and is “tokenized.”
These digital items can now be bought, sold, and traded as NFTs, and they can also be digitally tracked when they are resold from that point forward.
Content creators only need a Mac or a PC, a cryptocurrency wallet that supports NFTs with some amount of cryptocurrency already in it, and an account on a blockchain-focused NFT marketplace in order to begin minting.
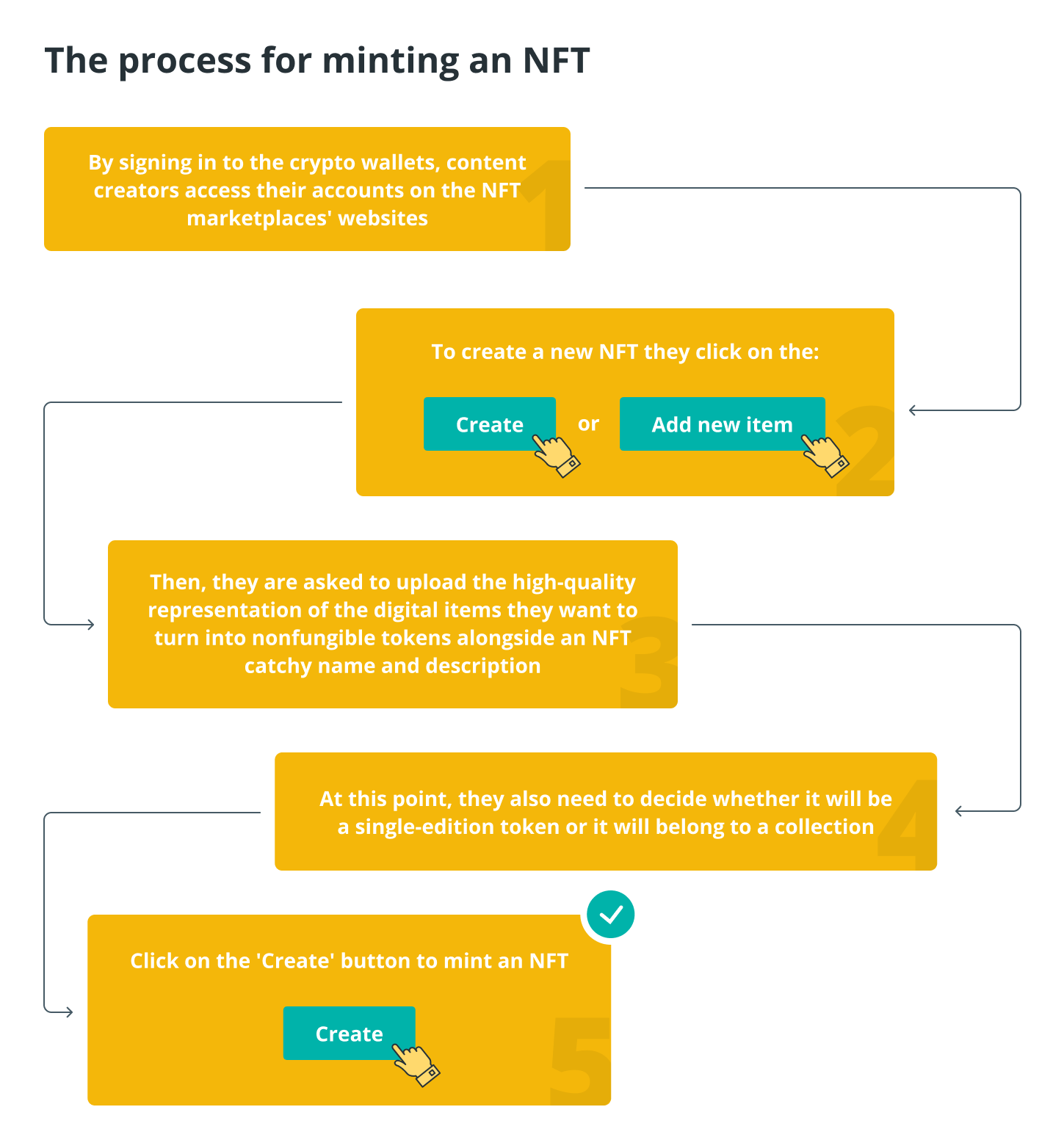
It is recommended that one perform one last check prior to clicking the “Create” button because mistakes can be costly. When the creators have paid their gas fees and signed their NFTs, the minting process will be finished.
After that, the transaction is regarded as having been successfully validated, and content creators are able to view their freshly minted NFT within their profiles on the NFT platform that was selected.
In addition, some NFT marketplaces may require content creators to specify a royalty percentage prior to the sale of NFTs. With the help of royalties, they are able to bring in a predetermined commission each time a new collector purchases an NFT.
Because of the fundamentals of the technology underlying nonfungible tokens, royalties have the potential to automatically establish passive income streams for content creators that could last their entire working lives.
While minting a token, the vast majority of NFT marketplaces also provide users with the opportunity to select a method for selling NFTs as well as a price for the tokens themselves. As a consequence of this, newly issued NFTs are frequently thought of as being put up for sale immediately after their creation.
In some circumstances, in order to sell NFTs, content creators are required to log into their accounts on the respective NFT marketplaces and locate the digital items that are part of their NFT collections. After they have located the necessary NFT items, they will be required to click on those items.
A button labelled “sell” or “list for sale” will become visible once you perform this action. When the creators have access to this option, they can select it to set the selling method, which can either be an auction or a “buy it now” price at a predetermined amount.
If they are fortunate enough, with the assistance of the representatives of the NFT platform, they will possibly be able to have the opportunity to create a drop for their nonfungible tokens. This will likely add a certain level of awareness and will likely assist them in successfully selling their creations.
How to sell NFTs you bought
It is not any more difficult to sell collected nonfungible tokens than it is to sell NFTs that have just been created; the two processes are virtually identical.
On the secondary market, collectors are able to easily resell their NFTs whenever they feel the slightest desire to do so. The term “secondary market” refers to any and all subsequent resales of the work, whereas the term “primary market” describes the initial transaction involving an NFT.
Collectors of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) need a few things that they probably already have in order to sell their NFTs. These things include an account on the collector’s preferred NFT marketplace, a crypto wallet that is connected to that marketplace, and some of the cryptocurrency that is used on that marketplace.
The most significant difference here is that collectors will not be eligible to receive royalties from the sale of NFTs that were part of their temporary collection. Royalties, expressed as a percentage of all future sales, will be paid out straight to the wallets or the original developers of the NFTs.
Collectors only receive nonfungible tokens in their collections on a temporary basis. In contrast, content creators are regarded as having an eternal association with copyright on their creative products in the form of NFTs.
Collectors of nonfungible tokens, similar to collectors in other traditional markets, have only the most fundamental ownership rights, such as the right to possession, the right to sell or gift the items they have purchased, and these rights are terminated upon the sale of the particular nonfungible token.
Collectors of NFTs need to navigate to their profiles on the respective NFT platforms in order to sell their NFTs. Once there, they must select the NFTs that they wish to sell. Once they have clicked on the saleable NFT, they need to look for a button that says “sell” or “list for sale.”
They will be able to choose the terms of the purchase after clicking on this button, which will take them to a page with pricing information. When that time comes, they will have the option of either establishing a price for the NFTs or beginning an auction.
In the event that collectors are interested in beginning an auction, they are required to investigate which kinds of auctions can be held on the NFT platform that has been chosen. It is possible that it is a Dutch auction, an English auction, or a timed auction most of the time.
Despite the high level of uncertainty regarding nonfungible token valuations and the volatile and underdeveloped nature of the cryptocurrency market as a whole, the renaissance of NFTs continues to spread.
Even though there is a possibility that content creators and collectors will not make a profit from the sale of nonfungible tokens (NFTs), the purchase of NFTs is still regarded as an excellent way to support artists, musicians, designers, and any other creative people collectors who are interested in such digital assets.
Summary
Nonfungible tokens, also known as NFTs, represent a new development in the realm of cryptocurrencies as well as a significant advance in the process of reinventing modern finance and other fields.
It is possible to regard non-fungible tokens (NFTs) as proof of authenticity and ownership certification for virtual or physical assets that are recorded on a blockchain.
Collectors buy tokens connecting their name with the content creator’s art on the blockchain when they purchase NFTs.
However, before they can do that, they will be required to link their cryptocurrency wallet to the NFT platform of their choice.
A non-custodial wallet is one that does not rely on the security of the user’s cryptocurrency being handled by a third party.









