Cross-chain crypto project Chainlink
If blockchains are going to make the Internet of Money possible, they will have to work together. But the types of data shared by blockchains, their network topologies, consensus mechanisms, and a lot of other things vary a lot depending on what they are used for.
For example, if a logistics company uses a blockchain to track its shipments but can’t talk to the one it uses to pay its bills, it could cause a lot of trouble.
The problem is that each chain of blocks is its own universe. The need to trust a source outside of the blockchain has always been a weakness when it comes to getting and sending information to and from the outside world. So, what’s the answer?
Chainlink is the answer. It is a decentralized blockchain oracle network that lets smart contracts securely talk to data and services in the real world that are not part of blockchain networks. But what’s so important about Chainlink?
Chainlink is important because it makes smart contracts much more useful by allowing access to data outside of the blockchain and off-chain computing, while still keeping the security and reliability guarantees of blockchain technology.
It works like a blockchain in that it uses oracles, which are a decentralized network of independent entities, to get information from different places. Chainlink also collects the data and sends a single, validated data point to the smart contract to start its execution. This reduces the risk of a single point of failure.
Among the many ways Chainlink can be used, decentralized finance (DeFi) applications can access interest rates and price assets to automate the settlement of contracts. Also, insurance companies can use Chainlink to settle crop contracts based on things like the amount of temperature and rainfall. Please read here about how oracles can be used in other ways.
In this article, we’ll talk about how Chainlink works, how to buy and store Chainlink crypto, and if Chainlink has a future.
LINK Token
The LINK Ethereum token is what makes the Chainlink (LINK) DON work. This network makes it possible for Ethereum smart contracts to securely connect to other data sources, payment systems, and the user interfaces of applications.
LINK tokens are also used to pay node operators for getting (honest) data for smart contracts and deposits that contract creators ask for. The LINK token is an ERC677 token that lets data payloads be sent along with token transfers. It is based on the ERC20 token standard, which is issued on the Ethereum network.
Holders of LINK tokens must stake them in a smart contract in order to become a node and send data to Chainlink oracles. This makes people less likely to act badly or send fake data to the network. In later sections, we will talk more about how to stake Chainlink crypto.
How does Chainlink work?
One part of the Chainlink network is the people who buy and sell data. In addition, five types of Chainlink contracts are part of the process.
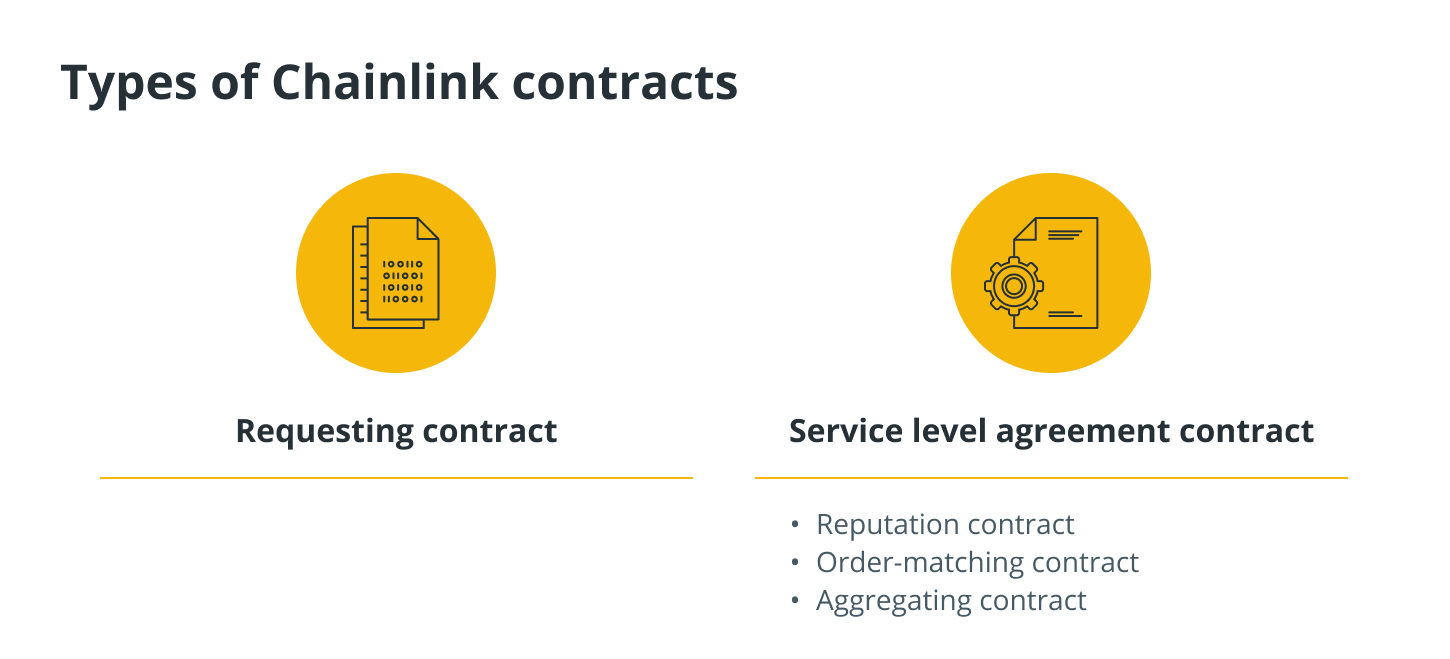 1. Requesting contract: When a smart contract needs information, the process starts on a blockchain, and the smart contract sends out a request for information. This is called a “requesting contract.”
1. Requesting contract: When a smart contract needs information, the process starts on a blockchain, and the smart contract sends out a request for information. This is called a “requesting contract.”
2. Service level agreement contract: To get the off-chain data, the Chainlink protocol logs this request as a “event” and makes a matching smart contract on the blockchain. This contract is called a Service Level Agreement (SLA) contract.
The SLA contract creates three subcontracts: a Reputation contract, an Order-Matching contract, and an Aggregating contract.
The SLA contract creates three subcontracts: a Reputation contract, an Order-Matching contract, and an Aggregating contract.
1. Reputation contract: The Chainlink Reputation Contract checks an oracle provider’s legitimacy and performance history before evaluating and getting rid of unreliable nodes.
2. Order-Matching contract: The Chainlink Order-Matching contract asks for Chainlink nodes, collects their bids, and then chooses the right number and type of nodes to meet the request.
3. Aggregating contract: The Chainlink Aggregating contract checks all of the data from the chosen oracles to get and confirm the results.
To meet each other’s needs, the above parties need to take the following steps:
Making a SLA contract for Oracle selection
A Chainlink user makes a SLA contract that says what data needs to be met. The Chainlink software then uses this SLA contract to match the user with the best oracles that can give the data. Buyers decide what kind of data they want, and sellers compete to give it to them.
In an Order-Matching contract, when a provider makes a bid, they must put up a stake of LINK tokens, which can be taken away if they act badly. Once the providers are chosen, it is up to them to make sure that the right answers are added to the chain.
Data collection and processing
In this step, the oracles talk to outside data sources to get the real-world data called for in the Chainlink SLA. After that, the oracles process the information and send it back to the buyers through the Chainlink service.
Aggregation and verification of results
The last step is to add up all the information collected by the oracles and send it back to an Aggregation contract. The Aggregation contract adds up all the data points, checks to see how accurate they are, and gives the customer a weighted score based on the total of all the data.
Chainlink uses an oracle reputation system, which can figure out how reliable the data sources are, to collect and weigh the data that is given. Data providers get paid for their honest work if everything goes as planned.
What role does LINK play in all of the above stages? Smart contracts that ask for data pay the people who run nodes in LINK for the services they provide. The price paid to the node operators is based on how much data people want and how the market is doing.
How do you buy Chainlink?
Here are the steps you need to take to buy Chainlink on your favorite cryptocurrency exchange:
 How do I buy Chainlink on Binance?
How do I buy Chainlink on Binance?
In contrast to the general steps listed above, if you want to buy Chainlink coin from Binance, you can do so in one of the following ways:
- Bank transfer: You can buy Binance-listed stablecoins with a bank transfer. Then, on Binance, you can buy Chainlink with these stablecoins.
- Trade Chainlink: Binance accepts more than 300 cryptocurrencies as deposits, and many of them can be traded for Chainlink at some of the best rates available.
- Credit card: On Binance, you can use a credit card or a debit card to buy LINK right away.
How do I buy Chainlink on Kraken?
Another safe way to buy LINK is through the Kraken exchange. To do the same, follow the steps below:
• If you don’t already have one, make an account on the Kraken exchange.
• Verify your account before you buy LINK with a cryptocurrency like Litecoin (LTC). On the other hand, if you want to use fiat currencies like USD, you will need more documents to prove who you are.
•Pay money into your Kraken account and buy LINK.
How do I buy Chainlink on Coinbase?
Fans of Coinbase who want to buy LINK can follow the steps below:
• If you don’t already have one, make a Coinbase account.
• Before you start trading, add a way to pay, like a credit card or bank transfer.
•After you click “buy,” type “Chainlink” into the search field to find it. Then, tap Chainlink in the search results to go to the page where you can buy it.
• Use the number pad to enter the amount you want to spend in your own currency. This will be turned into a Chainlink amount right away by the app.
•Tap “Preview buy” when you’re ready. After you’ve double-checked all the details, confirm your order. You now have the right amount of LINK.
 How do you store Chainlink?
How do you store Chainlink?
People hold on to Chainlink and other cryptocurrencies in the hopes that their prices will go up. You can store your Chainlink safely in your Binance wallet or in the TrustWallet app that Binance makes.
Also, you can keep your Chainlink funds safe if you use the most trusted hardware wallet. The funds can be kept in encrypted cold storage wallets that keep the user’s Chainlink assets offline. This gives the user an extra layer of protection against the risks that come with being online, which are always changing. You can protect your Chainlink assets with the Ledger Nano S (an independently certified Chainlink wallet) and the Ledger Nano X.
You can also use Coinbase Wallet to send crypto payments and Google Drive to store your keys, or you can use the MetaMask Wallet, which has both a mobile wallet and a desktop wallet and lets you store your LINK assets in a flexible way.
What is “staking” in Chainlink, and how do you stake Chainlink cryptocurrency?
In Chainlink, validators act as blockchain oracles. In exchange for LINK tokens, they offer a wider range of services. Still, if the node doesn’t meet any of the smart contract conditions or isn’t doing anything, it can mess up the way the decentralized application works (DApps). If that happens, the deposit will be lost as a penalty for not following the rules (slashing).
Staking in Chainlink, on the other hand, is different from staking on blockchains that work on their own. The point of staking in blockchains is to stop attacks on the network’s consensus. Chainlink’s goal with staking tokens is different: it wants to make sure that the right oracle reports are sent on time. A well-designed staking system for an oracle network should make bribery attacks unprofitable even when the target is a smart contract with a lot of money on it.
But at the moment, only people who run nodes on Chainlink can stake. You will be able to stake your LINK once the new way to do so is available. For now, you can lend out your LINK on other DeFi platforms to make money without doing anything. On the other hand, here are some steps you can take to get ready for Chainlink staking:
 What else does Chainlink offer in terms of oracle services?
What else does Chainlink offer in terms of oracle services?
Chainlink has a random function that can be checked and is a fair and safe way to generate random numbers for smart contracts that use nonfungible tokens. The protocol also has the Chainlink Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP), which lets users move tokens and send messages across different blockchains. The CCIP is an open-source standard for the ecosystem of many chains.
Chainlink proof-of-reserve also gives smart contracts the information they need to figure out the correct collateralization of any off-chain reserves-backed on-chain asset. This makes sure that the DeFi ecosystem is transparent from beginning to end.
What is off-chain reporting (OCR)?
The OCR protocol lets nodes use a secure peer-to-peer network to combine their observations into a single report that is sent off-chain. Then, one node sends a transaction to the chain with the compiled report. A certain number of nodes must sign the transaction. Most Chainlink Price Feeds already have OCR working on the mainnet.
The FluxAggregator model will be replaced by the OCR protocol. In the FluxAggregator model, each node submits its own price value, and once all responses are received on-chain, the contract adds them all together to confirm the price. The main problem with this model is that each node has to pay gas fees every time it sends a transaction.
So, the OCR protocol is better than the FluxAggregator model in the following ways:
Is it a good idea to buy Chainlink?
Chainlink is in a stable position because its services are becoming more popular and reliable, and it has a big lead over its competitors. Now, if you want to know if Chainlink is a good investment, the clear answer is that whether or not an investment is profitable depends on your investment goals and how much risk you are willing to take.
Also, practice makes perfect, and making mistakes is part of being human. This means that if you are a regular investor, you are likely to make money from crypto investments. But if the market goes against what you want, you could lose your money (which is a possible outcome of your actions). So, before you put your hard-earned money into any of the investments, make sure you know what the project is about, its goals, and its chances.
What’s next for Chainlink?
One of the most advanced parts of Chainlink’s upcoming updates will be off-chain networks that are built on top of the oracles. Off-chain networks are meant to move most of the complicated computing tasks away from the smart contract platform’s main layer.
For example, as the need for computing power has grown, Ethereum’s gas prices have been going up, which could make the network unusable for smaller transactions. Chainlink 2.0 aims to help users solve this problem by making it easier and cheaper to run DApps on computers.









