The Ethereum blockchain is regarded as the ruler when it comes to NFTs, it is considered by many to be the one-step platform for NFTs as its influence blooms over the NFT ecosystem.
However, a lot of other blockchains have emerged in the NFT space becoming popular and competing with the Ethereum blockchain considering the high transaction cost associated with it. A lot of users have continued to seek new places to mint and trade their NFTs.
The blockchain that supports NFTs includes; Ethereum, Solana, Tezos, Polygon etc. With the great potential polygon presents, a lot of users are migrating as it offers low fees and fast transactions.
It is sweeping across the NFT space as the primary blockchain platform. NFTs as an alternative asset class within the crypto world have set a revolutionizing pace in the world of gaming, art and various other industries. But first, we need to know what NFT is.
What are Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)?
In 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto invented Bitcoin which runs on a blockchain which is basically a public ledger. In 2015, Vitalik Buterin created Ethereum which is considered by many as a programmable Bitcoin. He introduced the idea of smart contracts wherein each access to the ledger we can put a program instead.
There are different types of programs in Ethereum and one of them is ERC721 which is what developers used in creating non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
This means that each item is peculiar and not inter-changeable. The ERC721 standard states that each token is matched to an owner. Think of it as a receipt that proves ownership of a digital or physical asset.
They are blockchain-based tokens with unique attributes attached to it that represents a peculiar asset like a piece of art, digital content or media. NFTs are structured to be cryptographically confirmable, unique and easily transferable.
It is regarded as non-fungible because there is only one of it in the whole system. NFTs turn your digital assets into one of a kind by creating a unique digital signature that defines the ownership of your assets. They are not interchangeable and each represents unique items that are owned by a particular individual.
NFTs contain distinguishable information about the items like the owner and buyer thereby making them distinct and verifiable. Unlike fungible tokens, they cannot be replicated or divided into several parts. For example, you can divide a hundred-dollar bill and get parts that when put together will still give you the hundred dollars you divided.
Getting the dollar divided doesn’t make it a counterfeit, but in a non-fungible token, you can get only one of them in the entire NFTs space and not pieces, for example, the Monalisa painting. Simply put, NFTs are used in tagging an item or asset in the digital world as your own and it is way more valuable than fungible items as it is considered rare.
Note that: That the NFT asset itself cannot be divided but ownership can be divided
Just like every other cryptocurrency, it is stored in a wallet and also provides proof of ownership for a digital asset.
NFTs Creation
A creator creates a digital good/asset either an image, video, tweet or anything else that lives in the online space (Internet). The creator further creates a token on a blockchain that supports smart contracts e.g. using Ethereum or Solana blockchain. This token holds within it information about the digital goods that are being sold.
This information includes the token name, symbol, unique hash that proves the credibility of the NFTs and a link to the goods sold. It is important to know that digital goods themselves are not stored inside the token, only attributes related to them are stored on them.
Once the token is created, the creator can trade it to anyone and that person automatically becomes the new owner of that digital good.
Note That: The creator and the buyer can also have some form of agreement as to if the new buyer sells the NFT in the future, the original creator can have a share percentage of the new sales. Hence, two or more people can co-own an NFT
In summary, an NFT is a token on a blockchain that acts as a digital certificate of credibility or authenticity. It can be verified immediately and also show the history of its previous owners.
NFTs Characteristics
- They are non-fungible (rare and unique)
- Indivisible
- Can be easily transferred
- Fraud proof and
- Are programmable.
Some examples of popular NFTs example include;
- Crypto Punks (A collection of pixel art images of punks)
- NBA Top Shots (A marketplace where NBA fans can trade NFTs of NBA moments. These moments include video clips packaged as NFTs.
Buying NFTs
Generally, there are two types of NFTs marketplaces; Centralized and Decentralized. The centralized marketplace permits users to sign in and fund their accounts using any form of payment or a credit card.
For example, Nifty Gateway is a centralized form of a marketplace owned by the exchange, Gemini. In a decentralized marketplace, the user would need a wallet that is compatible with the blockchain the NFTs were created on in order to make purchases.
For example, in the case of Ethereum, Metamask is regarded as one of the best options suited for it as a browser extension.
After funding their wallets, the users can ahead to buy or bid on the NFTs marketplace. Keep in mind that NFTs are not always liquid, this means that there is not always a crowd of people lining up to buy them.
It is very hype-driven because there are situations that occur sometimes where a person spends millions to buy an NFT only to discover that no one is willing to buy it from him probably because the interest in that particular item has diminished.
Another scenario is where some users have bought an NFT with the hope that the value will continue to increase but in reality, the value decreases causing the bearer to lose money, in crypto trading terms could mean buying the top and possibly selling the bottom.
Uses of NFTs
One may be wondering what NFTs are really used for. Here are some reasons why people use NFTs and what they use them for.
- Show off: Most users find creative ways to show their NFTs off. For example, some NFTs are displayed digitally across Art galleries. Some also use a digital frame to display the NFT and hang it on the wall of their house. Alternatively, a physical print of the NFT can be used to display ownership of the asset. There are also online galleries inside the virtual space where owners can display their NFTs.
- NFT is also used in tagging an item in the digital world as your property. (kind of proof of ownership) Decentraland (MANA) for example is a sort of digital land that users can buy and is like a space used for advertisement, events and tournaments, etc.
- Online games can also use NFTs to prove ownership of rare digital items that players can trade among themselves.
- Unstoppable domains employ the use of NFT to set up ownership of domain names. NFTs can equally be used as collateral in DeFi instead of cryptocurrencies.
How does it work?
NFTs use the same underlining technology and programming as other cryptocurrencies. It uses a programming language called ‘Ethash’ or ‘Script’. NFT basically creates a blockchain-based certificate for all your digital collectibles (Art, Music, Sports, Games etc.) This certificate gives your collectibles a unique identity. It majorly exists on the Ethereum blockchain (the distributed ledger that records all transactions). It is however different from Bitcoin (BTC) and Ether as these two can be placed as ‘fungible’.

Understanding the Polygon Blockchain
Before the rebranding to polygon, the project was widely known as ‘Matic’ or ‘Matic network’. Three founders who were active participants in the cryptocurrency community in India started Matic in 2017. They decided to come together and tackle Ethereun’s scaling problems, these founders worked on two main solutions; Plasma chains and Layer-2 scaling solutions, based on the Matic implementation of plasma chain and the proof-of-stake chain. The token behind the Matic network, ‘Matic’ was distributed through the Binance Launchpad (initial exchange offering) in April 2019 and the team was able to raise 5.6 million dollars.
In mid-2020, the Matic mainnet went live after a few years of hard work, attracting a lot of attention. This success was extremely fueled by the increasing gas fees on the Ethereum (ETH) network which showed an urgent need of finding robust scaling solutions. At the beginning of 2021, the Matic team decided to expand the scope of their project and rebranded themselves as POLYGON (MATIC).
Polygon aims at establishing a more generalized solution. There are two main ways they came up with, Layer-2 scaling and Sidechains.
Layer-2 scaling relies on the security of the main layer while Sidechains on the other hand rely on their own security models, usually by having a separate consensus mechanism.
Polygon serves as a multi-chain network for Ethereum-compatible blockchains. Instead of providing one or two scaling solutions, polygon created an ecosystem that enables easy connection to multiple different scaling solutions.
From Sidechains with different consensus mechanisms to layer-2 options such as optimistic rollups, and plasma. This also included Proof of Stake (PoS) and Plasma chains as one of the many scaling options available in the whole polygon ecosystem.
Polygon also provides a framework that makes it easy for new projects to build their own highly customizable scaling solutions if they want. Polygon supports two major types of Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks and they are;
- Stand-Alone chain network and
- Secured chain network
Stand-Alone chains rely on their own security. They are fully sovereign which gives them the highest level of independence and flexibility but this makes it more difficult to establish a more reliable security model. Secured chains employ the security service model which can either be directly provided by Ethereum or by a number of professional validators on the polygon ecosystem.
Secured chains offer the highest level of security but lack independence and flexibility. It is usually preferred by start-ups and security-focused projects.
Polygon as a blockchain network provides scalable, secure and instant transactions with Ethereum currencies like ETH, USDC, MATIC, and DAI.
Polygon promotes lesser transaction fees or gas and offers a better option when compared to Ethereum’s flexibility and scalability. It is obviously a great option for the development of decentralized applications, it provides a great tool for developers as it enables not only the creation of cross-platform dApps with its Finity Design system and polygon bridge but can also create a platform where blockchain networks connect with other compatible networks to transfer assets such as ERC-20 tokens and NFTs to the polygon sidechain.
This resulted in it being a more preferred option as developers are inclined to create NFT projects with a high rate of lesser value transactions, using it to set up an NFT marketplace that promotes the listing of NFTs by users for a small fee.
How to create free NFTs on Polygon
Platforms such as OpenSea and Rarible have made it easier for users to create NFTs without paying any fees. This is widely considered as “Lazy-minting” because it lets users create NFTs and put them up for sale without them being written on the blockchain. These platforms made this option available in order to boost the number of artists and content creators that uses NFTs.
They even made it easier for users to be able to mint their NFTs directly from the polygon network. This means that you can have a brand-new NFT without having to go through a secondary market to purchase them.
Minting on polygon promotes a cheaper gas fee and shorter transaction sections. There are steps to follow in order to create NFTs on a Polygon blockchain. We will go further to explain them below:
- The first step is preparing or selecting an item or asset that can be turned into a non-fungible token. This asset could range from Art, Meme, and Video game items. As long as it is in a digital format, it can be turned into an NFT.
- The second step is setting up a crypto wallet with a reasonable amount of funds in it. This is basic and very essential for users, especially those seeking to create an NFT. It will enable the payment of fees attached to selling or putting the NFTs up for sale. It is used to make sales and receive funds when the NFTs have been sold.
- The next step after these two is to decide among the arrays of platforms which is best suited for you to sell your NFTs on after weighing their accessibility and security. These platforms embody different terms, and specializations and charge fees. Also, these platforms offer different blockchains to host the NFTs you have. The users will have to choose from the various NFT marketplaces available on the Polygon. The two biggest NFT platforms are; OpenSea and Rarible.
- After this, the user goes ahead to ‘mint’ their NFTs by transferring them to their wallet which depends on the platform and blockchain they chose. They do this by clicking on the ‘free minting’ option and signing the minting permissions that are required in the marketplace. Upon uploading, the users can add various features to make their NFTs intriguing and attractive.
- The final step is hitting on the ‘sell’ button. The user sells their NFTs on the chosen platform. It can be sold for either a fixed or a scheduled auction (where buyers bid to get the NFT). This final step qualifies it as being available for acquisition.
While all its allied data is being stored on the Interplanetary File System which allows anyone with a computer to store and share files as part of its peer-to-peer network, the NFT still remains listed on the chosen marketplace. The linking of crypto wallets to the marketplace and obtaining minting permission assures NFT creators that their NFTs are mined as soon as funds are deposited by potential buyers and their crypto is distributed without any extra difficulty. The gas fee also applies in case of situations where the creators of the NFT wish to remove the NFTs from the market.
How to purchase NFTs on Polygon
Buying NFTs on Polygon is just the same way it’s been done on the Ethereum mainnet. Just the same way you make a purchase with ETH, to purchase an NFT on Polygon, the buyer would be making use of the polygon-based ETH or MATIC tokens. To start this process, the potential buyer has to look out for NFT marketplaces or aggregators on the blockchain network. polygon NFT marketplaces such as Floor, TixHive, NFTrade, Candyshop, HdoI My Moon, OpenSea and Rarible are options the buyers could choose from. There are different other multichain marketplaces that can be an option in simplifying transactions over blockchain networks such as Ethereum, Solana, and BNB smart chain.
In other to buy NFTs on Polygon, users will be required to attach their polygon NFT wallet to the market of their choice and then browse through the NFT collectibles presented on Polygon.
The process of buying NFTs differs faintly across the platforms depending on its nature of either being at a fixed price or on auction. For the NFTs that have fixed-price sales, the buyers will go ahead to add one or more such NFTs to their cart and pay for them in one acquisition flow.
Once you’ve found the item of your choice, simply click the ‘Add to cart’ option. After browsing through and selecting the items of your choice, the user will need to click on the ‘complete purchase’ option and with this done, he will be directed to the wallet window to process his signature request.
To complete the signature request, the user would be prompted to switch his wallet network to polygon (if the present wallet is not on the Polygon network before shopping for NFT). When these are all carried out successfully, the purchase should be handled speedily.
A user is also required to lock ETH in a wrapped Ether (WETH) smart contract in order to place a bargain or a pre-authorized deal for an NFT without having to get additional contributions from the buyer.
A corresponding quantity of WETH tokens is mined when ETH funds are housed in a WETH smart contract with the WETH tokens displayed in the user’s wallet until it is being used in a bid.
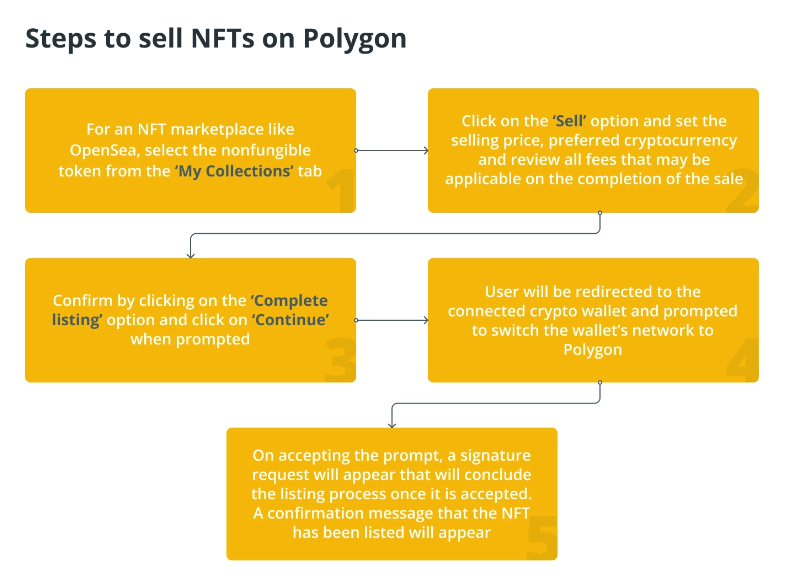
How to sell NFTs on Polygon
First, the user is required to navigate to the item page tagged ‘my collections’ and click on the ‘sell’ option. They will be directed to a new page where they can set their selling price, and currency and also view any potential fees attached to your sale. There is also an option to schedule your sale in advance. Once you’ve established your sale details, click on ‘complete listing’ which will prompt a new window to pop up. When this happens, click on the ‘continue’ option. It is important to remember that your crypto wallet will direct you to sign the transactions, you will also need to switch your crypto wallet network to the Polygon network in order to complete the signature request. Following this, you click on the ‘sign’ option to finish your consent process. Immediately after your NFT listing is established, you will get a confirmation that reads, “Your item has been listed”.
How to find Polygon NFTs on OpenSea
Despite the OpeanSea NFT marketplace running on the Ethereum (ETH) blockchain, it allows users to purchase, sell, or trade NFTs from different other blockchain platforms such as Solana, Klayton and Polygon. On multichain NFT platforms such as the ones mentioned above, the symbol used to represent the item in the Polygon NFT will have a polygon logo.
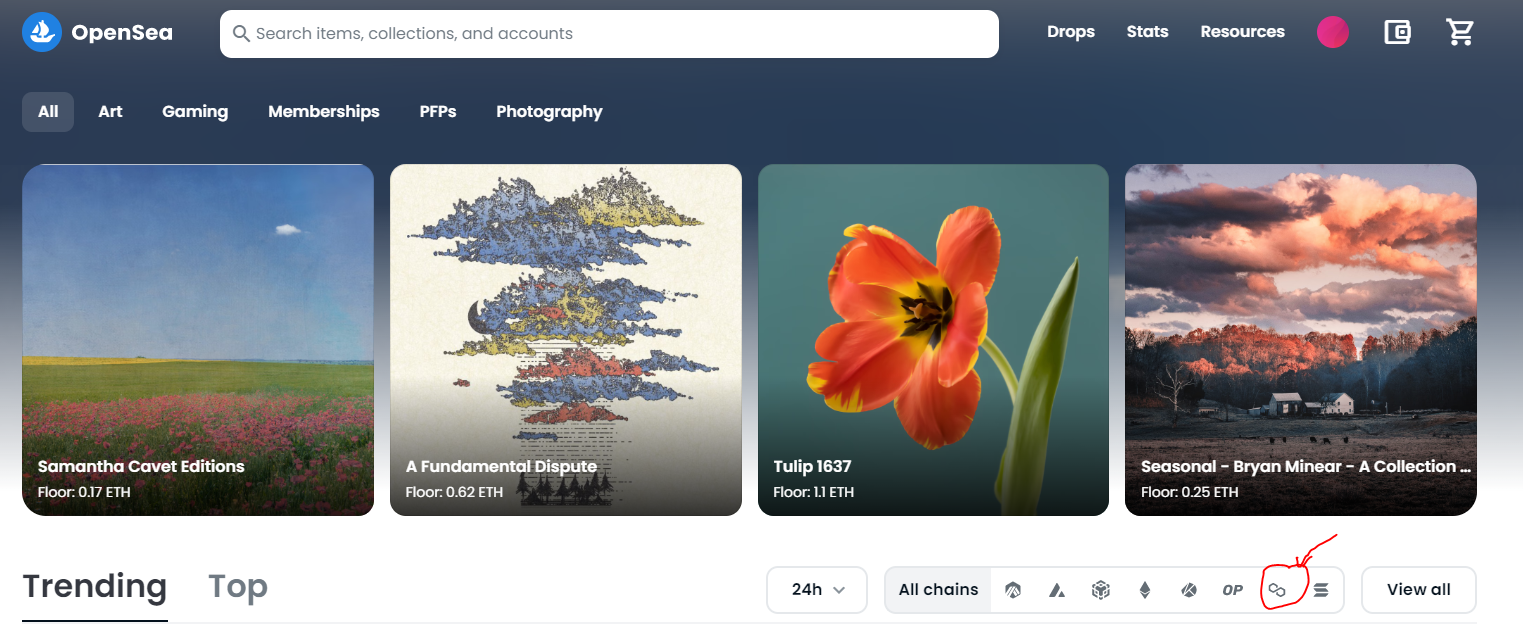
A user can also select Polygon from the list of blockchains that the platform supports to find out the NFTs hosted on the polygon network.
Having over 43 million OpenSea Polygon NFTs already registered through categories such as Art, Philosophy, Sports, Game items collectibles etc. users also have the option of using the range of filters available on the OpenSea platform to narrow down their purchase. The OpenSea marketplace is regarded as the world’s first and largest digital marketplace for NFTs with over 2.4 million active users. It has become a great tool for creating NFTs by providing users with the option to browse popular NFT collections or even selecting NFTs that are placed inside a specific budget variety.
Polygon accommodates pretty much all scaling solutions, because of its versatile nature, it has attracted a lot of attention over time. NFTs have proven to be of great benefit in the lives of many enthusiasts.
Owing to its increasing popularity, it has inspired a lot of artists and enthusiasts by creating opportunities for new Art platforms.
It has aided in motivating artists and promoting the originality of digital assets. It has joined in the events of the internet by becoming the infrastructure of the metaverse.
However, the tricky thing with NFTs is that consumers decide their uniqueness or worth. Their worth is measured or determined by what a buyer is willing to pay and the attention they accumulate is dependent on the hype people back it with, hence the saying that it is ‘hype-driven’. Although a lot of people find it hard to grasp this concept, it is still making waves as one of the forces of the digital world and it has a lot of potential in the years to come.









