Many people are interested in the Ethereum network due to the blockchain, the massive development of decentralized finance (DeFi) smart contracts, and the acceptance of nonfungible tokens (NFTs). Despite the fact that they have a high market value, DeFi and NFT transactions consume a significant amount of energy.
The proof-of-work (PoW) consensus model, which was widely used for a time, is what Ethereum was indeed based on. Nevertheless, the combination of this problem and the high cost of gas has caused it to become Ethereum’s primary concern.
An Ethereum consensus layer was developed as a means of rescuing the situation after it became clear that the blockchain’s low scalability and high transaction fees would need to be addressed. Solutions such as zero-knowledge rollups, zkSync, and optimistic rollups were the primary focus of this work.
ZkSync gives users the ability to leave and rejoin the Ethereum mainnet in a manner that is decentralized, and it does so at transaction fees that are lower than those in the legacy ecosystem. Transmission speed and low gas fees, which had become two sources of frustration for Ethereum users, were two of the benefits that could be gained from using zkProofs.
This guide will explain the zk-Rollup technology, the history of zkSync, the advantages of zkSync’s technology, the zkSync token, decentralized applications (DApps) on zkSync, and the zkSync bridge.
What basically is zkSync?
ZkSync is a mainstream scaling technology that implements innovative solutions to the scaling problems faced by Ethereum. Zk is shorthand for “zero knowledge,” and rollups is an abbreviation for “smart contracts.” The way that smart contracts work is that they take a number of separate transactions that take place off of the main layer and combine them into a single transaction.
Zk-Proofs, also known as zero-knowledge proofs, are active forms of cryptographic security. For example, zk-Rollup solutions can determine the legitimacy of a transaction without divulging the evidence that supports their conclusion. For a better comprehension of the ecosystem, it is necessary to have an understanding of the following aspects:
Comparing other L2 solutions and zkSync
Attempts to scale Ethereum are being made by layer-2 chains such as Polygon, Optimism, Arbitrum, and Immutable X. Each solution provides remedies for scalability, security, throughput, gas fees, and functionality, to name a few of the most important features. Some of these remedies are more comprehensive than others. There is no one single answer that will solve everything. Rollups, on the other hand, are an attempt to improve upon all of these features.
Rollups for Layer 2
As was stated, zk-Rollup is a layer-2 scalability solution that makes it possible for transactions in Ethereum to be validated more quickly at a lower cost. It merely combines a number of layer-2 transactions so that all of them can be carried out off-chain at the same time and then posts the combined results to Ethereum’s blockchain as a single transaction.
Scalability can be improved with optimistic rollups because, by default, they don’t perform any computation. Following a transaction, they simply update the mainnet with the new state information. Optimistic rollups improve the efficiency of transactions by lowering the amount of gas cost and congestion experienced by the base lawyer. These rollups publish very little information about transactions directly on the blockchain, and the rollups themselves consider transactions automatically.
In the same way that Optimistic transactions batch up transactions to be executed off-chain, zk-Rollups do the same thing. Having said that, there is a distinction. Zk-Rollups do not make the standard practice of presuming the validity of transactions until it is demonstrated that this is not the case; rather, they use validity proofs to provide immediate evidence regarding the validity of transactions.
Developing zk-Rollups that are compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a difficult task due to the complexity of the underlying technology as well as EVM’s capacity to run arbitrary code.
Bridges compatible with zkSync
A blockchain bridge is a framework that synchronizes the minting and burning processes of two different blockchains in order to maintain a constant token supply. Bridges are considered to be of great value by developers due to the fact that they allow for more efficient processing. The following are examples of zkSync bridges:
zkSync Portal: On Ethereum, it is a trustless protocol that hooks zero-knowledge proofs to enable the rolling out of scalable low-cost transactions. The system performs computation and stores data off-chain, but it keeps track of all of the assets in a single smart contract that is stored on the mainchain.
ZigZag Bridge: ZigZag is a decentralized exchange that is both simple to use and secure, and it is built on zk-Rollups. There, users can make it easier to transfer funds from one network to another by using an interface called ZigZag Bridge. You also have the ability to view the history of transfers on the bridge.
Who is the mastermind behind zkSync?
Zero-knowledge In the year 2020, Matter Labs, based in Germany, developed rollups to make Ethereum scaling better. In 2019, Matter Labs started working on the project, and in 2020, they finally released the first version of zkSync, which they referred to as zkSync 1.0, as will be explained in more detail below.
The first version of zkSync was released in the year 2020, and it was called zkSync 1.0. This scaling technology for Ethereum can process up to 3000 transactions every second (TPS). However, as the network expanded, there was a requirement for a greater throughput, which resulted in the development of a new version called zkSync 2.0.
Recently, Matter Labs launched a zkEVM testnet, which means that zkSync is the first zk-Rollup to perform Ethereum native smart contracts. zkSync 2.0 was introduced in conjunction with this launch. In comparison to its earlier iteration, zkSync version 1.0, the newly released zkSync version 2.0, along with its accompanying zkEVM infrastructure alpha version, represents a significant step forward.
They developed zk-Porter to reduce the amount of time spent on Ethereum transactions while maintaining the same efficiency level. Through the use of a sharding solution known as zk-Porter, zkSync hopes to achieve higher levels of throughput. When zkPorter is implemented, Ethereum’s scaling could increase from 3,000 TPS to 20,000 TPS, which is a significant increase.
zkSync token
ZkSync does not yet have a native token associated with its name; however, investors should expect something from the zero-knowledge proof systems in the near future. One can see, for instance, from their official page that zkSync will generate tokens for investors to stake with and become validators on the zkSync network.
Additionally, the company gave the impression that a zkSync airdrop would be made available to be claimed by users and supporters who had shown their loyalty. There is a possibility that this airdrop will be comparable to the optimism airdrop. Since the announcement was posted on the official tokenomics page of the company, users of the zkSync network are feeling optimistic.
How does the ecosystem of zkSync work?
Zk-Rollups are used to scale Ethereum by rolling up transactions that take place off the Ethereum mainnet (layer 1) while still submitting transaction data on layer 1. Comparatively speaking to layer 1, it offers superior throughput, security, and scalability, and its fees are significantly lower. However, due to the fact that the data is stored on layer 1, the fundamental framework of the primary Ethereum chain has been preserved.
To make use of zkSync, you will need to carry out the following steps:
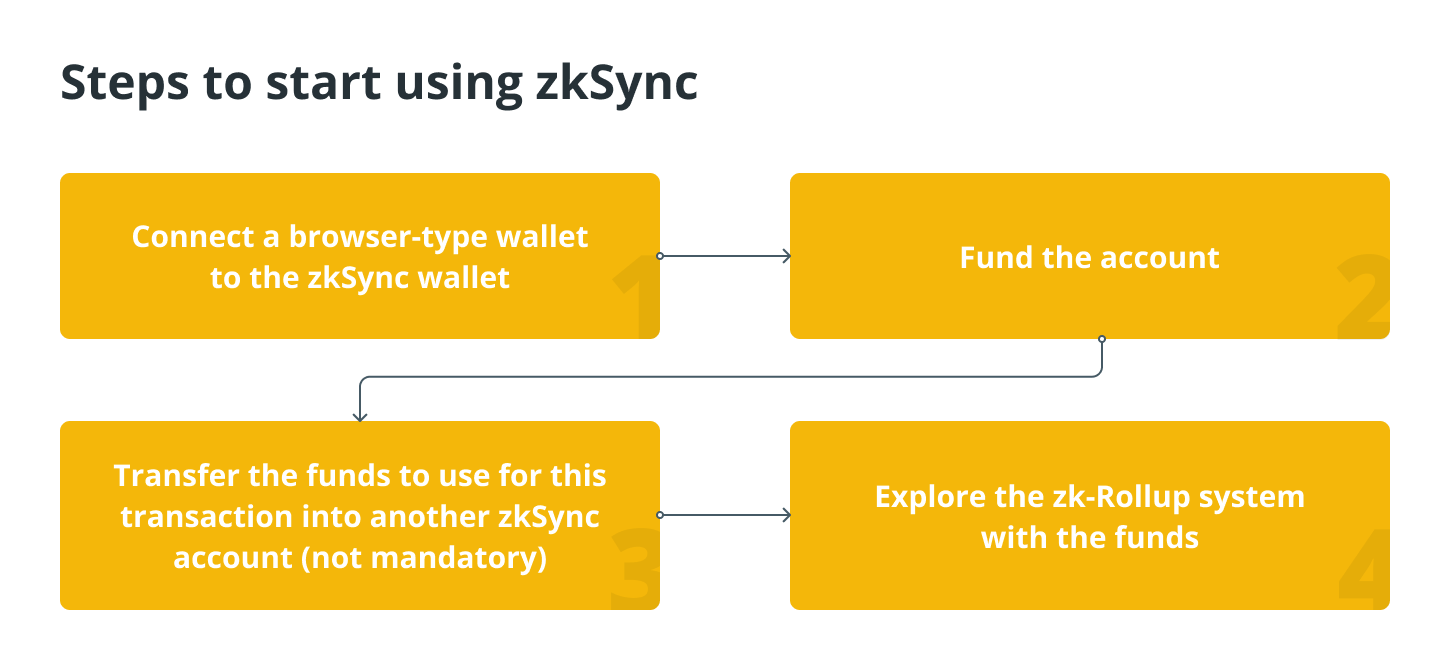
zkSync’s pros and cons
Let’s take a quick look at the benefits and drawbacks of zkSync:
Pros
One of the benefits of using zkSync is that the user-friendly support token payment fee on zkSync does not require the payment of Ethereum. This is one of the advantages of using zkSync. You can use another cryptocurrency to pay the support token fee. For example, if you are transferring tethered tokens, also known as stablecoins, on the platform, you may pay the fee with Tether instead of another cryptocurrency (USDT).
Additionally, the amount of time it takes to complete a transaction on zkSync is significantly less. The zkSync system was developed in such a way that increased transaction volume reduces the amount of time required to withdraw coins. Three hours is roughly the amount of time before a user’s account is credited with the currency withdrawn from their account.
In addition, the transaction fee that is assessed when using zkSync is absurdly low. On the Ethereum mainnet, the fee for transferring tokens is currently estimated to be about RMB 75, while the fee for transferring tokens using zkSync is approximately RMB 1.5.
Cons
Consensus networks, such as practical Byzantine fault tolerance (pBFT) and delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS), which are adopted for faster speed, pose a threat to the security of the consensus mechanism that zkSync uses. There is an increase in the speed of layer-2 networks. On the other hand, the protocols that are typically used to improve its speed are centralized.
Some of the most popular wallets and exchanges are not synchronized with one another, but they do support layer-2 networks. This may cause users to send transactions that were meant for an exchange to layer 2 by mistake. As a consequence of this, transactions may be lost permanently, particularly in the event that the transaction in question is not acknowledged by the layer-2 networks.
zkSync is currently exposed to a significant amount of danger as a result of the complexity of general support for EVM. This is due to the fact that general EVM is still in the process of being developed. These complexities, along with the difficulty of generating proof, are significant sources of pain points during the processing of transactions.
DApps on zkSync
According to the Twitter account Zk Daily, which serves as an educational resource for ZKSync awareness, over 100 projects are currently being run on zkSync. This demonstrates that the zkSync ecosystem is developing into a sizable business and is growing larger. ZkSync has a diverse group of investors, but the following applications are currently being powered by ZKSync:
Curve
Curve was one of the earliest exchanges that was instrumental in popularizing the automated market maker (AMM). On the other hand, the total value locked (TVL) of Curve is significantly lower on zkSync compared to its value on other blockchain protocols. The bright side, however, is that zkSync is gaining widespread recognition and popularity, which indicates that there is still room for optimism.
ZigZag
A noncustodial order book that is powered by zkSync is what makes up the ZigZag decentralized exchange (DEX). ZigZag’s spot trading is made possible with the help of zk-Rollups. Investors can use the ZigZag project to swap tokens and perform spot trading directly out of their wallets without incurring any additional charges or gas fees thanks to the zk-Proof technology. ZigZag has also established a bridge connecting zkSync with Ethereum to better serve its customers.
Yearn Finance
Users on Yearn Finance’s platform can choose from a variety of investment strategies to increase their return on investment (ROI). Before expanding to other chains, the platform first achieved widespread success on the Ethereum blockchain. zkSync, which is provided by the wallet provider Argent, can be used to gain access to the yield-compounding platform.
Taker Protocol
Another decentralized application (DApp) that can be found on zkSync is called Taker Protocol. This platform, which is based on a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO), is primarily a liquidity framework for cryptocurrency tokens, synthetic assets, and NFTs. On the Taker protocol, lending and borrowing in cryptocurrencies, lending and borrowing in NFTs, and even renting are all permitted.
Mute.io
The decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) governs all aspects of the Mute.io platform. It accomplishes this by acting as an automated market maker exchange, initial DEX offering (IDO), and farming protocol. Additionally, it eliminates gas fees, which are typically a challenge, so transactions are completed at the speed of light. The zkSync technology helps to improve privacy, in addition to its other benefits.
Should you rely on the zkSync ecosystem?
In point of fact, zk-Rollups have resulted in beneficial changes to the Ethereum blockchain. Their progression from zkSync 1.0 to zkSync 2.0 is illustrative of their unceasing pursuit of growth and advancement. However, what are the plans for zkSync proofs in the near future? Because of the importance that Ethereum will have in the long run, the decentralized system must be managed by a system that is capable of living up to the challenges it faces.
The question that needs to be answered is, “How reliable are zero-knowledge-proof systems as a long-term utility?” zkSync has demonstrated tenacity ever since it first appeared in 2019. ZkSync makes it possible for Ethereum transactions to be completed more quickly, without any interruptions, and at a lower cost.
As was mentioned earlier, certain decentralized applications run on the trustless layer-2 protocol. As a result, it would appear that zk-Rollups have progressed much more rapidly than was originally anticipated. In any event, Ethereum will eventually act as a data availability layer for the technologies that fall under the L2 category.









