What is Ethereum 2.0: A description of the consensus layer on Ethereum
Ethereum 2.0, also known as ETH2, is a multi-phased upgrade that aims to improve the scalability and security of the Ethereum network by making infrastructure modifications. The most notable of these changes is a transition away from a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus process and toward a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus process.
The Ethereum Foundation renamed Eth2 to “consensus layer” in January 2022 because it is an upgrade to the existing network rather than the construction of an entirely new network from the ground up.
In light of the aforementioned, the layer of Ethereum 1.0 that stores network and smart contract rules are referred to as the “execution layer.” It is essential to take into account that the total upgrade will be finished by the year 2023.
What is ETH 2.0 staking?
As a result of the current level of congestion on the Ethereum (ETH) network, the costs of conducting transactions have skyrocketed to levels that make them unfeasible for many applications.
This is partially due to the success of DeFi projects, in which customers are willing to pay high transaction fees due to the tremendous financial value of the transactions. This is one reason why this is the case.
Since they fund actual applications that are running on the Ethereum blockchain and not just transactions, the fees associated with transactions in Ethereum are referred to as “gas” costs.
Because of the high cost of gas, non-financial decentralized applications, or DApps, that are built on top of Ethereum have a difficult time functioning properly on the Ethereum network.
The Ethereum Foundation has been hard at work on a network upgrade that was formerly known as ETH2 and that aims to improve the stability, speed, efficiency, and scalability of the Ethereum network. This work has been done in order to address the problems that have been identified.
Because of its high level of security and its ability to scale, the Ethereum network can handle a greater volume of transactions, which helps to eliminate bottlenecks and makes room for additional use cases, particularly those that are not related to finance.
As was mentioned earlier, the existing mining process for Ethereum will be replaced with a model known as “staking” as part of this upgrade.
Staking is the process of actively participating in the validation of transactions on a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchain (similar to mining).
On these blockchains, anyone possessing at least the required minimum cryptocurrency balance can validate transactions and earn staking rewards.
On exchange platforms for cryptocurrencies such as Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken, amongst others, Ethereum can be staked.
The current transaction throughput for Ethereum is 15 per second, which is considered rather slow in financial transactions.
On the other hand, proof-of-stake is going to be able to enable the processing of 100,000 transactions per second, which will significantly broaden the range of projects and applications that can be built on the Ethereum blockchain.
This guide will walk you through the basics of staking ETH, including how to stake Ethereum, how the Ethereum staking process operates, and the rewards for staking ETH 2.0.

The Move from mining to the staking model
Proof-of-stake is a method for reaching distributed consensus that is utilized by blockchain networks.
Staking is a process that Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains use to generate new blocks and keep the blockchain itself secure. Staking refers to the process of selecting validators in order to create a new block and is used in cryptocurrency.
The number of coins a validator has is directly proportional to the likelihood that they will be selected to produce or validate a block.
As a consequence of this, anyone with a modest amount of coins can participate in betting and earn additional coins in direct proportion to the amount of money they wager.
Users are required to stake their ETH in order to become validators on the network (the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum blockchain).
In the same way miners are responsible for organizing transactions in the proof-of-work system, validators are in charge of constructing new blocks and arranging existing ones so that all nodes can reach a consensus on the network state.
The Beacon Chain is Ethereum’s new consensus model, and it is the responsibility of Validators to process transactions, store data, and add blocks to the chain. Validators are also sometimes referred to as “stakers.”
As a thank you for their active participation in the network, validators are rewarded with interest on the coins they have staked. These coins are denominated in Ether.
The Ethereum platform requires users to make an investment of 32 ETH in order to qualify as a validator. Validators are tasked with the production of blocks at random and are held responsible for double-checking and confirming any blocks that they did not produce themselves.
The user’s stake is also used as an incentive for positive validator activity as part of this system. For instance, a user may lose all of their investment if they intentionally collude with other users, or they may lose only a portion of their share if they go offline (and therefore fail to validate).
Additionally, depending on the PoS system, users may be able to “delegate” their stake to another user, allowing that user to act as a validator on their behalf and carry out the responsibilities associated with that role.
The consensus layer upgrade (previously known as Ethereum 2.0), which is going to be the next version of the Ethereum network, can be secured with the help of this type of staking, which also gives contributors the opportunity to earn passive income.

How does Ethereum staking work?
In contrast to a blockchain that is powered by proof-of-work, also known as PoW, a blockchain that is powered by proof-of-stake bundles 32 blocks of transactions together during each round of validation, which takes an average of 6.4 minutes to complete.
These blocks assemblages have been named “epochs” for convenience. When the blockchain adds two more epochs after it, it is regarded as irreversible; in other words, an epoch is thought to have reached its conclusion at this point.
Stakeholders are grouped into committees of 128 by the Beacon Chain, and then each committee is randomly assigned to a different shard block.
Each committee is given a “slot,” or time slot, and given a specific amount of time to propose a new block and validate the transactions that have occurred within it.
Because there are 32 openings in each epoch, the validation process needs to be carried out by 32 separate committees.
After a committee has been allotted to a block of transactions, one member of the committee is selected at random and given the sole authority to suggest a new block of transactions.
The remaining 127 members, on the other hand, cast their votes on the proposal and attest to the transactions.
The Beacon Chain is responsible for maintaining synchronization across the network by gathering state data from individual shards and sending it to all of the shards in the immediate vicinity.
The Beacon Chain will be in charge of managing the validators. This means that it will be responsible for registering the validators’ stake contributions as well as awarding rewards and imposing punishments.
The Ethereum network can be sharded, which simply refers to the process of dividing it up into many smaller networks. Each shard would have its own state, which would consist of a unique collection of account balances and intelligent contracts.
Once a majority of the committee has confirmed its veracity, the new block will be added to the blockchain, and a “cross-link” will be created to validate its incorporation into the chain.
Only after this step is completed does the staker who was selected to propose the new block receive their reward.
During the process of cross-linking, the individual shard states are brought into agreement with the main chain, also known as the Beacon Chain. The final state of each shard has to reflect on the Beacon Chain in order for cross-linking to take place.
A transaction is said to have “finality” in a distributed network when it becomes part of a block that cannot be altered after it has been committed.
In order to accomplish this in proof-of-stake, Casper, a finality protocol, gets validators to agree on the state of a block at particular checkpoints.
If two-thirds of the validators are in agreement, the block will be completed. In the event that validators try to undo this at a later time using a 51% attack, they will lose their entire stake.
How much do you make staking Ethereum?
The calculation of rewards in ETH 2.0 makes use of annualized interest rates in conjunction with an inverse square root function.
In terms that are easier to understand, this indicates that the incentives for each validator will decrease in proportion to the total amount of ETH that is staked.
The incentive structures for block proposers and attesters are fundamentally different. The attester receives the remaining 7/8 of the base reward, which is adjusted based on the amount of time it takes the block proposer to submit their attestation. The block proposer is awarded 1/8 of the base reward, which is denoted by the letter “B.”
In order for the attester to be eligible for the full 7/8 B award, they must submit it as quickly as they can. The payment is reduced by one unit for each slot that goes by without the attester being present. This reduction also applies to the attestation to the block.
If two slots are passed before the attestation is included, the prize is reduced by 7/16 B, and if three slots are passed, the reduction is 7/32 B, and so on.
The base reward is the primary factor that decides how quickly Ethereum 2.0 will be distributed. When the base reward for each validator is reduced, there will be a corresponding increase in the total number of validators connected to Ethereum 2.0.
This is the situation that exists due to the fact that the base payment is inversely proportional to the square root of the total balance of all Eth 2.0 validators.
Why stake ETH for Ethereum 2.0?
One can obtain the annual percentage rate, or APR, from 6% to 15% from investing in Ether. This is the primary reason why many people would want to invest in Ether.
Given that you will need a minimum of 32 ETH, you can reasonably anticipate earning anywhere from 2 to 5 ETH given the current prices.
Where exactly does the catch lie? You are required to keep your ETH stored for many years.
It’s possible that some people won’t feel comfortable accepting this choice if they don’t have 32 ETH to lock up immediately or if they’d rather use their ETH to pay for other decentralized applications.
You are required to carry on in this manner until the release of the Ethereum 2.0 protocol, which could be a number of years away.
People who have a limited amount of ETH or who use it frequently will not have a practical option to stake their ETH in order to participate in Ethereum 2.0 because this will not be a realistic alternative.
If you put your tokens on an exchange, you can still stake them and receive rewards, but this does not mean that you are running a validator node or participating in Ethereum 2.0 staking.
One more reason someone might want to stake their Ether is in order to provide support for the network. Validation of the network is the responsibility of nodes, which can be thought of as individual computers that have staked ETH and are actively operating.
If you want to validate the network, give it a hand, and earn a reasonable payout in the process, staking might be the activity for you to get involved in.
How to stake Ethereum?
There are many different approaches to taking part in Ethereum’s staking process. Custodial staking systems are designed to manage the entirety of the staking process on your behalf.
The only thing you need to do is make an Ether deposit, and they will set up the node for you. In addition to this, they will run and manage the node on your behalf so that you do not have to.
The fact that you do not have control over the private key of the validator node is the primary feature that sets solo apart from other platforms for stake taking.
Your assets are in good hands with the staking provider, who is in charge of managing them. In exchange for their services, they will deduct a certain percentage from the rewards you earn.
To participate in staking on the new Ethereum network, you will need to set up a staking node by utilizing clients for Ethereum 1.0 and Ethereum 2.0.
Ethereum clients are software programs that enable different nodes on the Ethereum network to interact.
Clients of the following software can stake using any of the following nodes:

As a bare minimum requirement, users will need a computer with sufficient memory space in order to download both versions of the Ethereum blockchain, the old and the new.
The amount of data stored in Ethereum 1.0 is currently estimated to be close to 900 terabytes and is expanding at a rate of approximately 1 gigabyte per day.
In addition to this, validators are required to maintain a constant connection between their nodes and the blockchain. Because of this, having a reliable connection to the internet is an absolute necessity.
After you have completed the installation of the validator software on your computer, you will be required to send a minimum of 32 ETH to the address listed for the Ethereum staking contract.
To accomplish this, you will need to generate two keys: the first will be used to sign and validate transaction blocks, and the second will be used to withdraw cash from your wallet.
However, until Eth1.0 and Eth2.0 merge in 2022, you won’t be able to create your withdrawal key.
You are required to go to the ETH 2.0 launchpad and follow the procedures there before sending any funds to the address associated with the staking contract.
Your legitimacy as a validator will be confirmed once you have received this payment. Additionally, it gives the network a way to punish rogue validators who intentionally or unintentionally undermine the authenticity of the Ethereum blockchain.
When the blockchain identifies inconsistencies in the activity of validators, it will “slash” the staked funds of those who are responsible.
Slashing is the term used to describe the process that occurs when an Ethereum 2.0 validator willfully disobeys network rules and then is removed.
As a form of punishment, some of the ETH that they have staked will be taken away, and in certain circumstances, the full 32 ETH that they have staked will be taken away.
Validator nodes that offline receive a penalty in order to encourage them to remain online and connected to the network.
The protocol will issue both penalties and incentives once every six and a half minutes, which is referred to as an epoch.
Is it a good idea to stake Ethereum?
The total amount of ETH that was staked and the number of validators that were present on the network combine to determine the amount that will be awarded to stakers. When there are fewer ETH in the pool to be staked, the annual interest rate goes up.
As soon as there are sufficient participants in the ecosystem to maintain its decentralized nature, the interest rate will begin to decrease.
On the other hand, stakeholders cannot withdraw staked coins or earned rewards at this time — at least not until the Ethereum 2.0 and Ethereum 1.0 networks are combined.
In addition, staking Ethereum makes it simpler to operate a node, which is another reason why it is a good idea to do so.
It does not require significant investments in hardware or energy, and if you do not have enough ETH to stake, you can join staking pools. Staking does not require significant investments in hardware or energy.
The act of staking is carried out in a manner that is less centralized. It makes greater participation possible because, in contrast to mining, adding additional nodes does not result in a higher percentage of profits.
Staking enables safe sharding. Shard chains will make it possible for Ethereum to construct a large number of blocks all at once, which will speed up the processing of transactions.
In a system that is based on proof-of-work, sharding the network would lower the amount of power that is needed to compromise a portion of the network.
staking Ethereum on Coinbase?
As was mentioned earlier, ETH can be staked on Coinbase and other cryptocurrency exchanges, making it easy for anyone, with no required minimum investment, to stake their Ethereum tokens.
To stake ETH on Coinbase, various steps need to be followed, all of which are explained in the following sections in more detail.
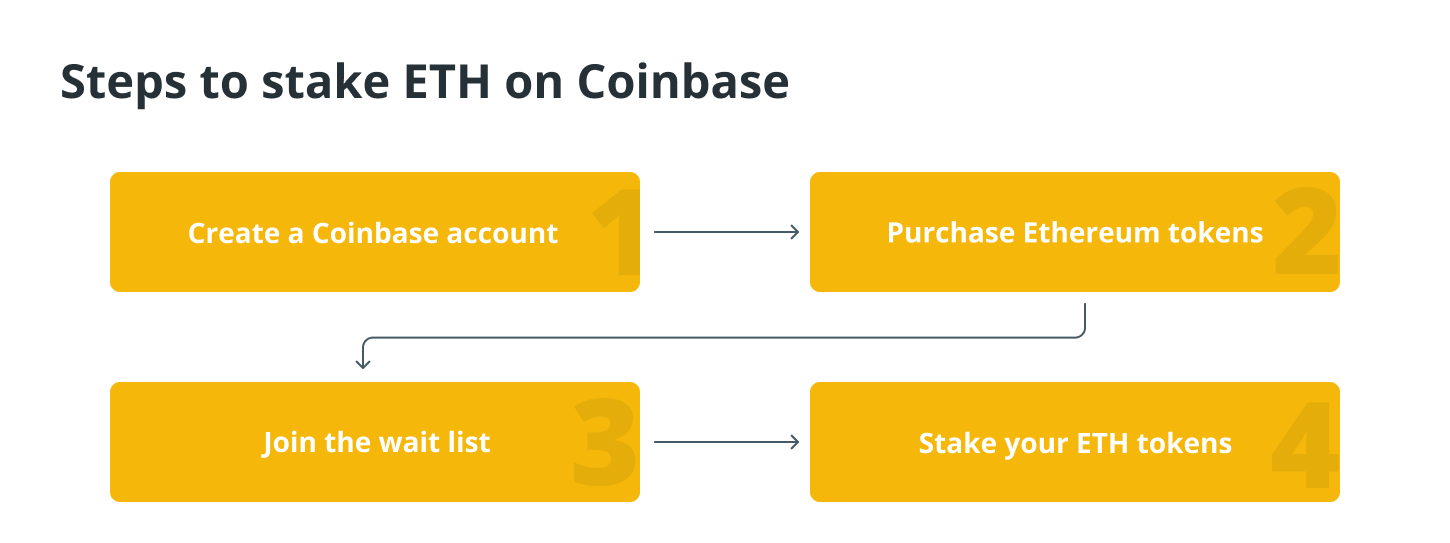
Create an account with Coinbase.
In the event that you do not already have a Coinbase account, you will be required to set one up using the Coinbase mobile app.
Coinbase makes it simple to create an account; all you need to do is enter your name, email address, and location and then come up with a secure password.
After you have established an account, you will be required to authenticate your identity for tax purposes. This will necessitate the submission of your driver’s license, the last four digits of your Social Security number, and your date of birth.
Once your identity has been verified, you will be able to buy any cryptocurrency that is listed on Coinbase’s exchange.
Buy Ethereum tokens.
The purchase of Ether tokens is required in order to participate in staking activities on Ethereum. Coinbase gives you the ability to make direct purchases of Ethereum tokens, making it simple to purchase and stake all of your Ethereum tokens in a single location.
Tokens based on the cryptocurrency Ether can be acquired through a limit or market order, just like traditional stocks and shares. You can only buy Ether tokens with limit orders if the price of Ether reaches the price that you specified when you created your limit order. Market orders buy Ether tokens at market price.
Join the waitlist.
To our regret, Coinbase will not immediately support the staking of Ethereum tokens in the near future. As a result of the extremely high level of demand, Coinbase has introduced a waitlist that will put you in line to stake your Ethereum tokens.
The length of time you have to wait before you can start earning interest on your Ethereum tokens varies, but the sooner you sign up, the sooner you can start doing so.
Stake your ETH tokens.
Since Coinbase is in charge of maintaining the validator nodes, all that is required of you is to stake some of your Ether tokens, and the exchange will handle everything else.
After you have staked your Ethereum tokens on the Eth 2.0 network, you can kick back, put your feet up, and enjoy passive interest generation in your cryptocurrency portfolio without having to do anything else.
Where can I find information about the benefits of staking ETH on Coinbase?
You can earn up to 5% annual percentage rate (APR) on each ETH that you stake on Coinbase. This is an incentive for helping to protect the network.
Payouts for ETH2 staking are determined according to the amount of ETH that is validated and the rewards that the network is paying out over the course of time.
Users are encouraged to stake a greater quantity of ETH because the protocol payments increase when even a small amount of ETH is staked.
However, the reward will be lessened in the event that a significant amount of ETH has already been staked in the past.
What are the possible risks of staking ETH?
Although this might not be a concern in the long run if the value of Ethereum 2.0 is exceptionally high, you should be aware that the value of Eth 2.0 is currently unknown and will almost certainly be distinct from that of Ether. This is something you should keep in mind.
If you think Ethereum 2.0 will be successful, then you should also think that hosting a validator node will be beneficial. This is because hosting a validator node is how new transactions are verified.
One more significant problem is that there is insufficient liquidation. Until Ethereum 2.0 is released, which could take as long as two years or even longer, you won’t be able to withdraw any ETH that you have either earned or staked.
If you are not a holder for the long term and you intend to sell Ethereum during either the current bull run or the next one, this may not go over well with you.
The risk that you could end up losing your staked assets, also known as your “primary funds,” because of slashing is an important one that you need to keep in mind. A protocol-level punishment that is imposed as a response to a network or validator failure is referred to as slashing.
The path that lies ahead
To this point, Ethereum has been met with tremendous levels of success. Many talented individuals, such as application developers and core protocol developers, have joined the Ethereum community.
The process of upgrading the core protocol is a massive undertaking that has been meticulously planned and carried out to this point.
It would appear that the core team responsible for Ethereum will not stop working until each and every one of the complexities, such as rollups and migration, are finished. The only question that needs answering is how long this process will take.
Ethereum is losing some of its use cases to other, more recent blockchains, but the blockchain market as a whole is growing rapidly, so it’s not a zero-sum game by any stretch of the imagination.
The fact that many of these new blockchains are developing solutions for Ethereum interoperability is evidence of both the platform’s potential and its current success. It should not come as a surprise that Ethereum will not fade away into obscurity any time in the near future.









