What exactly is cryptocurrency mining?
Mining digital currencies is an essential component that makes it possible for cryptocurrencies to function as a peer-to-peer (P2P) decentralized network. This eliminates the requirement for third-party intermediaries.
It is the process by which transactions carried out over a blockchain network by its participants are validated and added to the distributed public ledger.
Mining for cryptocurrencies results in the addition of new blocks to the cryptocurrency’s already existing supply. Let’s use the mining of Bitcoin as an example to better understand how other cryptocurrencies are mined.
Bitcoin (BTC), the world’s first truly decentralized digital currency, is managed by a peer-to-peer (P2P) network of miners who are tasked with the maintenance of the Bitcoin blockchain. A node in the network that is responsible for gathering transactions, validating them, and adding them to the blockchain is known as a miner.
When a participant in the Bitcoin mining process successfully adds a valid block to the blockchain, the network will award that miner with a cryptocurrency. In this case, the miner will receive Bitcoin. This is how new bitcoins are added to the circulation of the currency.
This article will discuss the many different types of cryptocurrency mining, the equipment that is used to mine digital assets, as well as the costs that are associated with the mining process.
How does the mining of cryptocurrencies work?
In order for miners to successfully add a block to the distributed ledger, they are required to solve a cryptographic puzzle that is a part of the consensus mechanism. This method prevents malicious nodes from attempting to forge blocks and incorrectly claiming the reward for their work.
Since its inception in 2009, however, hackers have shown interest in Bitcoin due to the fact that users can send and receive payments without revealing their identities. For example, malicious software that mines cryptocurrencies, such as cryptojacking, is being used, enabling bad actors to acquire virtual currencies without spending any real money.
Mining cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and other altcoins that use a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism typically requires expensive hardware equipment and a significant amount of electricity.
Mining is the name given to this technique because it is similar to the process of looking for gold in a mine. In contrast, Ethereum is transitioning to a different form of consensus mechanism known as proof-of-stake (PoS), in which validators are “randomly” selected in proportion to their current stake in the system rather than having to expend processing resources to create legitimate blocks. In this model, validators are selected in accordance with the system’s current state.
How to mine cryptocurrency?
Mining for cryptocurrencies is accomplished by specialized hardware in the form of computers and other hardware known as mining machines. The evolution of mining hardware includes everything from CPUs to ASICs. The cyclical increase in mining difficulties led to the creation of new machines that were more effective than the ones that had been created in the past.
Are you having trouble deciding which method of mining cryptocurrency is the most effective for you? The straightforward response is that it depends on the cost of mining cryptocurrency and your available funds. There are many distinct approaches to mining cryptocurrencies, each of which is broken down into its own section below.
CPU mining
CPU mining is the process of adding transaction records to the public ledger of a cryptocurrency. This is accomplished by using a central processing unit (CPU) to carry out the necessary calculations in order to mine the cryptocurrency.
The term “central processing unit” (CPU) refers to a computer component that provides the processing power necessary for actions to be carried out by software installed on that computer.
In the early days of cryptocurrency mining, CPU mining software such as cpuminer was effective for mining hash rates of less than or equal to 10 MegaHashes per second (MegaHashes per second). Is it worthwhile to mine cryptocurrencies with regular computers like laptops and desktops?
The earlier versions of Bitcoin clients mined using their central processing units (CPUs) until the high hash rate of the network rendered this method unprofitable.
However, coins such as Monero (XMR) use CPU mining to mine XMR coins profitably. Anyone with access to a computer is able to mine cryptocurrencies using a central processing unit. XMR coins can be mined profitably.
In addition, the CPU mining rig requires a cooler for the hardware, a processor for high-frequency competition, memory channels and bandwidth using random-access memory, a power source for efficient hash rate and quiet support, and a motherboard for the smooth communication of all elements. All of these components are necessary.
One has the option of working alone or joining a group of other miners in order to begin CPU mining. The ability of solo miners to add new coins to their cryptocurrency wallets is contingent on the hash rates of both the hardware and the network.
However, before getting too involved in a mining business on your own, you should calculate the revenues and compare them to the costs of electricity and other expenses.
On the other hand, individual miners are drawn to mining pools where they can collaborate with one another and combine their computing resources to find new blocks. This allows individual miners to cover the costs of the necessary hardware as well as the necessary electricity.
However, in order to join a mining pool, participants are required to meet certain hardware requirements, give up some of their mining autonomy, and agree to abide by the pool’s rules.
GPU mining
Mining cryptocurrencies required the use of graphics processing units (GPUs) and conventional central processing units (CPUs), as the former’s processing power was insufficient to meet the ever-increasing demand. Utilizing graphic cards containing GPUs allowed for solving difficult mathematical calculations.
The first time graphics processing units were utilized was in October of 2010, when online access to Bitcoin mining software for GPUs was made available. After that, it underwent some speedy optimization and modification so that it could be used in a variety of open-source projects.
The performance of a GPU can vary widely depending on its age and price; however, many modern GPUs offer 2,000 times the hashing power of a CPU miner operating at 20 kilohashes per second (kh/s).
In addition, GPU miners are able to handle multiple operations simultaneously, and some miners even combine multiple GPU mining rigs in order to run 24-48 GPUs at the same time. A mining rig is a collection of individual mining machines that work together to increase the amount of mining output power, also known as hash rates, and the amount of money earned.
FGPA mining
The consistent increase in mining costs, when compared to the coins that were obtained, had a negative impact on the profitability of mining. As a consequence of this, GPU mining was no longer profitable due to the high costs of mining combined with the low returns.
The urgent need for machines that could make mining profitable so that miners could continue working in the mines led to the development of field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs).
A field-programmable gate array, also known as an FPGA, is a type of electronic circuit that can be programmed to carry out a variety of different logical operations. Having said that, an FPGA miner can be programmed to mine a particular coin of your choosing.
On the other hand, if necessary, it can be reprogrammed to mine a different cryptocurrency by employing a different mining algorithm, although this will require additional training for the miner.
FPGAs are able to break even on their total cost of ownership in as little as a year or two, despite being up to five times more energy-efficient than GPUs. However, FPGA miners enjoyed a brief period of dominance before being overtaken by ASICs, which offered superior cost and energy efficiency performance.
When it came to the cost per GH/s, FPGAs had a hard time competing with high-volume GPUs that ran on more advanced process nodes.
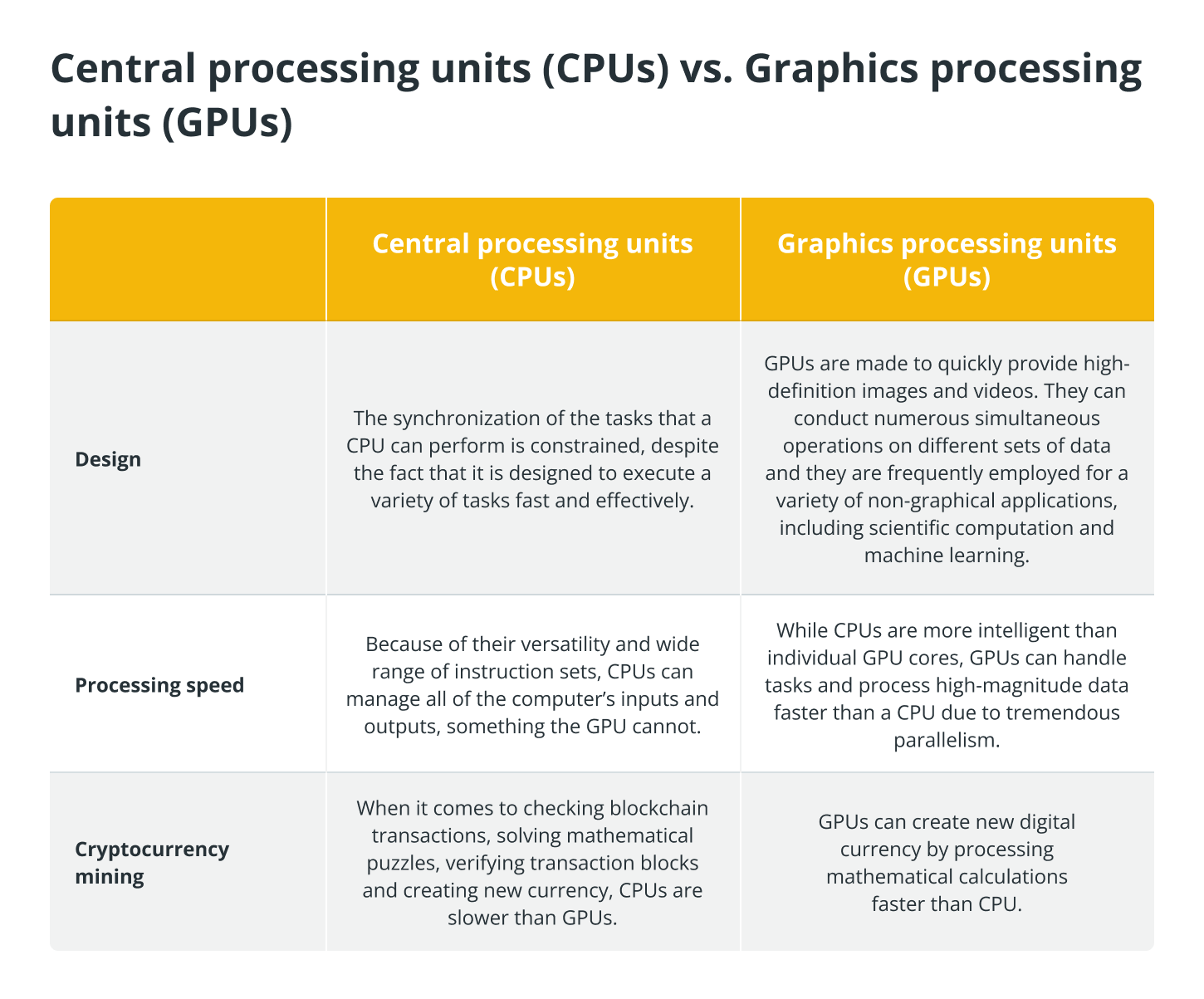
The following table provides a summary of the key differences between central processing units and graphics processing units:
 ASIC mining
ASIC mining
Due to the ever-increasing difficulty of mining, it became necessary to locate more advanced machinery at more affordable prices over time. This created intense competition among miners.
FPGAs are used for mining purposes, and while they are flexible to build and program, they consume a significant amount of power in comparison to the returns they produce.
However, when utilized for large-scale mining, which is what both ASICs and FPGAs were designed for, ASICs delivered superior performance to that of FPGAs.
The performance of application-specific integrated circuits, also known as ASICs, is significantly higher than that of general-purpose computing devices such as graphics processing units (GPUs) or central processing units (CPUs).
Installing an ASIC miner requires a number of components, the most important of which is a power supply, followed by an internet connection, access router, IP address, wallet, and mining pool. However, because of imbalances in computer power, the decentralized nature of blockchain networks is still susceptible to attack.
Mining with CPUs and GPUs is no longer profitable due to the significant increase in the network’s total hash rate caused by the introduction of ASIC mining hardware.
However, in order for the general public to participate in the mining process, they will need to make an investment in specialized equipment. This creates a high barrier to entry for ASIC-based mining.
Additionally, ASIC Bitcoin miners, such as the Antminer S19, cost between $10,000 and $12,000, making it impossible for people with lower incomes to purchase one.
In addition, organizations that are capable of purchasing and maintaining a significant number of ASIC systems have the potential to take control of the blockchain network. Mining done with ASICs is consequently more vulnerable to the 51% attack.
The fact that one manufacturer can monopolize the market for ASIC-based mining systems is yet another flaw that these systems have.
For instance, a backdoor application that was pre-installed on Bitmain’s ASIC mining hardware was sent along with the equipment. This allowed the company to remotely manage a significant portion of the hashing power distributed across the network.
Backdoor programs are pieces of software that can be used by hackers or other cybercriminals to gain remote direct access to a system.
Cloud mining
Anyone who wants to mine cryptocurrency can do so using a service known as crypto cloud mining. This service eliminates the need to purchase, install, or maintain any specialized hardware or software.
Instead of spending money on more powerful servers, the miners can use the computing capability of the cloud to either supplement or replace their existing internal computing resources.
The fundamental idea is that miners can carry out mining operations without having to purchase an ASIC on their own. Instead, they can rent one. Hosted mining is the name given to this business model, which requires miners to pay monthly rental rates.
Additionally, renting these machines provides the miner with more available exit options in the event that losses are unavoidable as a result of falling BTC prices or an increase in the difficulty of network mining.
Cloud mining also significantly reduces the costs incurred by businesses for the upkeep of their computer hardware and software.
As a result of the requirement for fewer servers and less hardware, the costs associated with maintenance are decreased. Because of the reliance of all software applications on cloud servers, virtually no maintenance is required.
Miners can rent virtual computers to run their own software by using hosted platform mining, which is different from hosted mining machines. Miners use hosted platform mining as an alternative option.
Customers only pay for the services that they actually use on platforms like Amazon EC2, which is an example of such a platform. In addition, renting hashing power enables miners to rent the processing power of multiple powerful ASIC processors that are controlled by mining corporations. These processors are used to mine cryptocurrency.
Is it profitable to mine cryptocurrencies?
Mining profitability is heavily influenced by a number of fundamental factors, including a mining machine’s purchase price, performance, design, and implementation.
As mentioned above, Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICS) currently holds a dominant position in the mining industry due to their superior performance compared to other machines on the market.
On the other hand, it is difficult to predict how much longer they will be able to maintain their quality in the face of continually rising mining difficulties and the development of increasingly sophisticated mining equipment. But is mining cryptocurrency risky? Or is it risky to mine cryptocurrency on a personal computer?
In general, desktop graphics processing units (GPUs) are more powerful and cost less than their laptop counterparts. Mining cryptocurrencies requires a significant amount of computational power and has the potential to use up your entire graphics processing unit (GPU). This results in a significant amount of heat being generated while the GPU processes data to validate transactions.
On the other hand, Desktop GPUs come equipped with active cooling mechanisms like fans or water cooling to assist in the process of removing the heat that they generate.
In addition, there is the possibility of wearing out the miniature fans, which can further complicate matters and cause damage to the GPU; consequently, more powerful cryptocurrency mining equipment is required in order to remain safe.
Can cryptocurrency be mined at home?
Mining cryptocurrency at home is not an impossible task. On the other hand, one must be aware of the high residential electricity rates as well as the costs associated with purchasing and installing a cryptocurrency mining rig.
In addition, ever since the introduction of digital currencies, mining techniques have advanced at an astounding rate in an effort to boost hash rates and, as a result, revenues.
However, stability has consistently been a problem despite the fact that crypto mining hardware and technologies are becoming obsolete at astonishingly rapid rates.
Due to the fluctuating prices of various cryptocurrencies, it is impossible to make a long-term investment without taking on a significant amount of risk.
In addition, considering the risks involved with mining on a personal computer, the fact that mining with a graphics processing unit (GPU) or a central processing unit (CPU) is not profitable, and the high cost of mining with an ASIC, cloud mining seems to be the best option moving forward.
Cloud mining requires a much smaller starting investment but has higher potential profit and more flexible exit options than traditional mining.
However, in order for cloud mining to be effective, a greater number of miners will need to adopt it. Only then will the upfront costs of cloud service providers be able to be justified.









